Last Updated on October 16, 2023
Foot deformities can be congenital or acquired conditions which occur due to structural abnormalities or muscular imbalances.
Foot is formed of bones, joints, muscles, tendons, and ligaments. While provides structural arrangement and strength, muscle tendons and ligaments are responsible for maintaining shape and carrying functions of the foot. This unique arrangement makes foot stable, strong, mobile and flexible to adapt to the roughness of the terrain. T.
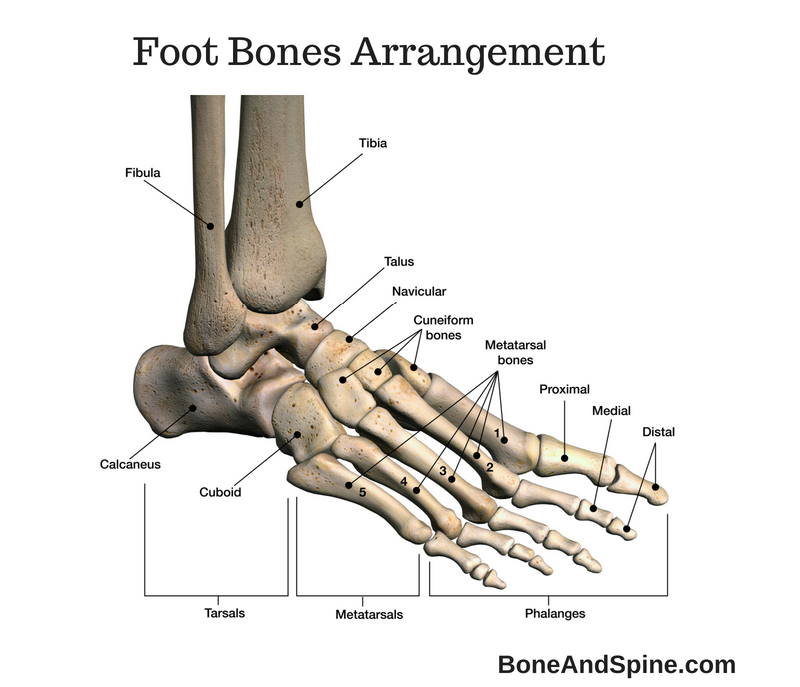 There is no universal ideal foot and what we call as the normal foot has a wide variability. In fact, most people have slightly deformed feet and they function normally.
There is no universal ideal foot and what we call as the normal foot has a wide variability. In fact, most people have slightly deformed feet and they function normally.
The deformity in the foot can arise from congenital causes or due to persistent external forces like diseases of joints or muscles, trauma. neuromuscular disorders and even wrong postures or tight footwear.
Clubfoot is a common congenital foot deformity characterized by plantar flexion of the ankle, inversion of the foot, and adduction of the forefoot. Another commonly seen deformity is hallux valgus.
Effect of Foot Deformities
Foot deformities can lead to pain and change in your walking style. Undue pressures could lead the skin to become hard and cause pressures sores.
One deformity could lead to misalignment of the other bones and further deform the foot.
The strain on muscles and tendon can cause injury to these structures and wear and tear of the joint.
Eventually to osteoarthritis may ensue.
A painful deformed foot may have reverberating effects on the knees, hips, and back.
It is worth reiterating that all deformed feet do not necessarily cause the symptoms.
Let us briefly discuss these deformities one by one
Clubfoot
Clubfoot is mostly congenital or rarely acquired .
The deformity is bilateral in about 30–50% of cases.
For congenital clubfoot, there are many theories which include malposition of the bones as the child grows and lack of enough space in the uterus causing the malposition of the foot.
There is dominant posterior musculature, especially tibialis posterior and weak peroneus muscles. Achilles tendon is shortened.
The foot points downwards and inwards [equinus and varus]. There is cavus of the midfoot and adduction of the forefoot.
Dorsiflexion is limited.

Most of the diagnoses are clinically made after birth through ultrasound is also able to detect prenatally.
In any newborn with clubfoot, spine and muscular diseases should be ruled out.
X-rays can confirm the diagnosis by showing long axis of talus and calcaneus are parallel.
Serial casting is used to correct the deformity over a period. Surgery is required when serial casting fails or the clubfoot is rigid.
Splayfoot
It is also called pes planotransversus or pes transversoplanus.
In this condition, the metatarsal bones spread out and their heads lower. The front end of the foot becomes wider which lead to . This leads to more stress on the middle bones in the forefoot which causes pain.
This is usually painful, and can make the skin hard and thick, leading to calluses. People with splayfeet are also more likely to develop hallux valgus [bunion] [see below]
It is a very common foot deformity and occurs due to muscle and connective tissue weakness.
The pain is called metatarsalgia [because it occurs in metatarsals due to abnormal strain on the metatarsal heads II to IV.
These patients are more prone to develop hallux valgus where the great starts moving laterally and digitus quintus varus where Vth toe start moving medially.
Morton neuroma may develop, worsening the pain further. It is characterized by den, shooting pain on the plantar side of the foot (between the 3rd and 4thmetatarsal)
X-rays show spacing of metatarsal heads. Erosion of second, third and fourth metatarsal may be seen along with misalignment of first and fifth ray.
The treatment involves plantar support to the metatarsal heads and foot muscle training.
Metatarsus Adductus or Metatarsus Varus
Metatarsus adductus is adduction of the forefoot. It is also called a curved foot. The cause of the condition is not known. Uterine malposition is thought to be causative factor. An association with hip dysplasia is seen.
An adductor and peroneus imbalance is thought to contribute.
It presents immediately at birth
The condition is painless. The foot appears curved and there is intoeing of the forefoot.
In severe adduction, medial skin crease is seen over the forefoot.
If the curve is flexible [correctible], no treatment is required. Rigid curved feet [non-correctible]should be treated by splintage, orthotics or inserts.
Surgery is done in cases where conservative treatment does not help. The procedures include reduction osteotomy of cuboid bone or wedge-insertion osteotomy of the cuneiform bone. The former shortens the lateral ray and the latter lengthens the medial ray.
Pes Cavus or High Arched Foot
The foot has an unusually high foot arch, and the upper surface of the foot (the instep) is higher than normal too.
This results in biomechanics so that ball of the foot carries more weight, causing pain and calluses.
They are often seen in paralytic disoders such as polio. Claw toes may occur and there is an increased risk of ankle injuries.

The cavus was due to post-polio residual paralysis.
Flat Foot or Pes Planus
It is also called fallen arches. In this deformity, the foot is flatter than usual because the arch of the foot is not well developed. In the normal foot, the middle part of the foot does not touch the ground but in case of a flat foot, most of the foot – from the heel to the ball of the foot – touch the floor.
Fallen arches can become painful over a long period when you walk on them. Often, these could be managed by orthotics or suitable footwear.
Structural causes of fallen arches or pes planus may require surgery.
It must be noted that the feet of the children are flatter when compared to adults. The foot arch, midfoot and hindfoot reach their normal position by age of ten. Therefore, the flat foot does not need to be treated in children.
Pronated Foot
There is pronation of the foot. That means the heel leans inward. They are seen in the childhood and is often associated with fallen arch and obesity.
They are often asymptomatic till 3 or 4 decades of life.
Pronated feet already arise in childhood, often together with a fallen arch or flat foot.
Learn more about hyperpronation
Equinus foot
Equinus deformity of the foot occurs at the ankle and occurs when the foot is fixed in the position of plantar flexion. This leads to shortening of the calf muscles, preventing lowering of the heel to the floor.
The person with this kind of deformity walks only on the front and middle foot as they can not bring the foot in the smooth heel to toe movement.
Polio, head injury and cerebral palsy are common causes. Patients who are on bed for prolonged periods also develop equinus as the foot is in plantar flexion on lying.
Often it requires surgical treatment. Equinus foot may arise following brain damage that affects the communication between nerves and muscles. It can also develop in people who are bedridden for a long period of time, or who have had an injury (e.g. an ankle injury).

The photograph shows equinus and cavus deformity of the foot in a patient who had post polio residual paralysis as a result of poliomyelitis that he had in childhood.
The deformity is actually equino-cavo-varus but in this picture, only two deformities can be appreciated. Equinus is the deformity at the ankle in which angle between the foot and leg increases. Cavus is the deformity of the arches of the foot. When the arch of the foot becomes exaggerated, it is called cavus.
Look at the convexity at the anterior surface near the ankle. Normally, it is not so. A normal person keeps his foot and ankle at slightly more than 90 degrees in resting position. This angle in the picture is almost 180 degrees.
Similarly, look at the arch of the foot. It seems unusually high.
Tarsal Coalition
Coalition means fusion or joining.
