Last Updated on October 27, 2023
An erosive osteoarthritis is a form of osteoarthritis with additional erosive or inflammatory phenomena though the patients are negative for rheumatoid factor negative.
It most commonly affects the distal and proximal interphalangeal joints of the hand. The first carpometacarpal joint is affected less frequently. Joints of the foot are affected less commonly. Joints such as the hip and shoulder may also be very rarely affected.
Female are affected 12 times more than males. The typical presentation is seen in postmenopausal females.
Clinical presentation of the erosive osteoarthritis can be confused with seronegative rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis.
Criteria for Diagnosis
- Osteoarthritis of hands
- Erosions in at least 2 interphalangeal joints of which one must be a distal interphalangeal joint
- Negative rheumatoid factor and/or negative anti-citrullinated protein/peptide antibody
- The absence of personal and family history of psoriatic arthritis
- The absence of the history of Gout and Chondrocalcinosis affecting hands
- Presence of central subchondral erosions
- Normal (or near-normal) erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- Normal (or near-normal) wide range C-reactive protein
The first 2 points are essential for the diagnosis of EOA.
The last 3 points add to the specificity of diagnosis.
Symptoms and Signs
Pain, swelling, and warmth of the distal and proximal interphalangeal joints are the most common presentation. The presentation is often bilateral. Pain is often of abrupt onset and is usually followed by intermittent inflammatory episodes and progressive joint destruction.
Morning stiffness lasting as long as one hour may be present. One of the characteristic symptoms is throbbing paresthesia.
Examination often reveals tenderness and the presence of Heberden and Bouchard nodes. Deformities like subluxations, flexion contractures, and ankylosis may also be seen.
Systemic symptoms are absent.
Differential Diagnosis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Gout
- Hypothyroidism
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Chronic renal failure
- Amyloidosis
Laboratory findings in Erosive Osteoarthritis
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, antinuclear antibodies, and rheumatoid factors are usually negative. Sometimes, a slight increase of ESR and CRP may be found.
Imaging in Erosive Osteoarthritis
Distinction from other rheumatic diseases affecting the small joints of the hand is based on the radiographic appearance and demonstration of typical erosions.
Radiological features of erosive osteoarthritis are
- Joint space narrowing
- Subchondral sclerosis
- Marginal osteophytes,
- Erosions of the joint [Gull-wing and saw-tooth deformities.] The x-ray below shows gull-wing deformity. For easier comprehension, flying seagull is also shown
- Joint ankylosis
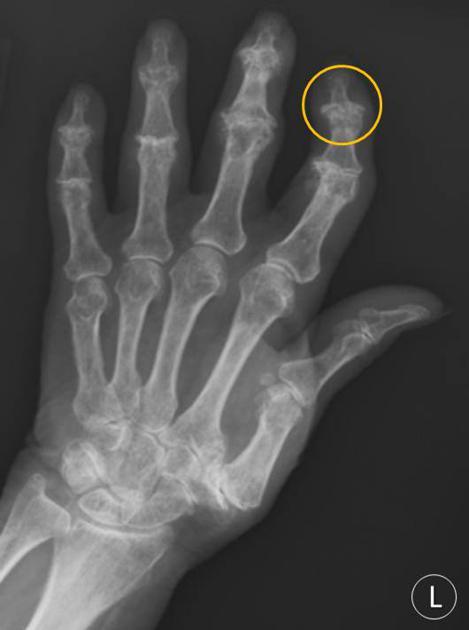 There is the characteristic absence of marginal erosions, fusiform soft-tissue swelling, and osteopenia.
There is the characteristic absence of marginal erosions, fusiform soft-tissue swelling, and osteopenia.
Ultrasound might help detect erosions early and additionally provide valuable information on the presence of synovitis and inflammatory changes in other soft tissues.
Treatment of Erosive Osteoarthritis
As with OA, treatment of EOA is often restricted to controlling symptoms and improving or maintaining function
Treatment is conservative unless joint destruction and/or contractures require surgical arthrodesis, arthroplasty, or tendon repair.
The prognosis is generally good with remission after several years being seen in most patients. The degenerative changes of course remain and are then merely those of osteoarthritis.
Drugs
- NSAIDs
- Intra-articular injection of corticosteroids
- Chondrotoin sulphate
- Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs and biological therapies like anakinra, infliximab, and adalimumab are being investigated and results seem promising.
Non-Drug Therapy
- Moist heat application
- Paraffin baths
- Splinting
- Exercises
Image Credit: Radiopaedia
