Last Updated on March 17, 2020
Hand osteoarthritis, like generalized osteoarthritis, is considered a degenerative disease that is caused by the breakdown of cartilage.
Cartilage covers the ends of bones in the joint.
Hand osteoarthritis results in pain, stiffness, tenderness, and swelling in the affected hand joints.
Hand and wrist are formed by multiple small joints that enable complex and fine functions of the hand from threading a needle to throwing a ball with accuracy.
Osteoarthritis of hand is a painful condition and can affect activities of daily living by limiting the motion of the hand.
Arthritis refers to the inflammation of one or more joints. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are the most common types of arthritides affecting the body.
Sites of Hand Arthritis
Some authors consider hand osteoarthritis not one single disease, but a heterogeneous group of disorders
Hand osteoarthritis most often develops in three sites
- The base of the thumb (the trapezio-metacarpal joint)
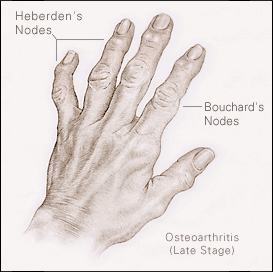
- Distal interphalangeal joint [distal most joint of the finger]- Heberden Nodes
- Proximal interphalangeal [first joint beyond the knuckles] – Bouchard Nodes
It also often develops in the wrist.
Heberden node is a bony deformity at the distal interphalangeal joint and is one of the early signs of hand osteoarthritis. The deformity is a result of the bone spurs from the osteoarthritis in that joint.
A similar deformity at proximal interphalangeal joints is called the Bouchard node. Often, these nodes develop gradually, with little or no discomfort.
These nodes
However, they may present acutely with pain, redness, and swelling, which sometimes triggered by minor trauma.
These nodes may not be painful but can cause limitation of motion of the joint.
Types of Hand Osteoarthritis
Hand osteoarthritis can develop as a separate entity or may occur as part of generalized osteoarthritis. Hand osteoarthritis can be of three types
Generalized Hand Osteoarthritis
Generalized osteoarthritis is characterized by the involvement of three or more joints or groups of joints (distal interphalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints are counted as one group each). Heberden and Bouchard nodes are prominent.
Symptoms may be episodic, with marked by soft tissue swelling, redness, and warmth. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate may be elevated, but serum rheumatoid factor tests are negative.
Erosive Hand Osteoarthritis
In erosive osteoarthritis of hand , distal and proximal interphalangeal joints of the hands are most prominently affected. Erosive osteoarthritis tends to be more destructive than typical nodal Osteoarthritis.
Radiographic imaging shows collapse of the subchondral plate and bony ankylosis may occur.
In erosive arthritis, joint deformity and functional impairment may become very severe. There is a history of pain and tenderness. The synovium is much more extensively infiltrated with mononuclear cells than in other forms of Osteoarthritis.
Thumb Base Osteoarthritis
Thumb base is the second most frequent area of involvement in osteoarthritis. Swelling, tenderness and crepitus on the movement of the joint are typical.
In contrast to Heberden nodes, which usually do not interfere significantly with function, thumb base osteoarthritis frequently causes loss of motion and strength.
Pain with pinch leads to the adduction of the thumb and contracture of the first webspace, often resulting in compensatory hyperextension of the first metacarpophalangeal joint and swan-neck deformity of the thumb.
Risk Factors for Osteoarthritis of Hand
- Older age
- Female gender
- Being overweight or obesity
- Family history
- Joint injuries [fractures and dislocations]
- Infection of joints
- Ligamentous laxity
- Repetitive injury to joint
Symptoms of Hand Osteoarthritis
Patients may be symptomless in spite of the disease. Stiffness, swelling, and pain are chief complaints. Here is list of possible symptoms
- Pain
- Intermittent first
- Worsens with hand use
- Eases with rest
- Morning stiffness and pain is common
- Becomes constant pain in severe disease
- Joint Stiffness
- Morning stiffness
- May worsen with cold temperature
- Grinding Sound or Crepitus
- This occurs due to rubbing of bone surfaces [due to loss of cartilage]
- Can be a grinding, clicking or cracking sensation
- Swelling
- Tenderness to touch
- Difficult to use hand for daily activities like opening the lock or lid from a jar.
The clinical examination may reveal Heberden’s nodes and/or Bouchard nodes.
Pain at the base of the thumb is a common presentation of the base of thumb osteoarthritis. Pain and decrease in the motion of the joints may cause problems in daily activities like opening jars or turning of keys.
Diagnosis
History and examination is the mainstay of the diagnosis. X-rays will reveal the presence of bony and joint abnormalities. Blood investigations are usually normal.
Treatment of Hand Osteoarthritis
Treatment may not be necessary for hand osteoarthritis with minimal or no symptoms. Treatment is designed to relieve pain and restore function.
Treatment of hand osteoarthritis includes
Anti-inflammatory Medications
Pain medications like acetaminophen are helpful in relieving the symptoms of mild hand osteoarthritis. Other commonly prescribed drugs are ibuprofen, ketoprofen, naproxen, and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Food Supplements
Food supplements like glucosamine and/or chondroitin can be added in therapy. These medicines do not benefit all the patients though.
Local Therapy
Local heat/cold applications and topical pain creams are helpful for relieving pain. Steroid injections at the site receive the symptoms.
Splints
Finger or wrist splints may be added especially in the night to provide the rest to affected joint(s).
Surgery
Surgical treatment is considered when medical treatment does not help. There are two main options for surgically treating the affected joint.
- Joint fusion or arthrodesis
- Joint replacement or reconstruction
The decision for surgical treatment needs to be made on an individual basis depending on the needs and expectations of the patient.
References
- Caspi, D. et al. Clinical, radiologic, demographic, and occupational aspects of hand osteoarthritis in the elderly. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 30, 321–331 (2001).
- Thaper, A., Zhang, W., Wright, G. & Doherty, M. Relationship between Heberden’s nodes and underlying radiographic changes of osteoarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 64, 1214–1216 (2005).PubMed
- Egger, P. et al. Patterns of joint involvement in osteoarthritis of the hand: the Chingford Study. J. Rheumatol. 22, 1509–1513 (1995).PubMed