Last Updated on October 27, 2023
The popliteal artery is the direct continuation of the superficial femoral artery in the popliteal fossa as the vessel courses posteriorly behind the knee.
It gives the main branch as the anterior tibial artery and continues as the tibioperoneal or tibiofibular trunk or posterior tibial artery. It supplies knee, lower leg and foot.
Course of Popliteal Artery
 Femoral artery, a continuation of the external iliac artery is the main artery of the lower limb. In thigh, it travels through adductor canal and comes out of the adductor canal through adductor hiatus, an opening in the adductor magnus, at the junction of the middle and lower thirds of the thigh. It is anterior to bone in the femoral canal and as it travels below becomes anteromedial first and then medial at adductor hiatus and then travels posterior to the bone.
Femoral artery, a continuation of the external iliac artery is the main artery of the lower limb. In thigh, it travels through adductor canal and comes out of the adductor canal through adductor hiatus, an opening in the adductor magnus, at the junction of the middle and lower thirds of the thigh. It is anterior to bone in the femoral canal and as it travels below becomes anteromedial first and then medial at adductor hiatus and then travels posterior to the bone.

After it comes out of adductor hiatus, it is called popliteal artery. It travels downward and lateralward to the intercondylar fossa of the femur. The popliteal artery is the deepest or anteriormost structure in the popliteal fossa and the artery runs in close proximity to the joint capsule of the knee as it spans the intercondylar fossa.
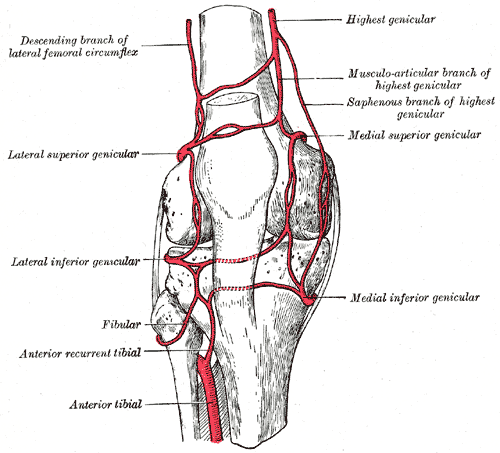
In its course, it gives off branches some of which participate in the formation of the periarticular genicular anastomosis, a network of vessels surrounding the knee that provides collateral circulation.
In the lower part of the popliteal fossa, it is sandwiched between the gastrocnemius and popliteus muscles. It travels vertically downward to the lower border of the popliteus muscle, where it divides into anterior and posterior tibial arteries.
The anterior tibial artery, passes anteriorly between the tibia and fibula, through a gap in the interosseous membrane. It then moves inferiorly down the leg.
The posterior tibial artery [ proximal to the fibular artery origin, it is sometimes called the tibial-peroneal trunk or tibial-fibular trunk] and continues further posteriorly and supplies the posterior compartment of the leg.
The artery sometimes divides into the anterior tibial and peroneal, the posterior tibial being wanting, or very small. Occasionally it divides into three branches, the anterior and posterior tibial, and peroneal.
Anatomic Relations of Popliteal Artery

Anteriorly
In front of the artery from above downward are
- The popliteal or posterior surface of the femur [a layer of fat lies between the two]
- Posterior aspect of the knee joint
- Fascia covering the popliteus muscle
Posteriorly
- Semimembranosus above, and Gastrocnemius and Plantaris below
- In the middle, it is crossed from the lateral to the medial side by the tibial nerve and the popliteal vein, the vein being between the nerve and the artery
Laterally
- Above – Biceps femoris, the tibial nerve, the popliteal vein, and the lateral condyle of the femur
- Below- Plantaris and the lateral head of the gastrocnemius.
Medially
- Above semimembranosus and the medial condyle of the femur
- Below, the tibial nerve, the popliteal vein, and the medial head of the gastrocnemius.
Branches of Popliteal Artery
The branches of the popliteal artery are
Apart from main divisions of the anterior tibial artery and posterior tibial artery, the other popliteal artery branches are
Muscular Branches
The superior muscular branches, two or three in number, arise from the upper part of the artery and are distributed to the lower parts of the adductor magnus and hamstring muscles, anastomosing with the terminal part of the profunda femoris, a branch of the femoral artery.
Sural Arteries
Also called inferior muscular arteries, these are two large branches, which arise opposite the knee joint and supply to the gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris.
Cutaneous Branches
The cutaneous branches arise either from the popliteal artery or from some of its branches; they descend between the two heads of the gastrocnemius, and, piercing the deep fascia, are distributed to the skin of the back of the leg. One branch usually accompanies the small saphenous vein.
Genicular Arteries
Superior genicular arteries, two in number, arise one on either side of the popliteal, and wind around the femur immediately above its condyles to the front of the knee joint.
One of the branches of medial superior genicular artery supplies vastus medialis also.
Middle genicular artery is a small branch, arising opposite the back of the knee joint. It pierces the oblique popliteal ligament and supplies the ligaments and synovial membrane in the interior of the articulation.
The inferior genicular arteries (two in number, arise from the popliteal beneath the Gastrocnemius.
Genicular arteries, apart from supplying structures around the knee, create anastomosis around the knee called circumpatellar anastomosis.
Variations of Popliteal Artery
- The popliteal artery may divide into its terminal branches above the level of the popliteus. The anterior tibial artery then descends deep (anterior) to the popliteus.
- It may divide into the anterior tibial and the peroneal arteries, and the posterior tibial may be completely absent or rudimentary.
- It may divide into three branches, the anterior and posterior tibial arteries, and the peroneal artery.
Clinical significance of Popliteal Artery
- Popliteal pulse examination helps to localize the lesion
- Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome