Last Updated on October 30, 2023
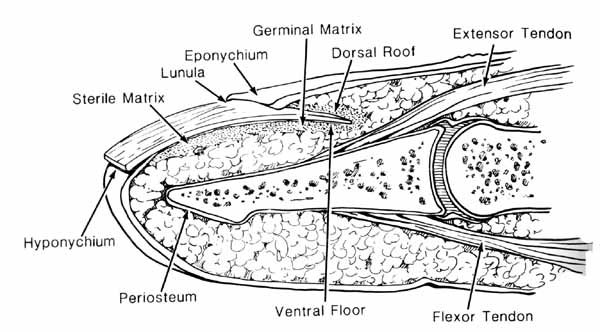
Fingernail injuries are injuries to nail bed which consists of the nail matrix. Fingernail injuries can be divided into that of the sterile matrix and germinal matrix.
In general, germinal matrix injuries are more serious. An injury in this region has a higher likelihood of permanently affecting nail growth.
The nail is an integral component of the digital tip. It is a unique hardened structure formed by keratinized squamous cells. Nail functions to protect the fingertip and provides a counterforce to tactile sensation and for aiding in the grip formed by fingertips [ as in pinching].
It is also involved in temperature control [thermoregulationion] which is regulated by glomus bodies in the nail bed and matrix.
Nails are similar to claws in other animals.
Parts of The Nail
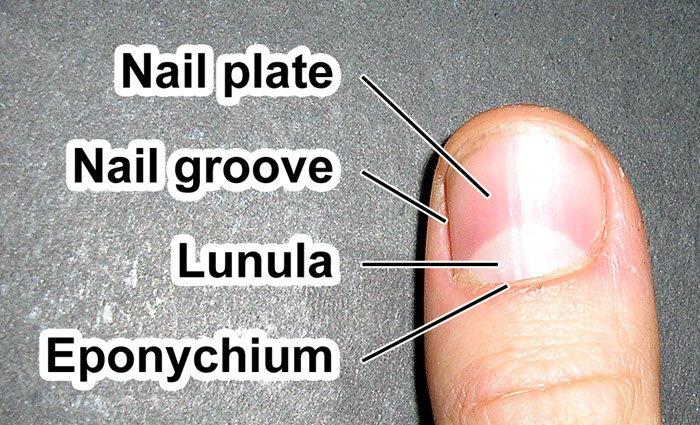
Nail Plate
The nail plate is also called corpus unguis. It is the hard visible part of the nail. The nail plate is composed of hard, keratinized, squamous cells that are loosely adherent to germinal matrix but strongly attached to the sterile matrix.
Matrix
Matrix is the tissue that a nail [nail plate] protects. It lies beneath the nail and contains nerves, lymph and blood vessels. The matrix is responsible for producing cells that become the nail plate. It has two parts sterile and germinal.
Lunula
Lunula is the white area at the base of a fingernail. Lunula means little moon. Lunula represents distal extent of the germinal matrix.
It is located at the proximal end of the nail and lies under the nail.
It is white only when seen through the nail. The lunula damage to lunula will cause permanent deformation of the nail.
Hyponychium, Eponychium and Paronychium
The hyponychium is the epithelium located beneath the nail plate at the junction between the free edge of the nail and the skin of the fingertip.
The eponychium is the small band of epithelium that extends from the posterior nail wall onto the base of the nail.
Paronychium are the lateral nail folds on either side of nail plate.
Blood Supply
Terminal branches of the radial and ulnar proper palmar (volar) digital arteries supply the nail.
Nail growth is separated occurs from the germinal matrix, sterile matrix, and dorsal roof of the nail fold.
Nail growth is estimated at 3-4 mm per month.
Classification of Acute Fingernail Injuries
Van Beek et al. classification of acute fingernail injuries is –
Germinal Matrix Injury
- GI: Small subungual hematoma proximal nail (25%)
- GII: Germinal matrix laceration, large subungual hematoma (50%)
- GIII: Germinal matrix laceration and fracture
- GIV: Germinal matrix fragmentation
- GV: Germinal matrix avulsion
Sterile Matrix Injury
- SI: Small nail hematoma (50%)
- SII: Sterile matrix laceration, large subungual hematoma (50%)
- SIII: Sterile matrix laceration with tuft fracture
- SIV: Sterile matrix fragmentation
- SV: Sterile matrix avulsion
This classification system is important for determining the appropriate treatment regimen.
Treatment of Fingernail Injuries
Treatment of fingernail injuries depends on the severity of the injury. A radiograph must be obtained to rule out an underlying fracture.
Grade I Fingernail injuries
Grade I injuries are treated nonoperatively in most of the cases. If the injury is very painful, decompression or nail removal can be performed.
Grade II, III, and IV Injuries
All grade II, II and IV injuries require nail removal and repair of the nailbed.
After removal of the nail, debridement of the nailbed is done if required and nailbed is repaired using appropriate sutures.
A splint or K-wire fixation may be required for distal phalanx fracture.
After repair, the nail is replaced as it serves as a template for the newly growing nail and provides a biologic dressing.
The finger is protected and motion is restricted for 7-10 days.
Nail Bed Avulsion
Nail bed avulsions account for approximately 15% of all traumatic injuries to the nail. For treatment, the avulsed nail bed is sutured in an anatomic position. If the avulsed nail cannot be sutured back, a split-thickness nail matrix graft can be used.
Nail Abnormalities After Trauma
Nail bed injuries can lead to a number of nail abnormalities. Commonly encountered nail deformities are nonadherence, split nails, linear ridging, crooked nails, and hooked nails.
Nonadherence
Nonadherence occurs when the nail does not adhere to the abnormal scar that has formed within the injured nail bed.
Nonadherence is the most common nail deformity after nailbed injury. It could be distal nonadherence or proximal one.
Distal nonadherence can cause a problem of dirt being lodged underneath the nail.
Proximal nonadherence can cause instability of the nail.
Treatment is by scar excision and primary repair. Split-thickness nail grafting may be done where required.
Split Nail
Split nails occur because of a longitudinal scar in the germinal or sterile matrix. The nail, therefore, grows on either side of the scar in the germinal matrix.
Treatment is done by scar excision and replacement with a split-thickness matrix graft.
A split nail due to an abnormality in the germinal matrix requires a germinal matrix graft from another finger or toe.
Linear Ridging
Linear ridging is often secondary to a bony protuberance beneath the nail bed.
Incising the nail bed over the involved area, removal of protruding bone and reapproximation of the nailbed is the treatment performed.
Lateral Deviation
Full-thickness avulsion of the lateral aspect of the nail bed causes the deviation of the nail. Elevation of the entire nail bed and placing it in a straight position is the recommended treatment.
Hooked Nail
A hooked nail involves volar displacement of the distal aspect of the nail. It can occur following a malunited fracture or a deficiency of skin of the digital pulp.
It is treated by freeing the tethered pulp and nail bed, splinting the freed nail bed, and reconstructing the soft-tissue defect of the pulp.
Total Nail Loss
Total nail loss can be treated by split-thickness skin grafting, nail prosthesis, or total nail reconstruction.