Last Updated on December 7, 2023
The bones in human body form the main supporting framework of the body. The skeleton is comprised of an arrangement of different bones in human body for the more efficient production of movements by the attached muscles.
There are 206 bones in human body (The count may vary to 208 depending on whether the sternum is counted as three bones instead of one bone with three parts.
At birth, there are 270 bones in the human body. The count decreases to 206 as many of the bones in childhood fuse with growth.
Another important point to make is that the coccyx and sacrum are fused in adults but these are not counted single bone but as the number of individual vertebrae they have. Thus, the count will decrease further if sacrum and coccyx are considered as single bone each.
Many small accessory bones, such as some sesamoid bones, are not included in this count.
Let us familiarize ourselves with bones in human body. We start from the top and move down.
It is important to understand normal structures and functions to locate abnormality. Only then we can recognize abnormal functions. Our skeleton is our basic structure on which everything else is laid.
The Human Skeleton
The human skeleton is divided into
- Axial skeleton
- Appendicular skeleton
The axial skeleton is the central part of the skeleton and comprises of 80 bones that form
- Head Spine
- Chest
- head
The appendicular skeleton refers to the limbs and comprises of 126 bones in the form of
- Shoulder girdle
- Arms
- Pelvic girdle
- Legs
Thus, there are a total of 206 bones in human body across the entire skeleton.
Region-wise Bones in Human Body
Skull [28 bones]
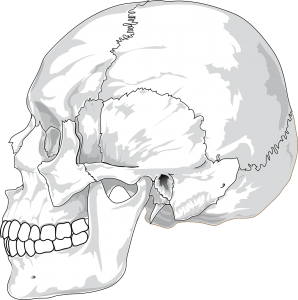
Skull is formed by cranium and mandible. Cranium is further composed of multiple bones that are united to each other. The lines of the union are called sutures. these sutures are lax in children to allow brain growth. Mandible constitutes our lower jaw that we used the whole day for speaking, eating or gesturing.
There are 22 bones in the skull and 6 in the middle ear, making a total of 28 bones. The skull has 8 bones in cranium and 14 in the face
Cranial bones (8)
- Occipital bone (1)
- Parietal bones (2)
- Frontal bone (1)
- Temporal bones (2)
- Sphenoid bone (1)
- Ethmoid bone (1)
Sphenoid bone and ethmoid bone are considered as facial bones by some authors.
Facial bones (14)
- Nasal bones (2)
- Maxillae or upper jaw (2)
- Lacrimal bone (2)
- Zygomatic bone or cheekbones (2)
- Palatine bone (2)
- Inferior nasal concha (2)
- Vomer (1)
- Mandible (1)
Middle ears (6 bones)
Each ear has 3 bones making a total of 6 bones in both ears.
- Malleus (2)
- Incus (2)
- Stapes (2)
Spine
This is formed by multiple vertebrae which are named according to area
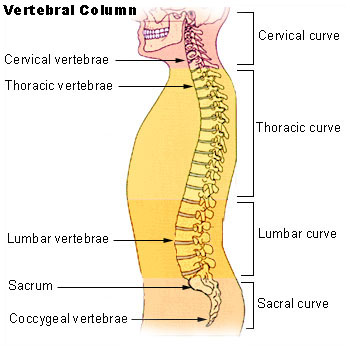
A child has 33 vertebrae. In adults, sacral and coccygeal vertebrae fuse. The number of bones each region has are
- Cervical vertebrae (7 bones)
- Thoracic vertebrae (12 bones)
- Lumbar vertebrae (5 bones)
- Sacral vertebrae (5 bones at birth but fuse later)
- Coccygeal vertebrae (4 bones)
If sacrum and coccyx is considered as a single bone, the count of bones in the vertebral column would be 26
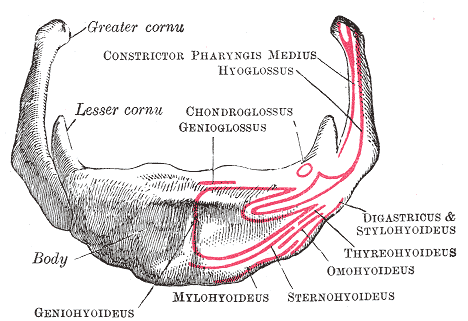
Throat
The hyoid bone is present in the throat and serves as support to cartilages of trachea or windpipe. It also serves as attachments to various muscles that help in movement of the trachea.
