Last Updated on November 20, 2019
Retrocalcaneal bursitis or insertional bursitis is a common cause of pain in the posterior heel or ankle due to inflammation of either retrocalcaneal bursa or subcutaneous calcaneal bursa.
Retrocalcaneal or subtendinous bursa is located between the Achilles tendon and the calcaneus. This bursa is anterior to Achilles tendon.
Subcutaneous calcaneal bursa is, superficial to the Achilles tendon. It is also called the Achilles bursa. This bursa is located between the skin and posterior aspect of the distal Achilles tendon.
Inflammation of either or both of these bursae can cause pain at the posterior heel and ankle region.
Causes of Retrocalcaneal Bursitis
Calcaneal bursae can get inflamed due to repetitive injury or overuse. It often occurs when athletes increase their running distance substantially.
Following factors are known to be associated with retrocalcaneal bursitis
- Overtraining
- Poorly fitting footwear [See Pump bump]
- Haglund deformity
- Subtalar joint misalignment
- Systemic diseases
Presentation of Retrocalcaneal Bursitis
The patient presents with symptoms of posterior heel pain, usually on one side but may affect both sides. Limp may be present.
Some patients present with a noticeable swelling [also called “pump bump because of association with the wearing of high-heeled shoes or pumps].
A recent change of footwear, any underlying condition like gout, rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthropathies should be enquired. The level of activity of the patient must be noted.
On examination, the posterior aspect of the heel may reveal swelling and redness. The region might be tender to palpation and warm to touch.
The clinical examination may distinguish if the inflammation is superficial [posterior] to Achilles tendon [ subcutaneous bursa] or deep [anterior ] to the Achilles tendon (subtendinous bursa).
Differential Diagnoses
Lab Studies
Lab tests Not required for diagnosis but may be done to find the systemic conditions that can cause retrocalcaneal bursitis if it cannot be explained by local factors [like poorly fitting shoes, increased running, high heels.]
The laboratory studies to be considered are to evaluate the possibility of gout (hyperuricemia), rheumatoid arthritis (blood count, ESR, C-reactive protein, rheumatoid factor, and HLA B-27.
Imaging
Plain radiographs of the calcaneus may reveal a Haglund deformity. [Bony enlargement on the back of calcaneum]
An absence of the normal radiolucency posteroinferior corner behind the calcaneum may suggest the condition.
X-rays can be used to rule out stress fractures of calcaneum because of a stress fracture. If there is a constant clinical suspicion in presence of normal x-rays, bone scanning or CT scanning may be considered.
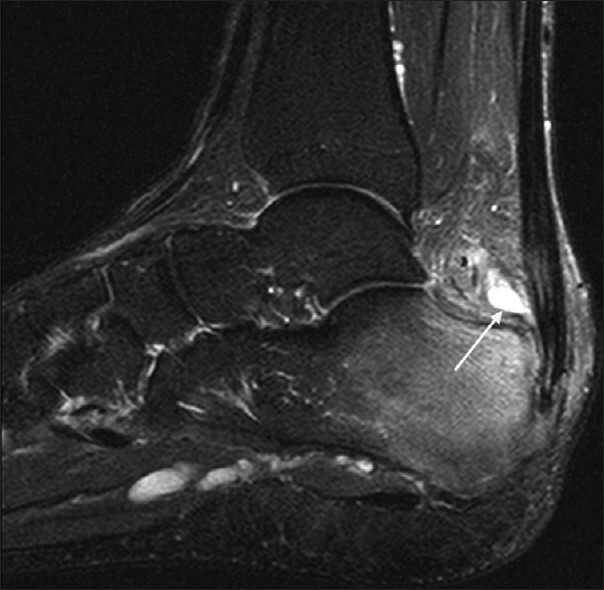
MRI can show inflammation of bursa and can differentiate if the involved bursa is subcutaneous bursa or the subtendinous bursa. It is also able to tell the condition of the tendon. But MRI is generally not necessary in retrocalcaneal bursitis.
Treatment of Retrocalcaneal Bursitis
RICE
Treatment in the acute phase consists of rest, ice, compression and elevation [RICE Therapy]. Ice can be applied for about 20 minutes by use of ice packs several times a day. The affected part is rested in an elevated position and a compression bandage may be applied.
Medication
The patient can be given NSAIDs for pain relief and reduction of inflammation. Topical NSAIDs are able to deliver a large dose of anti-inflammatory medication to a focal painful area with minimal systemic distribution.
Physical Therapy
Stretch exercises for Achilles tendon are initiated once symptoms resolve.
[Read more on Stretch exercises for Achilles tendon]
The patient should decrease the activity level but can do swimming, water aerobics, and other aquatic exercises.
Footwear
A proper footwear can work wonders in patients of retrocalcaneal bursitis and the change made on an individual basis. The patient might be benefited from the use of open backed shoe because it relieves pressure from the heel region.
If a patient has developed symptoms due to shifting to flat shoes from high heeled shoes, the patient may be provided with a heel height to relax Achilles tendon.
Corticosteroid Injection
Corticosteroid injection into the retrocalcaneal bursa can be considered but an inadvertent injection into Achilles tendon may increase the risk of Achilles tendon rupture. Therefore utmost care should be taken and injection preferably applied under imaging.
Immobilization
Immobilization in a brace or cast for 4-6 weeks can be considered in resistant cases.
During recovery, the patient should move to a range of motion and strengthening exercises with a gradual increase of activities till he could return to his previous level of athletic activity.
Surgical Treatment of Retrocalcaneal Bursitis
Surgery is considered in patients who do not show improvement with conservative treatment.
Surgical options include resection of a Haglund deformity, excision of the bursa and debridement of the Achilles tendon insertion
Endoscopic surgery may have better outcomes than open surgical techniques in the treatment of retrocalcaneal bursitis.
The patient should return to sports after resolution of symptoms and signs and if the symptoms do not recur in practice drills.
Prognosis of Retrocalcaneal Bursitis
Most patients of retrocalcaneal bursitis respond well to conservative treatment and those who do not respond to conservative treatment almost always respond to surgery.
Without treatment, the pain may become chronic. Achilles tendon rupture may occur in some cases.
Prevention
Patients with retrocalcaneal bursitis should consider the following preventive measures:
- Wear proper footwear
- Change running shoe frequently to avoid the use of worn out shoes
- Avoid high-heeled shoes.
- Stretch properly before exercise
- The proper performance of Achilles tendon stretching