Last Updated on October 27, 2023
Xrays and photographs of different kinds of shoulder injuries are presented.
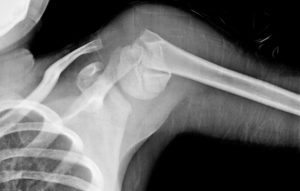
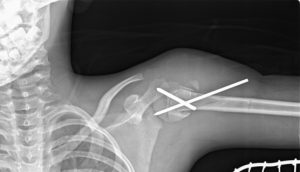
Image 1 – Fracture Upper-End Humerus In Child Treated With Closed Reduction and Internal Fixation With K Wires
Fracture upper-end humerus are common fractures in children as well in adults and elderly. However, fractures behave differently in different age groups.
While elderly patients can be treated on conservatively The fractures in an adult, on the other hand, would require operative treatment owing to the increased demands and active lifestyle.
Most of these fractures in children also unite on conservative treatment. Only those fractures which are severely displaced would need an operative intervention.
The following x-rays are of 10 years old child who suffered a fracture of upper end of the humerus after he fell from a height while he was flying a kite.
The fracture is severely displaced as can be seen in the picture.
The patient was treated with closed reduction and crossed K wire fixation.
The patient has been followed for 4 weeks and the fracture has united. The K-wires have been removed and the patient has been put on physiotherapy for shoulder mobilization.
Author Note
The K-wires are bit protruding inside the joint.
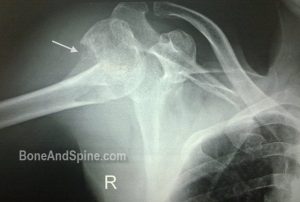
Image 2 – Post Reduction Xray Of Shoulder Dislocation With Fracture of Greater Tuberosity
The x-ray belongs to 70 years old female who fell in the bathroom and suffered from an injury in the right shoulder.
The x-ray revealed a fracture of greater tuberosity along with dislocation of the shoulder.
The patient was treated with closed reduction under general anesthesia.
The above x-ray is taken after the closed reduction. The patient was advised fixation for greater tuberosity fracture but refused.
Image 3 – Undisplaced Fracture Clavicle- AP Xray
An x-ray of undisplaced fracture of the clavicle.
Most of the clavicular fractures are managed by conservative methods.
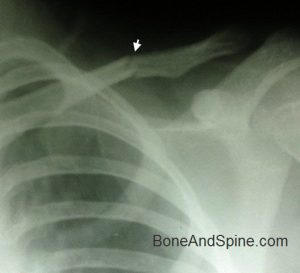
Image 4 – Xray Showing Fracture Of Scapula Including Spine Of Scapula
Xray of Shoulder showing fracture of body and spine of scapula
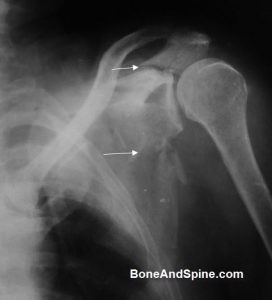
The Arrows have been put to show the scapular fracture.
Image 5 – Clinical Photograph of Acromioclavicular Dislocation
Clinical photograph of acromioclavicular Dislocation in 28 years old male following a fall from the bike.
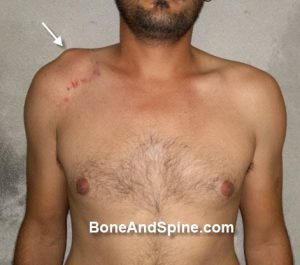
Note the bruises on anterior aspect too.
Image 6 – Xray of Nonunion of Clavicle
53 years old lady came to OPD with a history of injury to shoulder two years back. She complained of pain in the shoulder region.
Previous documents revealed a fracture of clavicle which eventually did not unite.
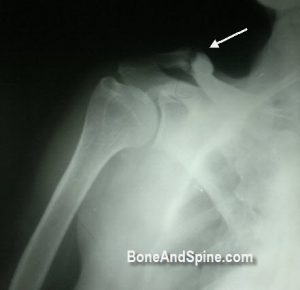
A fresh x-ray was done and revealed an ununited fracture of the clavicle with sclerotic fracture ends.
Image 7 – Peroperative Fluoroscopic Image of Operated Fracture Upper Humerus In Six-Year-Old Child
This is a peroperative image taken by C-arm Image Intensifier in a case of fracture of upper-end humerus in six-year-old child.
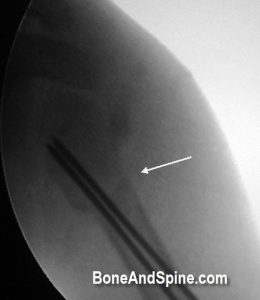
The fracture is well aligned.
Image 8 – Fracture of Upper-End Humerus In Six Years Old Child
Six years old boy fell from a roof while flying the kite and injured his shoulder. An x-ray of the region revealed a fracture of upper end of the humerus.
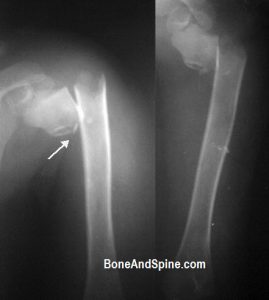
Closed reduction and internal fixation using K-wires was done. The patient is showing good improvement in the follow-up visits.
Image 9 – Xray Of Bullet Injury In Shoulder Region
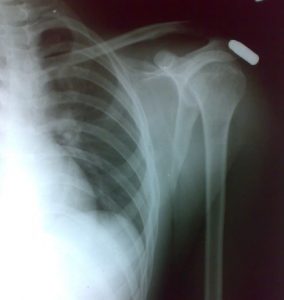 The x-ray in the picture belongs to a 23-year-old man who was shot in the market, probably because of ongoing rivalry.
The x-ray in the picture belongs to a 23-year-old man who was shot in the market, probably because of ongoing rivalry.
The x-ray shows a bullet in the shoulder region but there is no evidence of any bony injury.
There was no neural or vascular injury.
The bullet was superficial and removed by a surgical procedure.
The patient does not have any residual deficit and has full function of the affected limb.
Bullet injuries cause thermal injuries and the actual damage may not be reflected by the size of the entry wound. This man was quite fortunate to escape any devastating effect.
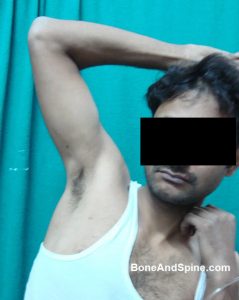
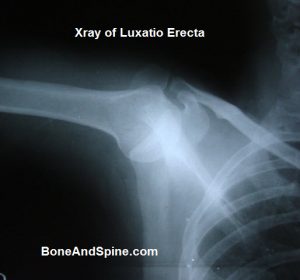
Image 11 – Luxatio Erecta – Clinical Photograph and Xrays
Luxatio Erecta is a term for inferior dislocation of the shoulder and occurs in less than 1% of all shoulder dislocation cases.
Here is clinical photograph and x-rays of luxatio erecta in a 35 years old male
This is the x-ray after injury.
The dislocation was reduced under general anesthesia and the following x-ray is a taken after the reduction of the dislocation.
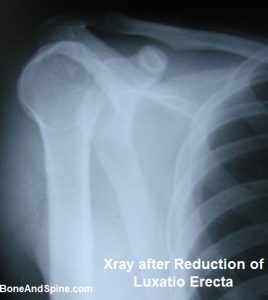
This shoulder dislocation is called luxatio erecta because the arm appears to be permanently held upward or behind the head. It is caused by a hyperabduction of the arm that forces the humeral head against the acromion.