Last Updated on August 1, 2019
Infrapatellar bursitis is inflammation of the infrapatellar bursa, a fluid-filled sac located just below the patella or kneecap. The superficial infrapatellar bursa is located between the patellar tendon and the skin. It lies anterior to patellar tendon and is subcutaneous.
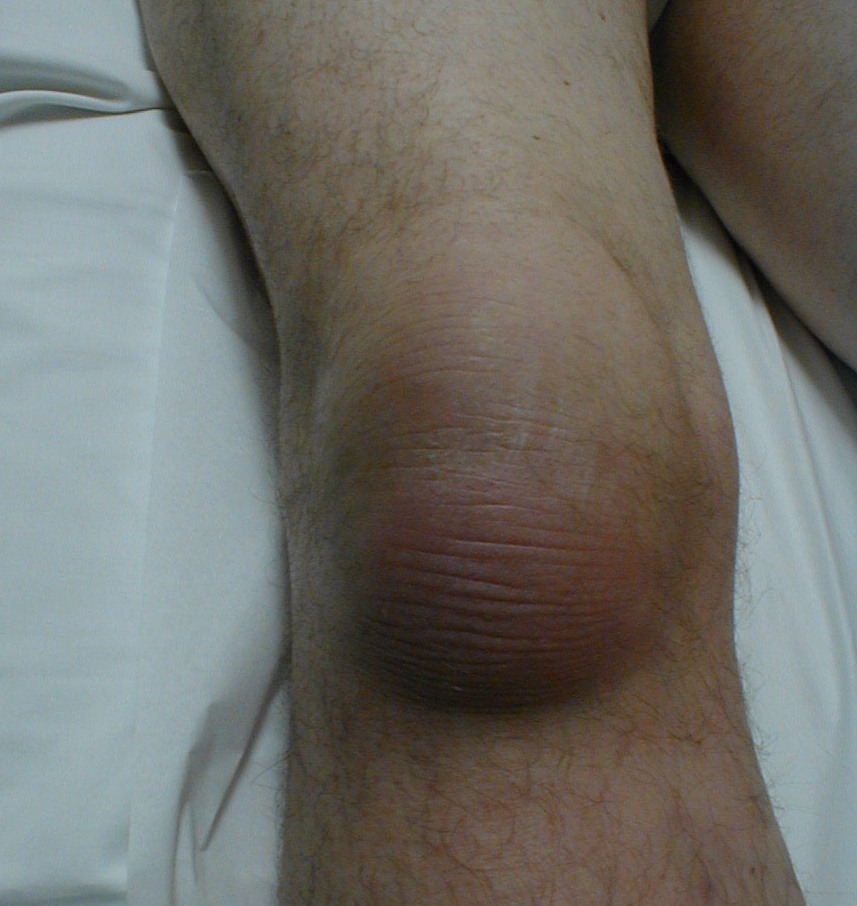
The deep infrapatellar bursa is situated between the patellar ligament and the upper front surface of the tibia. It is posterior to the distal patellar tendon, in the region of the infrapatellar fat pad.
Infrapatellar bursitis is also called or Clergyman’s Knee due to the occurrence in Clergymen kneeling frequently.
Infrapatellar bursitis may be a component of Osgood-Schlatter disease.
Pathophysiology of Bursitis
Friction between the skin and the bursa is a common cause of infrapatellar bursitis. Infection can also cause infrapatellar bursitis. As noted before, the condition could be part of Osgood Schlatter disease.
Repeated trauma or infection caused inflammation of the bursa which results in multiplication of synovial cells. This leads to increased formation of collagen and fluid.
Infectious bursitis usually results from direct inoculation of microorganisms through traumatic injury or spread from cellulitis. Less commonly, it could be due to contiguous septic arthritis or bacteremia.
Patients with diabetes mellitus, steroid therapy, uremia, alcoholism, skin disease have a higher risk of getting an infection.
Presentation of Infrapatellar Bursitis
The patient presents with pain in the anterior aspect of the knee and swelling on the lower side of the patella. The swelling is distal to the swelling of prepatellar bursitis though it becomes difficult to differentiate in cases of large swellings. There might be a history of frequent kneeling.
Extremes of flexion and extension would cause pain. There is tenderness in the area of swelling.
If the swelling is anterior to the patellar tendon, it is superficial infrapatellar bursitis. If the swelling is posterior to the patellar tendon, deep infrapatellar bursitis is presented. Both can be differentiated on MRI.
Lab Studies
CBC, ESR, CRP may be needed if the infection is suspected. Anitnuclear antibody, rheumatoid factor, and anti – citric citrullinated peptide tests should be done in cases of autoimmune diseases.
Aspiration and analysis of bursal fluid should be done to rule out infectious or rheumatic causes. Fluid is tested for biochemical and cytological analysis. Gram stain and culture for infection can be done in cases of infection.
Imaging
Xrays are normal in most of the cases but are done to identify any underlying bony pathology. Tendon calcifications may be found in chronic bursitis.
Ultrasonography may help in injection application or aspirations in deep bursae.
MRI is generally not done in routine but is able to define the lesion better and even differentiate from abscess and tumors.
MRI is able to differentiate between superficial and deep infrapatellar bursitis.
Treatment of Infrapatellar Bursitis
The treatment includes rest, ice compression and elevation [RICE therapy]. Anti-inflammatory drugs like NSAIDs decrease pain and swelling by reducing inflammation. In large swellings, bursa is aspirated and intrabursal steroid injections could be used.
The cause is identified and repeated trauma is avoided [e.g. frequent kneeling]
In infectious cases, antibiotics are used, first broad spectrum and the culture based antibiotic should be given.
Most of the infections can be treated by antibiotic therapy but some cases would require surgical drainage as well.
In chronic or recurring cases, removal of bursa may be sought.