Last Updated on March 29, 2022
Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis is a locally aggressive neoplastic synovial disease affecting joints, bursae, and tendon sheaths characterized by joint effusions, synovial thickening, and bony erosions.
Usually, pigmented villonodular synovitis affects a single joint [monoarticular presentation]. Polyarticular cases are rare and more likely in children.
Usually, patients between 30 and 40 years old are affected. However, the lesions are but are known to affect first to the seventh decade.
Overall It equally affects men and women.
Pigmented villonodular synovitis is relatively rare and accounts for less than 5% of all primary soft tissue tumors. Localized lesions are more common than diffuse. [see the classification below]
Diffuse PVNS affects predominantly large joints, with the knee being the most common (66-80%). The hip, ankle, shoulder, and elbow follow in descending frequency.
The localized intra-articular form of PVNS occurs almost exclusively within the knee. Tendon sheaths of the hand and wrist are affected more frequently, with the volar aspect of the index and long fingers being the most common sites of disease.
In a rare instance, pigmented villonodular tenosynovitis can coexist with other synovial conditions such as synovial chondromatosis.
Microscopically, pvpigmented villonodular synovitis has fibrohistiocytic origin [fibroblasts and histiocytic cells.]
Pigmented villonodular synovitis benign. Only a few cases of malignant transformation have been reported. However, it may cause significant morbidity.
Types of Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis
Pigmented villonodular synovitis can be classified as intraarticular and extraarticular. Intraarticular can be
- Intraarticular
- Diffuse – Diffuse involvement of joint synovium
- Localized – Polypoid or nodular joint synovial lesion within the joint
- Extraarticular
- Diffuse – Diffuse multifocal involvement of extraarticular synovial membrane (like tendon)
- Nodular or Localized – Localized extraarticular nodular lesion, also referred to as giant-cell tumor of the tendon sheath
Some authors just classify it to be nodular or diffuse.
The following table lists the major difference
| Feature | Localized PVNS | Diffuse PVNS |
| Age | 30-50 years |
Less than 40 years |
| Gender | Equally affected |
Slight female preponderance |
|
Imaging |
X-ray- may show bony erosion from pressure MRI- Well defined soft tissue mass |
X-ray shows degenerative changes of the joint Ill-defined soft tissue mass |
| Recurrence | Lesser | Higher |
Both diffuse and localized intraarticular forms, predominantly involve the major weight-bearing joints of the lower extremities.
The knee is the most common joint affected followed by hip, ankle, foot, elbow, and shoulder. The nodular extraarticular variant of pigmented villonodular tenosynovitis typically involves the acral [limbs and fingers] soft tissue and is predominantly found in the fingers and metacarpal and carpal areas. Tendons of the forearm are rarely involved.
Overall when all types are considered, the fingers are involved in nearly 60% of cases, whereas the knee is involved in approximately 30% of cases. The toes are involved in about 10% of cases.
Causes
- Overexpression of CSF1 gene
- Leads to clusters of aberrant cells creating focal areas of soft tissue hyperplasia
- Mutations
- Chromosome 1p13 in the majority of cases
- 5q33 chromosomal rearrangement
Giant Cell Tumor of tendon sheath is an associated condition.
Presentation of Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis
The symptoms can be intermittent or steadily progressive. The knee is the most common large joint affected.
Finger joints may present as n localized swelling of the palmar aspect.
The patient often presents with longstanding pain of insidious onset in the affected joint. About 50% of patients will have a prior history of trauma to the area.
Other symptoms are
- Stiffness in the affected joint
- Swelling in the affected joint
- Recurrent atraumatic hemarthrosis
- Hallmark of the disorder
On examination, there would be joint effusion. The overlying skin may be red [erythema]. There would be tenderness along the joint line and the motion of the joint would be limited.
The fluid aspiration yields hemorrhagic fluid.
Lab Investigations
- Bloodwork
- Mostly normal
- Arthrocentesis
- In recurrent hemarthrosis
- grossly bloody effusion
- Diagnostic arthroscopy
- Brownish or reddish inflamed synovium is typical of PVNS
- The frond-like pattern of papillary projections
- Gold standard for diagnosis
- Synovial biopsy should be Obtained
- Biopsy
- Gross findings
- Synovium is covered with tan to brown, irregular papillary projections and larger nodular protrusions.
- Microscopic Findings
- Gross findings
Imaging
X-rays
Findings on plain X-rays are not specific and in the early stages may appear normal.
AP and lateral of affected joint are the recommended views. An X-ray may show ill-defined soft tissue mass around the joint.
Frequently, degenerative joint diseases is seen along with multiple subchondral cysts in the bones, usually on both sides of the affected joint
Pressure erosion of the joints may occur leading to saucerization of the joint, a name given due to the typical pattern of saucer-like shape.
Narrowing of joint space and osteophyte formation may occur.