Tarsal Coalition is an abnormal connection between the bones in the midfoot and hindfoot. It is diagnosed in late childhood or early adolescence.
At that age, the coalition affects the movement of the foot, causes pain and sometimes stiffness. Walking on uneven surfaces results in greater pain.
Frequent ankle sprains may occur.
The coalition could be
- Calcaneonavicular
- The talocalcaneal
Non-operative treatment consists of rest and splinting. Surgical procedures are considered for those who do not improve on non-operative treatment.
Hammer Toe, Mallet Toe, Claw Toe

Image Credit: Wikipedia
A hammer toe is also called contracted toe. It is a deformity that occurs s due to an imbalance of musculo-ligamental forces resulting in flexion of prximal interphalangeal joint and resembling a hammer
A hammertoe can either be flexible or rigid. hammer toes cause difficulty in wearing shoes and pain.
Padding, modification of the shoes and surgery are the treatment options.
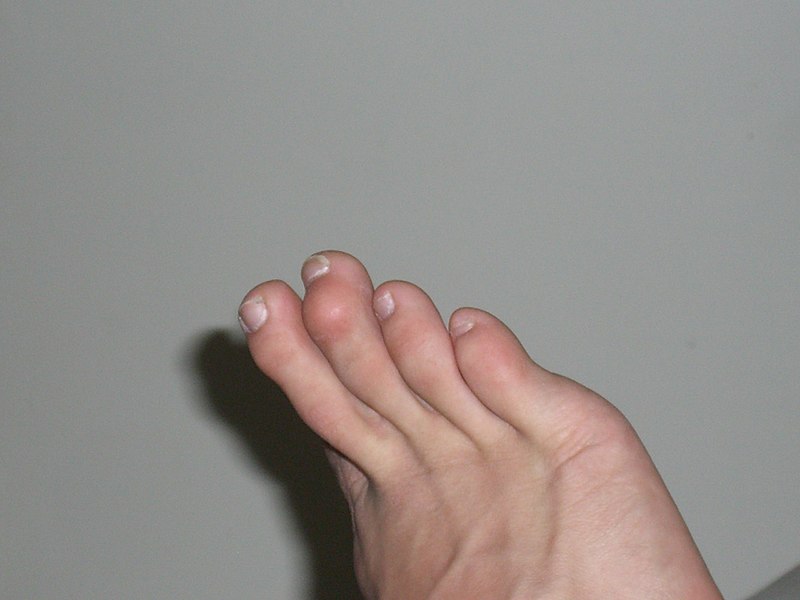
A similar deformity to hammer toe except that the distal interphalangeal joint is involved.
Claw toe is dorsiflexion of the metatarsophalangeal joint, and flexion of both the proximal and distal interphalangeal joints. It can affect toes 2-5.
Hallux Valgus and Bunion
Hallux valgus is a condition where there is lateral movement or abduction of the great toe. It causes a protrusion on the medial side of metatarsophalangeal joint where a swelling might develop. This swelling is known as bunion.
The bunions can be very painful, especially when wearing shoes that place pressure upon the area.
Haglund’s Deformity or Pump Bump
This refers to swelling in retrocalcaneal region.
[Read more on Haglund deformity]
It is also commonly called as a “pump bump because a number of pump-style footwear can cause this painful condition. It may be accompanied by retrocalcaneal bursitis.
It is seen more in the high arch foot type or tight tendoachilles.
Ectrodactyly or Lobster Claw Deformity
Ectrodactyly is the term used for the absence of one or more central digits of the hand or foot. It is also known as a split hand or split foot malformation.
Following photographs are of a patient with ectrodactyly of both hand and feet.
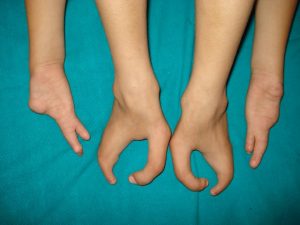
When the deformity is similar to feet deformity in this case i.e. middle digit rays are absent, the deformity is called lobster claw deformity.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Foot Deformities
The details of deformity should be noted. In addition, complete evaluation of feet, knees, hips, and spine should be done.
A flexible deformity is the one which can be corrected either by active contraction of the muscles ot passively by the physician.
The resistant deformity is the one which is not correctable.
Xray and CT are done to evaluate skeletal deformities.
Treatment requires an individual approach.
Correctable foot deformities are dealt with by foot orthotics and manipulative treatment whereas in resistant foot deformities, surgery is required.