Last Updated on April 5, 2020
Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic inflammatory, seronegative arthritis that develops in about 5% of the people who have psoriasis. Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder that mainly affects skin leading to a characteristic rash.
About half of the patients of psoriatic arthritis have often human leukocyte antigen HLA B27 associated spondyloarthropathy. Psoriatic arthritis is considered as the seronegative spondyloarthropathy.
Most common type is oligoarthritis [involves few joints].
Distal joint involvement and arthritis mutilans [destruction of digits] are characteristic features of psoriatic arthritis but less common.
The peripheral joint disease occurs in 95% of patients with psoriatic arthritis, and the spine is involved in 5%.
Psoriatic arthritis is more frequent in patients with severe psoriasis. However, the severity does not relate to the pattern of joint involvement.
Psoriatic arthritis has been found to be associated with greater risk of hypertension, obesity, hyperlipidemia, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular events compared with psoriasis without arthritis.
Both the genders are equally affected [spine more affected in males]
Any age group can be affected but most cases are seen in group 35-55 years.
Types of Psoriatic Arthritis
The patterns of psoriatic arthritis involvement are as follows:
- Asymmetrical oligoarticular arthritis
- Symmetrical polyarthritis
- Distal interphalangeal arthropathy
- Arthritis mutilans
- Spondylitis with or without sacroiliitis
Asymmetrical Oligoarticular Arthritis
Asymmetrical oligoarticular arthritis affects less than 5 joints. It affects fingers and toes first.
Inflammation of the flexor tendon and synovium occur at the same time. A large joint, such as the knee, is also commonly involved.
Symmetrical Polyarthritis
It is the most common type and the involvement is similar to rheumatoid arthritis. The hands, wrists, ankles, and feet are generally involved.
The condition can be differentiated from rheumatoid arthritis by being milder in nature and the involvement of distal interphalangeal joints.
The subcutaneous nodules are absent. The test for rheumatoid factor is negative.
Distal Interphalangeal Arthropathy
This involves the distal interphalangeal joint. This type occurs in only 5-10% of patients. Men are more commonly affected and are more common in men than in women.
Nail involvement in form of paronychia and swelling of the digital tuft may be prominent.
Arthritis Mutilans
It is quite rare [1-5% of patients]. The condition involves bone resorption and destruction of joint of digits. The peculiar destruction leads to a pencil in cup appearance in radiographs. It is also called pencil in cup deformity or pencil cup deformity.
Over the joint skin becomes redundant and a telescoping motion of the digit can be possible.
Spondylitis with or without Sacroiliitis
This is mostly found in males and affects about 5% of cases. It can occur along with other types of psoriatic arthritis.
There is an asymmetrical involvement of the vertebrae in contrast to ankylosing spondylitis where the involvement is symmetrical.
The characteristic finding in the spine is nonmarginal asymmetrical syndesmophytes [osteophytes from adjoining vertebrae joined together]. paravertebral ossification, and, vertebral fusion with disc calcification.
Risk factors of Psoriatic Arthritis
The exact cause is not known. Following factors are said to contribute
- Genetics
- Positive family history
- HLA-B7, HLA-B27, HLA-DR4, HLA-38, and HLA-DR7 increase susceptibility
- Mechanism unclear
- Immunologic factors
- Higher serum IgG A and IgG levels
- Decreased IgM levels may be normal or decreased.
- Autoantibodies against nuclear antigens, cytokeratins, epidermal keratins, and heat-shock proteins
- Decreased CD4 cells
- Bacterial and viral infections
- Trauma
- Unclear environmental factors
Clinical Presentation
Patient commonly complain of the following symptoms
- Painful and swollen fingers [dactylitis]
- pain back
- Pain in ankle [Achilles tendon insertion]*
*The term enthesopathy is used when there is pain at the insertion site of the tendons. Enthesopathy may occur in many other conditions too.
The symptoms may develop acutely or have an insidious development.
Often the patient has pre-existing psoriasis but arthritis can precede psoriasis in the minority of patients.
Other important symptoms include
- Eye involvement [about thirty percent]
- Conjunctivitis
- Anterior uveitis
- Iritis
- Sacroiliitis
- Aortic valve inflammation
- Tenosynovitis of the flexor tendon sheath
- Nails changes
- Beau lines- transverse groove within the nail plate
- Leukonychia [white nails]
- Onycholysis [nail destruction]
- Subungual hyperkeratosis
- Splinter hemorrhages,
- Cracking of nail edges
- Secondary amyloidosis [late stage]
The patients may have skin rash and scaly patches, typical of psoriasis.
Differential Diagnoses
Diagnosis
Lab Studies
There is no particular diagnostic test for psoriasis. Routine lab investigations are within normal limits.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein level are elevated in these patients.
90% of the cases are negative for the rheumatoid factor.
Serum IgA levels [a type of circulating antibody] are increased in 60% cases.
Synovial fluid aspiration shows increased cell count suggesting inflammation.
