Last Updated on March 10, 2020
There are 5-6 bursae around the shoulder. Bursae are the synovial fluid-filled sacs that are present between two surfaces that rub on motion. The purpose of the bursa is to reduce friction and protect the moving tissue.
Often these are found at tendon-tendon and tendon-bone interfaces.
There are five main bursae around shoulder. They include:
- Subacromial-subdeltoid bursa
- Subscapular recess
- Subcoracoid bursa
- Coracoclavicular bursa
- Supra-acromial bursa
Sometimes authors include medial extension of subacromial-subdeltoid bursa (SASD) as sixth bursal space.
The bursae have free nerve endings for pain perception and mechanoreceptors for providing proprioceptive information of shoulder joint position.
Thus bursae might have roles beyond lubrication and cushion as well. Different bursae around the shoulder are discussed below.
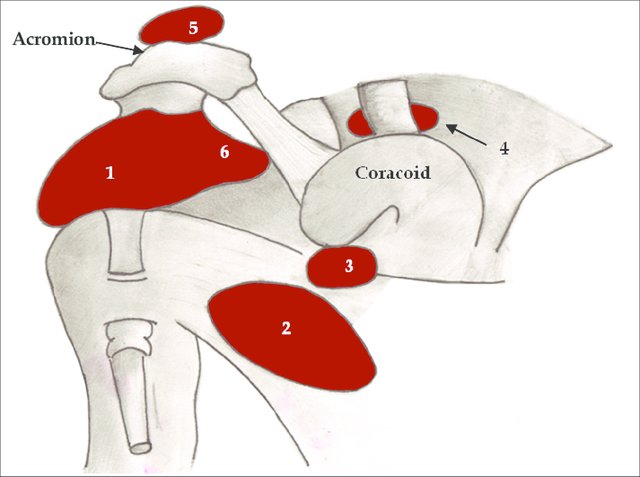
Image Credit: ResearchGate
Different Bursae Around Shoulder
Subacromial bursa or Subacromial-subdeltoid Bursa
The subacromial-subdeltoid (SASD) bursa comprise of two bursae that lie between the rotator cuff tendons and the undersurface of the acromion. They are located deep in the deltoid muscle and acromioclavicular joint but overlie the bicipital groove and rotator cuff.
The coracoacromial ligament, acromion bone, and the deltoid form the superior extent whereas the humeral head, the shoulder joint, and the supraspinatus form the inferior extent.
The main function of the bursa is to reduce friction in the space under the acromion.
Some authors keep subacromial and subdeltoid bursae as separate entities.
SASD bursitis is a common cause of shoulder pain and can occur due to many causes including:
- Shoulder impingement
- Tears of rotator cuff
- Infection
- Reaction to the glenohumeral joint disease such as crystal arthropathy
Pain between 60 and 120 degrees of abduction is considered indicative of subacromial deltoid bursitis.
Fluid-filled, SASD bursa is visible both on ultrasound and MRI but x-ray may be normal. However, MRI is rarely needed for diagnosis of bursitis.
Rest, anti-inflammatory drugs are the mainstay of the treatment. In selected cases, intrabursal steroid injections can be given. Surgical removal of the bursa is rarely needed.
Read more about Subacromial Bursitis
Subscapular Bursa
The subscapular bursa is also called subscapularis recess and it is a normal extension of the glenohumeral joint capsule in between the superior and middle glenohumeral ligaments. The subscapularis is a muscle of the shoulder region.
The bursa lies between the subscapularis muscle and the chest wall. Subscapular bursitis results in pain and popping sensation.
Pain and a popping sensation are typical complaints. Working overhead, reaching up and forward is painful.
A swollen bursa is visible on MRI.
Subcoracoid bursa
This bursa lies between the coracoid process and combined tendons of the short head of the biceps and coracobrachialis. It is superior to the subscapularis tendon.
This bursa decreases the friction between the subscapularis tendon and the tendons of the short head of biceps and coracobrachialis during the rotation of the humeral head.
Thus it facilitates internal and external rotation of the shoulder.
The subcoracoid bursa does not communicate with the glenohumeral joint. However, it may have communications with the subacromial bursa.
In subcoracoid bursitis, the passive external rotation in 90 degrees of abduction is negative and the passive external rotation in 0 degrees is painful.
A contrast fluid injected into the glenohumeral joint, thus, normally will not show in subcoracoid bursa during arthrography. But if it shows, it implies full-thickness rotator cuff tear of the shoulder.
Supra-acromial Bursa
As the name suggests, this bursa is located on the superior aspect of the acromion. It also does not communicate with the glenohumeral joint.
There are very few reports of supracromial bursitis in the literature.
Coracoclavicular Bursa
The coracoclavicular ligament is composed of two parts, the conoid and trapezoid ligaments. These ligaments are continuous inferiorly at the coracoid process attachment but separate at an angle before they attach to the inferior aspect of the clavicle superiorly.
A bursa separates the trapezoid ligament and the conoid ligament. There could be up to three coracoclavicular ligament bursae. These bursae can have bursitis though it is not that common.