Sometimes, the effusion may be visible as a dense shadow. This signifies the presence of hemosiderin.
CT
CT is able to reveal the extent of involvement and the extent of cystic lesions loss and bone erosions.
CT scanning is also useful for guiding needle biopsy when required.
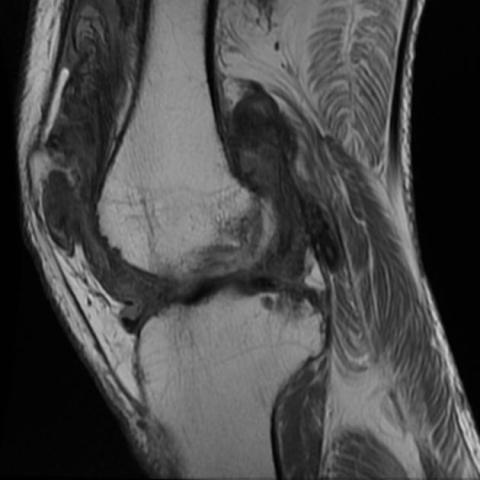
MRI
MRI is the modality of choice for imaging. MRI is able to provide excellent demarcation of both intra and extra-articular disease.
MRI shows joint effusion, hemosiderin deposits, synovial expansion, and bony erosion very well.
Nuclear Imaging
Bone and/or PET scans are not very important in the diagnosis of pigmented villonodular synovitis.
They add very little utility.
Differential Diagnoses
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Synovial hemangiomatosis
- Low-grade infectious arthritis
- Tuberculosis
- Gout
- Hemochromatosis
- Synovial Osteochondromatosis
- Synovial Sarcoma
- Hemophilia/hemarthrosis
Treatment of Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis
The treatment of choice is excision of the affected synovium. The recurrence rate after surgical treatment of synovium and adjacent bone require prostatic replacement. In clinically aggressive cases, low-dose radiotherapy is sometimes used to control the process and has been shown to be beneficial in preventing further destruction of the joint and in reducing the risk of recurrences.
In extremely rare cases, transformation to a spindle-cell malignancy with metastases to the contralateral thigh has been documented.
Though it is a benign condition, pigmented villonodular synovitis may result in significant morbidity if left untreated.
The primary treatment options include surgical resection via synovectomy or radiation therapy.
Following are the treatment options and strategies.
Nonoperative Treatment
Observation
It can be instituted in asymptomatic cases.
CSF-1 receptor antagonist (pexidartinib)
This is a recently approved drug that can be used in patients with extensive disease and who are not likely to benefit from the operative procedures.
This drug taken once daily for 24 weeks has shown significant improvement in disease burden in approximately 40% of patients. Liver toxicity is a major side effect.
Operative Treatment
Partial synovectomy
For accessible lesions, arthroscopic partial removal of synovium can be considered for a local form of PVNS. Otherwise open surgery should be done.
Total synovectomy
This is a kind of marginal excision that is done in overtly symptomatic and painful disease. It can be done arthroscopically or as open surgery.
Synovectomy improves symptoms and function. Recurrence is common and often due to incomplete removal of the synovium.
Radiotherapy
It is indicated in advanced disease. When combined with radiotherapy, it reduces rate of recurrence to less than 20%.
Total synovectomy and total joint arthroplasty
It is done in advanced disease with severe degenerative joint changes in knee, hip, and shoulder
Total synovectomy and arthrodesis
It is done in severe disease of the ankle
A long course of the disease and numerous recurrences may necessitate amputation.
Complications of PNVS
- Recurrence
- Most frequent complication
- Up to 50% rate despite complete synovectomy
- Rates are similar for both arthroscopic and open surgeries rates
- Can be reduced with addition of external beam radiation
- Joint destruction
- Can lead to moderate to severe joint deformity
- May lead to the need for arthrodesis or amputation
- Skin necrosis, radiation-induced sarcoma
- Due to radiation exposure
References
- Gouin F, Noailles T. Localized and diffuse forms of tenosynovial giant cell tumor (formerly giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath and pigmented villonodular synovitis). Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2017 Feb. 103 (1S):S91-S97.
- Kim DE, Kim JM, Lee BS, Kim NK, Lee SH, Bin SI. Distinct extra-articular invasion patterns of diffuse pigmented villonodular synovitis/tenosynovial giant cell tumor in the knee joints. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018 Nov. 26 (11):3508-3514.
- Cupp JS, Miller MA, Montgomery KD, et al. Translocation and expression of CSF1 in pigmented villonodular synovitis, tenosynovial giant cell tumor, rheumatoid arthritis and other reactive synovitides. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007 Jun. 31(6):970-6
- Jelinek JS, Kransdorf MJ, Utz JA, et al. Imaging of pigmented villonodular synovitis with emphasis on MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989 Feb. 152(2):337-42.