Thorax
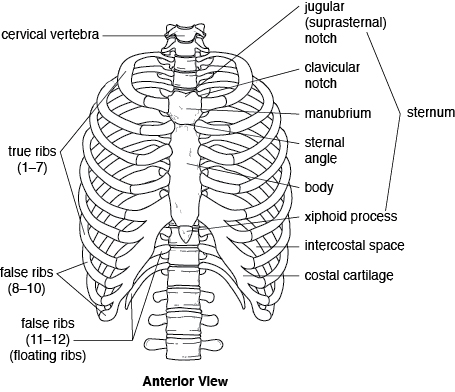
Thorax is a cage-like structure that functions to protect vital structures that it contains like lungs, heart etc. it is formed by ribs on either side which are connected to the sternum in front and to vertebrae on back.
- Sternum (1)
- Ribs (24, 12 on each side)
Upper limbs
Upper limbs include shoulder girdle, arm, forearm, wrist and hand. Upper limbs contain 64 bones, 32 on each side. Below the numbers are given for single extremity.
Shoulder Girdle
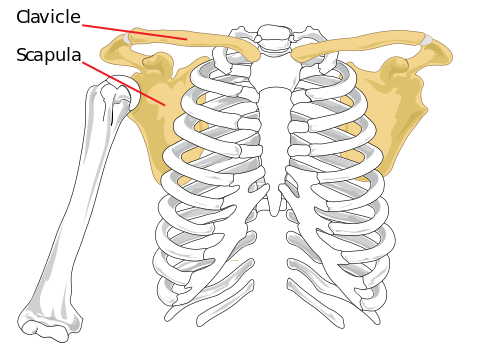
Shoulder Girdle is an area of the shoulder that is formed calvicle (1) and scapula (1) articulating with humerus (1).
- Clavicle : It is a bone that connects the thoracic cage to upper limbs and also functions for the transmittal of forces.
- Scapula: It is a complexly structured bone that articulates with the clavicle, thorax and takes part in the formation of the shoulder joint.
Arm
The humerus is the only bone that is in the arm.
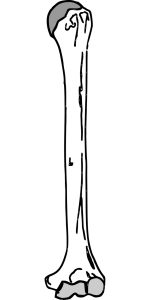
The bone that connects the shoulder to the elbow. This bone is normally cylindrical but flares when it comes near the elbow and becomes flat. It flares on either side to form ridges called condyles.
Ulna and Radius (1,1)
Ulna is the bone that forms elbow joint by articulating with the humerus. This is the bone that protrudes on back of elbow on flexion. It can be felt on the aspect of the forearm on side of the little finger.
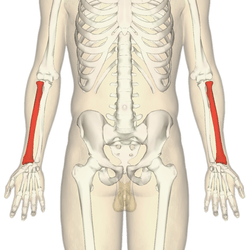
Radius is [depicted red in image] the bone on other side of forearm i.e. on side of the thumb. It forms a joint with ulna on the upper side. The part that takes part in this joint formation is called the head of the radius. This joint allows twisting movements of the elbow called pronation and supination.
Hand & Wrist
The hand is quite a complex structure and requires a separate discussion. Here are the names of bones. We would discuss them in detail in carpal anatomy and hand anatomy.
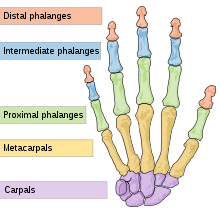

- Carpals or Wrist Bones (8)
- Scaphoid [A]
- Lunate[B]
- Triquetrum [C]
- Pisiform [D]
- Trapezium [E]
- Trapezoid [F]
- Capitate [G]
- Hamate [H]
- Metacarpals (4)
- Phalanges (14)
- Proximal phalanges (5)
- Intermediate phalanges (4)
- Distal phalanges (5)
*Thumb has only two phalanges – proximal and distal
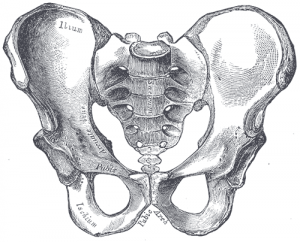
Pelvis (2 bones)
Pelvis or pelvic girdle is formed by many bones on either side which on one hand are connected to the spine and on the other side to lower limbs. Pelvis functions to transmit the weight to lower limbs and also protect the vital structures like rectum and bladder.