Imaging
X-rays
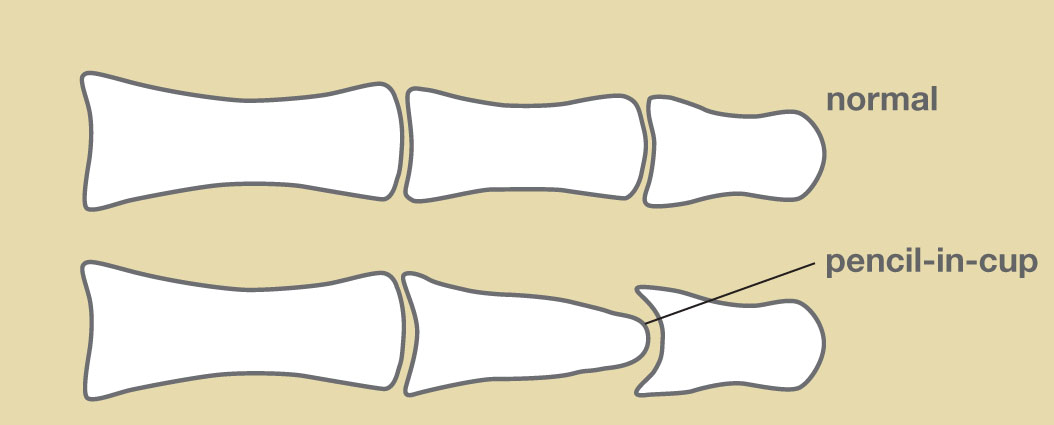
X-rays typically show the following changes interphalangeal, metatarsophalangeal, and metacarpophalangeal joints.
- Joint space narrowing
- Joint erosions
- Complete joint destruction
- Pencil-in-cup deformity
- Fusiform soft-tissue swelling
- Sacroiliitis
CT/MRI
These modalities may help in the early detection of synovitis, sacroiliitis, enthesitis, and erosions.
MRI can reveal inflammation in the small joints of the hands, the involvement of the collateral ligaments and soft tissues around the joint capsule [in contrast to rheumatoid arthritis].
CASPAR Diagnostics Criteria
The CASPAR criteria consist of established inflammatory articular disease with at least 3 from features given below
- Current psoriasis (2)
- A history of psoriasis if there is no current psoriasis (1)
- A family history of psoriasis if there is no current psoriasis/ history of psoriasis (1)
- Dactylitis (1)
- Juxtaarticular new-bone formation (1)
- Negative rheumatoid factor (1)
- Nail dystrophy (1)
Treatment of Psoriatic Arthritis
The treatment aims at
- Controlling the inflammation
- Pain relief
- Control and treatment of deformities.
The treatment is mainly medical. The patient should rest the joint in the acute stage.
Splints can be used for pain relief, especially for the hands, wrists, knees, or ankles.
Cold fomentation also decreases inflammation and provides pain relief.
The following drugs are used in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Oral
- Topical
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
- Methotrexate
- Sulfasalazine
- Cyclosporine
- Leflunomide
- Anti–TNF medications
- Infliximab
- Adalimumab
- Certolizumab
- Golimumab)
- Intralesional corticosteroid injections in the joints or enthesopathy sites
For skin lesions, retinoic-acid derivatives and psoralen plus ultraviolet light are used in cases of severe skin disease.
New studies have also reported the effectiveness of ustekinumab, interleukin-12, and interleukin-23 antagonist, in symptom reduction of psoriatic arthritis.
Synovectomy is done in severe synovitis involving a single joint. An arthroscopic synovectomy is followed by physical therapy.
Arthrodesis is used to fuse the small joints. In the case of the large joint deformity, arthroplasty may be done.
Assistive devices may be needed in certain patients. The type of device used would depend on the region involved and the functional limitation. These may include
- Orthotics
- Gait assistance devices
- Walker
- Sticks
The patient may require to modify home for easier use. A change in vocation may be needed.
Physical therapy has an important role in treatment. After the acute stage has subsided, the following are begun
- Isometric exercises
- Active movements
- Heat therapy for pain control
- Heat packs
- Paraffin wax
- Diathermy
- Ultrasound
- Gait activities
- Stretching exercises
Physical therapy should also be instituted after surgery.
The following can worsen psoriasis and need to be checked
- Lithium
- Withdrawal from systemic corticosteroids
- Beta blockers (used for high blood pressure treatment)
- Selected nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Stop and use another agent)
Juvenile Psoriatic Arthritis
When the condition occurs in children, it is called juvenile psoriatic arthritis. It affects females more than males.
Often a single joint is involved. Associated findings are nail changes and tenosynovitis.
Sacroiliitis is present in about a third of cases.
In children, in about half of the cases, symptoms of arthritis precede psoriasis.
References
- Alinaghi F, Calov M, Kristensen LE, Gladman DD, Coates LC, Jullien D, et al. Prevalence of psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational and clinical studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Jun 18.
- Taylor W, Gladman D, Helliwell P, Marchesoni A, Mease P, Mielants H. Classification criteria for psoriatic arthritis: development of new criteria from a large international study. Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Aug. 54(8):2665-73.
- Gladman DD. Psoriatic arthritis. Dermatol Ther. 2009 Jan-Feb. 22(1):40-55.
- Chamot AM, Benhamou CL, Kahn MF, Beraneck L, Kaplan G, Prost A. [Acne-pustulosis-hyperostosis-osteitis syndrome. Results of a national survey. 85 cases]. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic. 1987 Mar. 54(3):187-96.
- Coates LC, FitzGerald O, Helliwell PS, Paul C. Psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis: Is all inflammation the same?. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016 Dec. 46 (3):291-304.
- Kruithof E, Baeten D, De Rycke L, Vandooren B, Foell D, Roth J, et al. Synovial histopathology of psoriatic arthritis, both oligo- and polyarticular, resembles spondyloarthropathy more than it does rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005. 7 (3):R569-80.
- Ritchlin CT, Colbert RA, Gladman DD. Psoriatic Arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2017 Mar 9. 376 (10):957-970.