Last Updated on July 21, 2021
Classification of bones can be done in more than one way. It is important to understand the terms used so that confusion does not arise.
Classification of Bones According to Shape
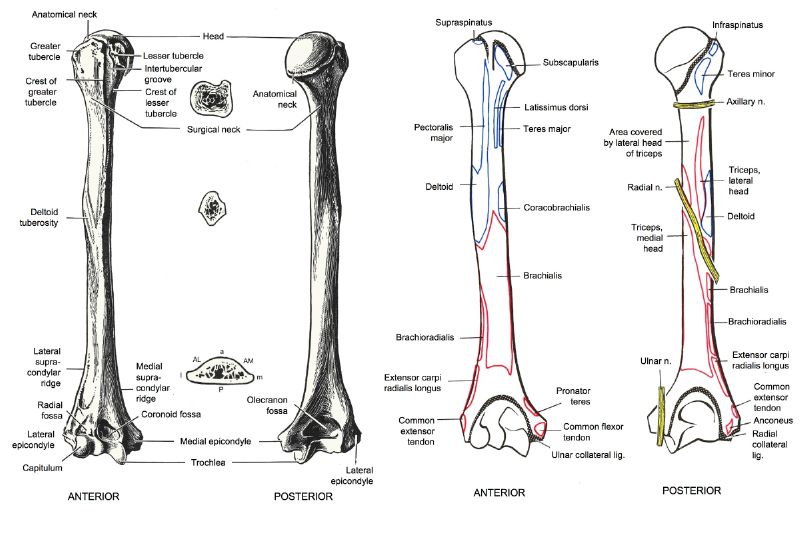
Long bones
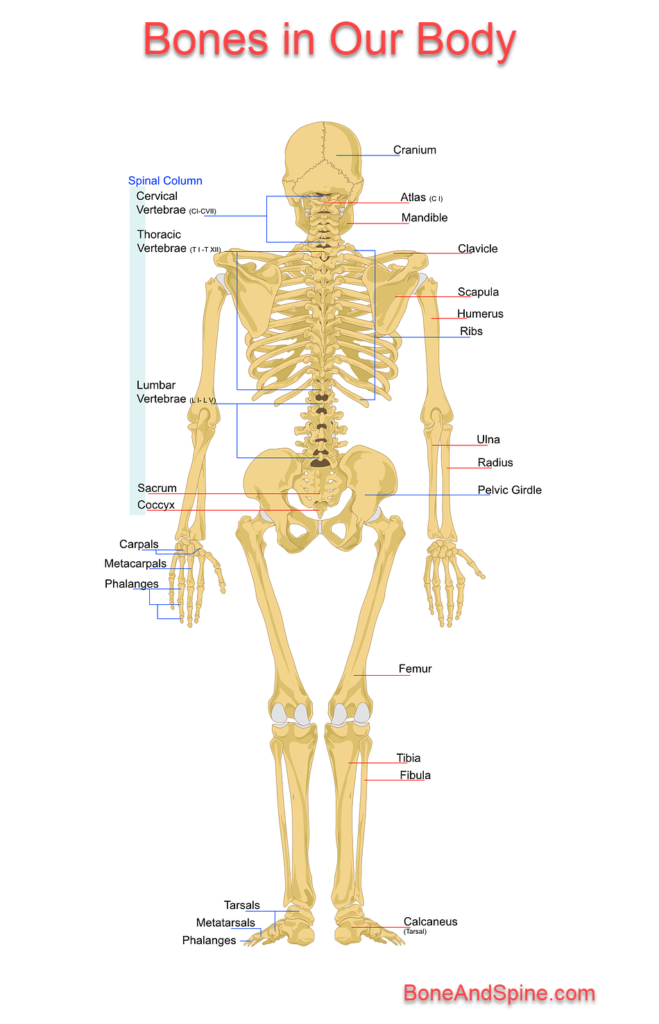
Each long bone has an elongated shaft or diaphysis and two expanded ends (epiphyses) which are smooth and articular. The shaft typically has 3 surfaces separated by 3 borders, a central medullary cavity, and a nutrient foramen directed away from the growing end. Examples of typical long bones are humerus, radius, ulna, femur, tibia and fibula, metacarpals, metatarsals, and phalanges
Short bones
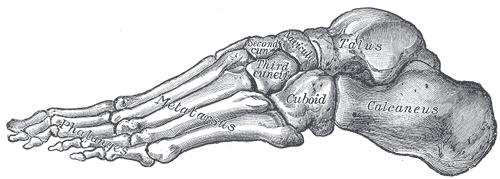
Their shape is usually cuboid, cuneiform, trapezoid, or scaphoid. Carpal and tarsal bones in the wrist and foot are examples of short bones.
