A person is said to have drug-resistant tuberculosis if the tuberculous bacteria that the person is infected with, will not respond to, and are resistant to, at least one of the main antitubercular drugs. Drug-resistant tuberculosis occurs when bacteria become resistant to the drugs used to treat TB. This means that the drug can no […]
Infections
Hydatid Disease of Bone
Hydatid disease of bone is very rare and is often misdiagnosed because of non-specific presentation and radiology. As its management is quite different from other conditions involving the bone, it is important to consider the differential of Hydatid disease of the bone in lucent bone lesions, especially where the echinococcosis is prevalent. Hydatid Disease or […]
Osteomyelitis Presentation and Treatment
Osteomyelitis literally means inflammation of bone and its marrow regardless of whether it is due to pyogenic organisms, tuberculosis, syphilis, a specific virus, or the presence of a foreign. However, its more accepted meaning is the infection by pyogenic bacteria or less commonly to the other organisms. The infection involves the marrow spaces, the Haversian […]
Tuberculosis of Shoulder Joint
Tuberculosis of shoulder is rare. It constitutes about 1-2 % of skeletal tuberculosis.[1] It is found more in adults as compared to children. Concomitant lung TB is found more commonly than other skeletal TB. Relevant Surgical Anatomy of Shoulder Joint The shoulder joint is a ball and socket synovial joint. The humeral head is large […]
Tuberculosis of Foot
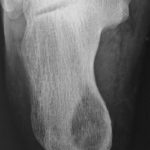
Tuberculosis of foot is rare and constitutes less than 10% of cases of osteoarticular tuberculosis. Calcaneum is the most common bone involved followed by subtalar joint and midtarsal joints. Pathophysiology Bonewise, the order of involvement in decreasing order is calcaneum, talus, first metatarsal, navicular, first and second cuneiforms cuboid and others. The infection first lodges […]
Tuberculosis of Ankle
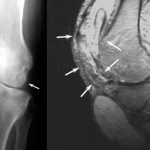
Tuberculosis of ankle joint is relatively uncommon. The incidence of ankle tuberculosis is less than 5 percent of all osteoarticular tuberculosis. Pathophysiology The mycobacteriaereachs the ankle joint viathe bloodstream. The initial focus may start in the synovium, especially in children, or as an erosion in the distal end of tibia, malleoli or talus. Rarely tuberculosis […]
Tuberculosis of Knee Joint – Diagnosis and Treatment
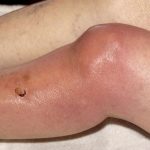
Tuberculosis of knee joint is third common osteoarticular tuberculosis after spine and hip. Knee tuberculosis or commonly called TB knee accounts for nearly 10 percent of all skeletal tuberculosis. Relevant Anatomy of Knee Joint The knee joint is the largest joint in the body. It is a superficial joint and because of its large size […]
Tuberculosis of Hip – Presentation and Treatment
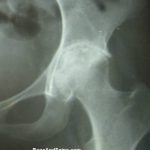
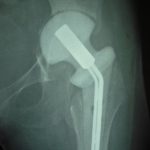
Tuberculous of the hip joint is common with a frequency of involvement next only to spinal tuberculosis. Hip tuberculosis accounts for 15% percent of all cases of osteo-articular tuberculosis and 1-3 % of all tuberculosis cases. Anatomy of the Hip Joint The hip joint is a ball and socket synovial joint. Fibrocartilaginous labrum attached to […]
Prosthetic Joint Infection
Prosthetic joint infection is a devastating complication of joint replacement surgery and occurs in1–3% of patients. Prosthetic joint infection can occur due to direct inoculation at the time of surgery or hematogenous spread of organisms to the prosthesis at a later time. One of the peculiarities of these infections is that the organism on attachment […]
Septic Arthritis or Infectious Arthritis
Septic arthritis is a term used when the joint space is infected with microorganisms which can be bacteria, viruses, mycobacteria, and fungi. Septic arthritis also includes prosthetic joint infections. Septic arthritis is also called infectious arthritis. Joints are quite resistant to infection but there are some risk factors that increase the risk increased infection. These […]