Ilium, pubis, and ischium are three bones that unite to form hip bone on each side. These articulate with sacroum and coccyx column to complete pelvis. Thus there is a total of 2 hip bones.
More on pelvic anatomy
Lower Limbs (60 bones, 30 each side)
The structure of the lower limb is quite similar to upper limbs with modifications done for weight-bearing purposes. The lower limb contains 30 bones each side.
There are a total of 60 bones in the lower limbs.
- Femur (2 bones, 1 each side)
- Patella or kneecap (2 bones, 1 each side)
- Tibia (2 bones, 1 each side)
- Fibula (2 bones, 1 each side)
- Foot (52 bones in total, 26 per foot)
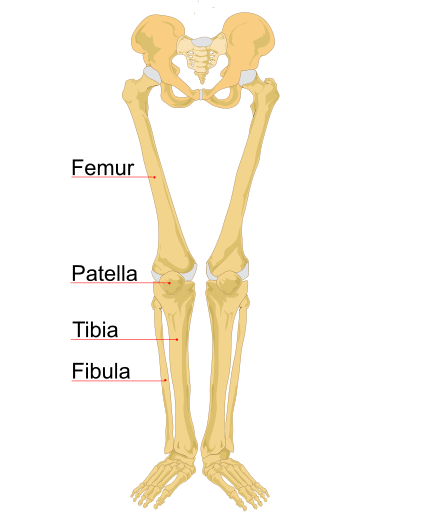
Femur, tibia, and fibula are long bones that form the lower limb. The femur is bone of thigh whereas the other two bones are present in the leg. Another important bone called patella is present on the anterior side of the knee joint and is commonly known as the kneecap.
Feet
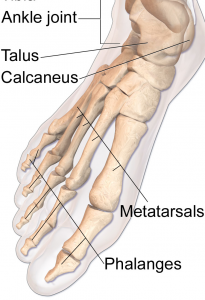
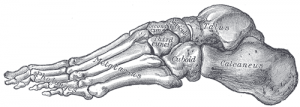
The foot contains 52 bones, 26 per foot.
- Tarsals (14 bones, 7 each foot)
- Calcaneus (2 bones, 1 each side)
- Talus (2 bones, 1 each side)
- Navicular bone (2 bones, 1 each side)
- Medial cuneiform bone (2 bones, 1 each side)
- Intermediate cuneiform bone (2 bones, 1 each side)
- Lateral cuneiform bone (2 bones, 1 each side)
- Cuboidal bone (2 bones, 1 each side)
- Metatarsals (10 bones, 5 each side)
- Phalanges ( 28 bones, 14 each side)
- Proximal phalanges (10 bones, 5 each side)
- Intermediate phalanges (8 bones, 4 each side)
- Distal phalanges (10 bones, 5 each side)
Bones can be classified by many methods. Here we discuss different types of bones one by one. Bone classification can be done by various parameters.
Functions of Bones or Human Skeleton
Support and Locomotion
Bones in human body provide basic structural shape and support. It provides a basic framework in form of skeleton on which everything is else is laid on and anchored to.
The human skeleton provides the surface for the attachment of muscles, tendons, ligaments, etc.
The bones serve as levers to the muscular actions and thus makes locomotion and other works energy efficient.
Protection of Underlying Structures
The bones in human body protect the underlying structures. The skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage protect the brain, spinal cord, and thoracic viscera, respectively.
Making Blood Cells
The bone marrow is present at the end of long bones and some flat bones. Bone marrow is the place where all the blood cells are formed.
Storage
Bones store 97% of the body calcium and phosphorus.
Immunity
Bone marrow contains reticuloendothelial cells which are phagocytic in nature and take part in the immune response of the body.