Last Updated on October 29, 2023
Spaces of hand are formed by fascia and fascial septae. Fascia and fascial septae of the hand are arranged in such a manner that many spaces are formed. These spaces are important as they can get infected and distended with pus.
Important spaces of the hand are
Palmar Spaces
- Pulp space of fingers.
- Midpalmar space
- Thenar space
Dorsal Spaces
- Dorsal subcutaneous space.
- Dorsal subaponeurotic space
The Forearm Space of Porona
These spaces are described below one by one
Palmar Spaces of Hand
Pulp Spaces of The Fingers

Fat in the tips of fingers and thumb contain subcutaneous fat which is arranged in light compartments formed by fibrous septa. These septae pass from the skin to the periosteum of the terminal phalanx.
As space has limited capacity, any infection of the space gives rise to severe throbbing pain.
If the infection is left without decompression, terminal phalanx may be involved.
In children, the blood supply to the diaphysis of the phalanx passes through the pulp space, and pressure on the blood vessels could result in necrosis of the diaphysis.
But the proximally located epiphysis of this bone is saved as blood supply to it is just proximal to the pulp space.
Pulp space is in close relation with digital synovial sheath and sheath could be involved in case of neglected pulp space infection.
Infection in the pulp space can be drained by a lateral incision which opens all compartments and avoids damage to the tactile tissue in front of the finger.
Midpalmar Space
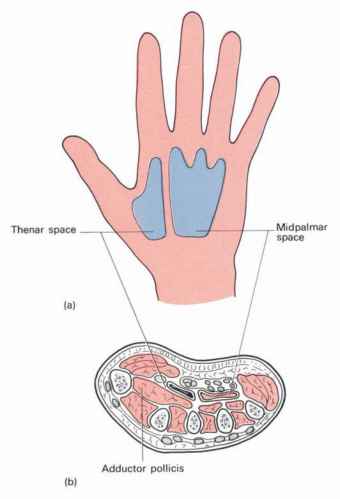
Image credit: ClicktoCureCancer
This is a triangular space situated under the inner half of the follow of the palm. Proximally, it extends up to the distal margin of the flexor retinaculum and communicates with the forearm space. Distally, it extends up to the distal palmar crease and communicates with the fascial sheaths of the 3rd and 4th lumbrical muscles.
Boundaries of Midpalmar Space
- Anteriorly – palmar aponeurosis:
- Posteriorly – 3rd, 4th and 5th metacarpals the fascia covering the interossei of the 3rd and 4th the spaces, and the medial part of the transverse head of the adductor pollicis
- Medially – medial palmar septum
- Laterally, by the intermediate palmar septum
Contents of Midpalmar Space
- The flexor tendons of third, fourth and fifth fingers
- Second, third and fourth lumbrical muscles;
- Superficial palmar arch
- Digital nerves and vessels of the medial three and half fingers.
Infection of the mid palmar space may result from tenosynovitis of the middle and ring fingers, or from a web infection which has spread proximally through the lumbrical canals.
The palmar space can distend quite a lot and swelling might extend to the dorsum of the hand.
The space can be drained by an incision in either the 3rd or 4th web depending on where the pus points.
Thenar Space
This is a triangular space situated in the thenar region.
It extends proximally to the distal margin of the flexor retinaculum and distally to the proximal transverse palmar crease. It communicates with the forearm space, subcutaneous web of the thumb through the fascial sheath of the first lumbrical muscle. It may also communicate with the second lumbrical canal.
Boundaries of Thenar Space
- Anteriorly – Palmar aponeurosis;
- Posteriorly – Fascia covering the transverse head of the adductor pollicis and the first dorsal interosseous muscle
- Medially – Intermediate palmar septum
- Laterally – Lateral palmar septum
Contents of Thenar Space
- The tendon of the flexor pollicis longus with its synovial sheath;
- The flexor tendons of the index finger
- The first lumbrical muscle
- The palmar digital vessels and nerves of the thumb and lateral side of the index finger.
The thenar space may be infected by a spread of any infection in the thumb or index finger. This results in marked swelling of the web of the thumb and thenar region. The thumb is held in an abducted position.
The space can be drained by an incision in the first web posteriorly, or where the pus points.
Dorsal spaces of hand
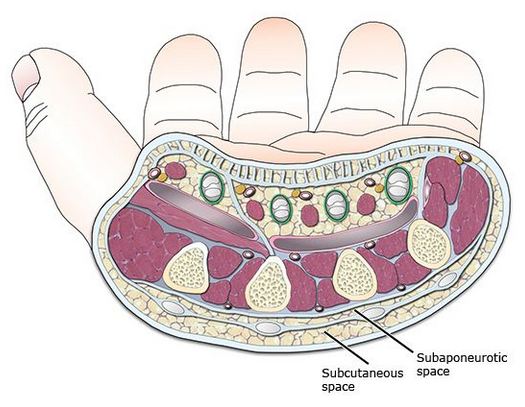
Image credit: Cursoenarm
Dorsal subcutaneous space and dorsal subaponeurotic space are the spaces on the dorsum of hand.
The dorsal subcutaneous pace lies immediately deep to the loose skin of the dorsum of the hand. The dorsal subaponeurotic space lies between the metacarpal bones and the extensor tendons.
In subaponeurotic space, infections the pus point either at the webs or at the borders of the hand, and can be drained accordingly.
Forearm Space of Parona

It is a rectangular space situated deep in the lower part of the forearm just above the wrist. It lies in front of the pronator quadratus and deep to the long flexor tendons.
Superiorly, the space extends up to the oblique origin of the flexor digitorum superficial
Inferiorly, it extends up to the flexor retinaculum and communicates with the midpalmar space, and possibly also with the thenar space parts of the flexor synovial sheaths protrude into the forearm space.
The forearm space may be infected through infections in the related synovial sheaths, especially of the ulnar bursa.