Flat Bones
Flat bones resemble shallow plates and form boundaries of certain body cavities. Examples: bone in the vault of the skull, ribs, sternum, and scapula.
Irregular Bones
Vertebra, hip bone, and bones in the base of the skull.
Pneumatic Bones
Certain irregular bones contain large air spaces lined by epithelium. Pneumatic bones examples are maxilla, sphenoid, ethmoid, etc. they make the skull light in weight, help in the resonance of voice, and act as air conditioning chambers for the inspired air.
Developmental Classification of Bones
Membrane (Dermal) Bones
These types of bones ossify in the membrane (intramembranous or mesenchymal ossification) and are thus derived from mesenchymal condensations. Examples: bones of the vault of the skull and facial bones.
A defect in membranous ossification causes a rare syndrome called cleidocranial dysostosis. It is characterized by three cardinal features:
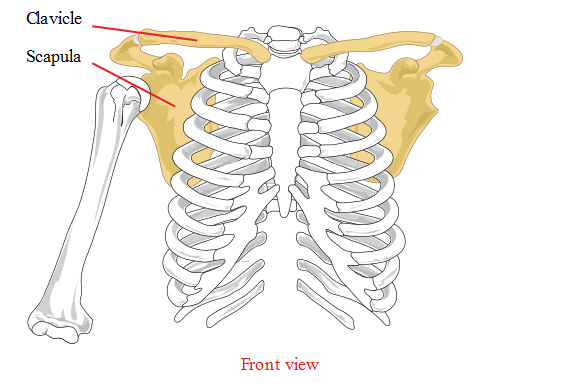
- Varying degrees of aplasia of the clavicle
- Increase in the transverse diameter of the cranium, and
- Retardation in fontanelle ossification. It may be hereditary or environmental in origin.
Cartilaginous Bones
These types of bones ossify in cartilage (intracartilaginous or endochondral ossification), and are thus derived from performed cartilaginous models. Examples: bone of limbs, vertebral column, and thoracic cage.
A defect in endochondral ossification causes a common type of dwarfism called achondroplasia, in which the limbs are short, but the trunk is normal. It is transmitted as a Mendelian dominant character.
Membrano-Cartilaginous Bones
These ossify partly in the membrane and partly in cartilage. Examples: clavicle, mandible, occipital, temporal, sphenoid.
Classification of Bones Based on the Bone structure
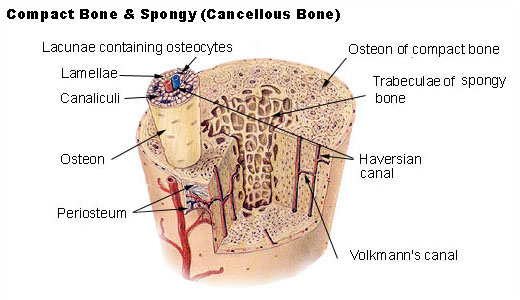
Cortical Bone
Cortical bone is also called compact bone or lamellar bone.
The shaft of bone in a long bone like femur is a typical example of the cortical bone.
Cortical bone forms the cortex, or outer shell, of most bones. It is much denser than cancellous bone, harder, stronger and stiffer. Cortical bone contributes about 80% of the weight of a human skeleton.
At the microscopic level, the structural arrangement of a cortical bone is different than cancellous.
Cortical bone is arranged for facilitating the following functions
- To support the whole body weight
- Protect organs
- Provide levers for movement
- Store and release calcium.
Cancellous Bone
Cancellous bone is also called trabecular bone or spongy bone.
Compared to compact bone, which is the other type of osseous tissue, it has a higher surface area but is less dense, softer, weaker, and less stiff.
It typically occurs at the ends of long bones, proximal to joints and within the interior of vertebrae.
Cancellous bone is highly vascular and frequently contains red bone marrow where hematopoiesis, the production of blood cells, occurs.
Read More on Cortical and Cancellous Bone
Sesamoid Bones
These are bony nodules found embedded in the tendons or joint capsules. They have no periosteum and ossify after birth. They are related to an articular or nonarticular bony surface, and the surfaces of contact are covered with hyaline cartilage and lubricated by a bursa or synovial membrane.
Patella, also commonly called the kneecap is the largest sesamoid bone. Pisiform, a carpal bone is another example.
The function of the sesamoid bones is not definitely known. Their possible functions are –
- To resist pressure
- To minimize friction
- To alter the direction of pull of the muscle; and
- To maintain the local circulation.
Accessory (Supernumerary) Bones
These are not always present. They may occur as ununited epiphyses developed from extra centers of ossification. Examples: sutural bones, os trigonum, os vesalianum, etc. In medicolegal practice, accessory bones may be mistaken for fractures. However, these are often bilateral and have smooth surfaces without any callus.