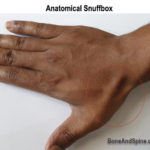
The anatomical snuffbox is a triangular deepening on the dorsoradial aspect of the hand at the level of the carpal bones. It is visible with ulnar deviation of the wrist and extension and abduction of the thumb. The name snuffbox is derived because this depression was used as a means of placement for the inhalation […]
Anatomy
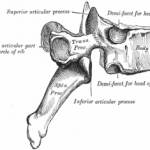
Pars interarticularis Anatomy and Significance
What is Pars Interarticularis? The Pars Interarticularis is a special region of the lamina between the superior and inferior articular processes. The term literally means part between the articulations in Latin language and is kind of bony bridge that joins these two upper and lower facets. Thus one vertebral has two pars interarticularis. Thus facet […]
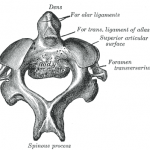
Axis or Second Cervical Vertebra [C2]
Axis is the second vertebra of the spine and is also called C2 bone vertebra. It articulates with C1 or atlas vertebra above and C3 vertebra below. The axis is an atypical cervical vertebra like atlas and vertebra prominens or C7 vertebra. It forms a pivot for atlas to rotate providing greater range of motion […]
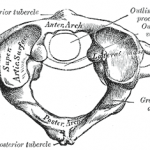
Atlas or First Cervical Vertebra [C1]
Atlas is the first cervical vertebra that sits just below the skull. It is also called C1 vertebra. Along with axis, the second vertebra and C7, it falls into the group of atypical cervical vertebrae. Atypical because these have unique features. Axis and C7 or vertebra prominens are discussed separately. Atlas is unique in its […]
Vertebra Prominens or Seventh Cervical Vertebra [C7]
Vertebra prominens is the common name for 7th cervical vertebra or C7, the largest and most inferior vertebra of the cervical region of the spine. It is named because it has a large spinous process that protrudes posteriorly and can be felt prominently on palpation. Vertebra prominens is easily recognized on palpation of the back of […]
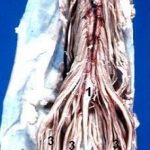
Anatomy of Cauda Equina
The cauda equina is a structure within the lower end of the spinal column of most vertebrates, that consists of nerve roots and rootlets from above[from second lumbar to coccygeal nerve] which originate in the conus medullaris of the spinal cord. Cauda equina is named so because it resembles horse’s tail. In humans, the spinal […]
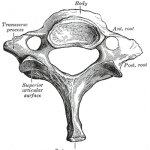
Typical and Atypical Thoracic Vertebra
The typical thoracic vertebrae are seven in number and atypical thoracic vertebra are five in number. Vertebra T2 to T8 are typical and rest of them are atypical. Both typical and atypical thoracic vertebrae are discussed. Typical Thoracic Vertebra The body of a typical thoracic vertebrae is heart shaped with roughly the same measurements from side […]
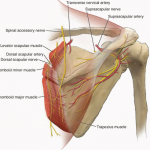
Dorsal Scapular Nerve Entrapment Syndrome
The dorsal scapular nerve entrapment is a relatively less common nerve entrapment that causes shoulder and arm pain. It is vulnerable during brachial plexus injections as the nerve passes through the middle scalene muscle. Dorsal scapular nerve entrapment is uncommon and therefore frequently underrecognized cause of pain in shoulder and neck area. The symptoms are […]
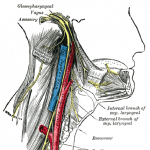
Spinal Accessory Nerve Anatomy and Significance
The spinal accessory nerve [ also called accessory nerve] is eleventh cranial nerve (CN XI) [see the controversy below] and is composed of two parts, the cranial part, and the spinal part. It has a purely somatic motor function, innervating the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. The sternocleidomastoid is a neck muscle that tilts and rotates […]
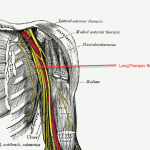
Long Thoracic Nerve Anatomy and Significance
The long thoracic nerve is a pure motor nerve that arises from anterior or ventral roots of C5, C6, and C7 and supplies serratus anterior muscle. Serratus anterior muscle is responsible for stabilization and protraction movement of the scapula. It is also called posterior thoracic nerve and the external respiratory nerve of Bell, after Sir Charles Bell who provided its first […]