Last Updated on July 31, 2019
Glasgow Coma Scale
Glasgow Coma Scale is a neurological scale developed by Teasdale and Jennett and is also known as Glasgow Coma Score. Glasgow coma scale is used to record consciousness levels of the person.
Glasgow coma scale is routinely used in head injuries and other central nervous system conditions
The scale comprises three tests: eye, verbal and motor responses.
The three values separately, as well as their sum, are considered. The lowest possible GCS (the sum) is 3 (implies deep coma or death), whilst the highest is 15 (implies fully awake person).
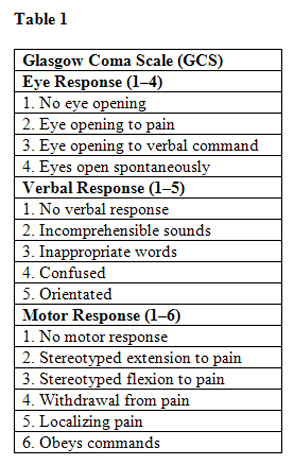
Best eye response (E)
There are 4 grades starting with the most severe:
- No eye opening
- Eye opening in response to pain. (Patient responds to pressure on the patient’s fingernail bed; if this does not elicit a response, supraorbital and sternal pressure or rub may be used.)
- Eye opening to speech. (This should not be confused with an awakening of a sleeping person. In such cases a score of 4 is given, not 3.)
- Eyes opening spontaneously
Best verbal response (V)
There are 5 grades starting with the most severe:
- No verbal response
- Incomprehensible sounds. (Moaning but no words.)
- Inappropriate words. (Random or exclamatory articulated speech, but no conversational exchange)
- Confused. (The patient responds to questions coherently but there is some disorientation and confusion.)
- Oriented. (Patient responds coherently and appropriately to questions such as the patient’s name and age, where they are and why, the year, month, etc.)
Best motor response (M)
There are 6 grades starting with the most severe:
- No motor response
- Extension to pain (adduction of arm, internal rotation of the shoulder, pronation of forearm, an extension of the wrist, decerebrate response)
- Abnormal flexion to pain (adduction of arm, internal rotation of the shoulder, pronation of forearm, flexion of wrist, decorticate response)
- Flexion/Withdrawal to pain (flexion of elbow, supination of the forearm, flexion of the wrist when supra-orbital pressure applied; pulls part of the body away when nailbed pinched)
- Localizes to pain. (Purposeful movements towards painful stimuli; e.g. hand crosses mid-line and gets above clavicle when supra-orbital pressure applied.)
- Obeys commands. (The patient does simple things as asked.)
How To Interpret The Score?
Individual elements, as well as the sum of the score, are important in the Glasgow Coma Scale. Hence, the score is expressed in the form “GCS 9 = E2 V4 M3 at 17:35”.
Generally, comas are classified as:
- Severe, with GCS less than or equal to 8
- Moderate, GCS 9 – 12
- Minor, GCS 13 or greater.
In a severely injured patient with intubation and severe facial/eye swelling or damage, it is not possible to test the verbal and eye responses. In these circumstances, the score is given as 1 with a modifier attached e.g. ‘E1c’ where ‘c’ = closed, or ‘V1t’ where t = tube.
A composite might be ‘GCS 5tc’. This would mean, for example, eyes closed because of swelling = 1, intubated = 1, leaving a motor score of 3 for ‘abnormal flexion’.
The Glasgow Coma Scale has limited applicability to children, especially below the age of 36 months because then the verbal performance of even a healthy child could be labeled to be poor).
To avoid this Pediatric Glasgow Coma Scale, a separate yet closely related scale, has been developed for assessing younger children.
Pediatric Glasgow Coma Scale
The Pediatric Glasgow Coma Scale or Pediatric Glasgow Coma Score (PGCS) is the equivalent of the Glasgow Coma Scale and is used to assess the consciousness of infants and children.
Pediatric Glasgow Coma Scale is used in cases of head injury of children mostly.
The scale has been modified from the original Glasgow coma scale as s many of the assessments for an adult patient would not be appropriate for infants and young children.
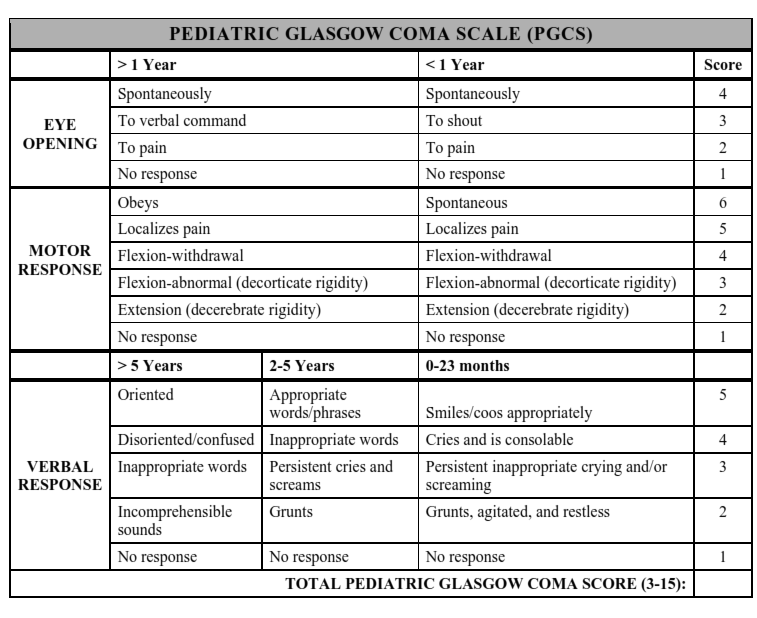
The Pediatric Glasgow Coma Scale comprises of three tests: eye, verbal and motor responses as in Glasgow coma scale(GCS).
Best eye response: (E)
4. Eyes opening spontaneously
3. Eye opening to speech
2. Eye opening to pain
1. No eye opening
Best verbal response: (V)
The main difference from adult Glasgow coma scale comes in the verbal response. Here the responses are different age wise
Age 0-23 Months
5. Infant coos or babbles or smiles appropriately (normal activity)
4. Infant cries but consolable
3. Persistent crying and or screaming
2. Infant moans to pain, grunts, agitated and restless
1. No verbal response
Age 2-5 Years
5. Appropriate words or phrases
4. Inappropriate words
3. Persistent Cries or screams
2. Grunts
1. No response
Age> 5 Years
5. Oriented
4. Disoriented, confused
3. Inappropriate words
2. Incomprehensible sounds
1. No response
In children greater than 5 years of age, the responses are similar to adult Glasgow Coma Scale.
Best motor responses: (M)
6. Infant moves spontaneously or purposefully
5. Infant withdraws from touch
4. Infant withdraws from pain
3. Abnormal flexion to pain for an infant (decorticate response)
2. Extension to pain (decerebrate response)
1. No motor response
Interpretation of Pediatric Glasgow Coma Scale
A Coma Score of 13 or higher correlates with a mild brain injury, 9 to 12 is a moderate injury and 8 or less a severe brain injury. Any combined score of less than eight represents a significant risk of mortality.
In writing the score, along with total score individual components are also mentioned. For example E3V3M5, GCS 11.