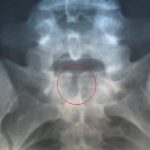
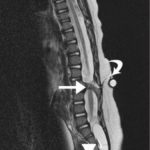
Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis is a type of spinal infection which may result from direct trauma, the spread of infection from adjacent structures or hematogenous spread from the distant focus of infection. It can have devastating complications if untreated which could be a pathological fracture, epidural infection, and compression of the neural structures. Vertebral osteomyelitis is […]
Spine
IDSA 2015 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Native Vertebral Osteomyelitis in Adults
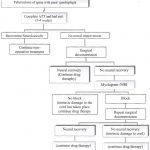
The guidelines are published by the Infectious Disease Society of America. These guidelines include evidence and opinion-based recommendations for the diagnosis and management of patients with native vertebral osteomyelitis treated with antimicrobial therapy, with or without surgical intervention. Native vertebral osteomyelitis in adults is often the result of hematogenous seeding of the adjacent disc space […]
Pott’s Paraplegia or Spinal Tuberculosis with Neural Involvement
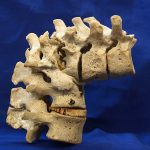
Spinal tuberculosis with neural deficit can occur in the lesions when disease comrpresses the cord. Potts paraplegia is term for this deficit in TB spine Spinal tuberculosis is the most common form of skeletal tuberculosis accounting for 50 percent of osteoarticular tuberculosis. Neural compression in spinal tuberculosis may lead to tetraparesis-tetraplegia or paraparesis-paraplegia. Pathology of […]
Kyphosis in Spinal Tuberculosis
Kyphosis in spinal tuberculosis is one of the most common complication of spinal tuberculosis. Neurological complications (paraplegia or quadriplegia) and spinal deformity especially kyphotic deformity are the most dreaded complications of tuberculosis of the spine. The sequelae of these two complications affect the quality and span of life. Almost all tuberculosis of the spine, even […]
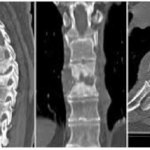
Imaging in Spinal Disorders – Xray, CT, MRI and More
Different modalities of imaging in spinal disorders play an important role in In modern spine practice. Imaging has a pivotal role in the diagnosis and treatment of the lesion. In this article, we discuss various modalities of imaging of spine disorders. X-rays Conventional plain film radiography initiates the investigation of any suspected spinal pathology. X-ray […]
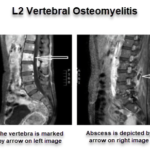
Pyogenic Infection of Spine
Pyogenic infection of the spine is rare, constituting only about 2-8% of overall pyogenic infection. The spectrum of pyogenic infections includes spondylitis, discitis, spondylodiscitis, pyogenic facet arthropathy, epidural infections, meningitis, and myelitis. The incidence of spinal infections has increased recently due to globalization, improved life expectancy, comorbidities like diabetes, overuse of antibiotics, immunosuppression and other immunocompromised […]
Segmental Instability of Lumbar Spine
Segmental instability of lumbar spine is one of the important causes of back pain. When the forces within physiological limits are applied to the spine, the movements occur within the specific physiological range, with small person-to-person variations. During spinal movements, the adjacent vertebrae maintain their relationship with each other due to the configuration, orientation and […]
Spinal Dysraphism Types, Presentation and Treatment
Spinal dysraphism is a group of anomalies where there are malformations in the dorsum of the embryo. There is often an abnormal fusion of the midline embryonic neural, vertebral and mesenchymal structures. The estimated incidence of spinal dysraphism is about 1–3 per 1000 live births. The incidence of the spinal dysraphism is declining in the […]
Split Cord Malformation or Diastematomyelia
Split cord malformation is an uncommon congenital anomaly in which a segment of the spinal cord is divided into two parts by a fibrous or rigid bony spur. It was previously known as diastematomyelia (diastema = a cleft, myelos = cord). Split cord malformation can involve any part of the spinal column and sometimes involve […]
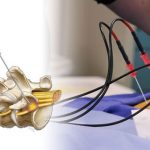
Radiofrequency Neurotomy – Indications and Procedure
A radiofrequency neurotomy is the use of radiofrequency energy mediated heat to ablate the nerve responsible for facet joint pain or sacroiliac joint pain caused by arthritis or other degenerative changes, or from an injury. Ablation if the nerve beaks the pain signals to the brain, thus eliminating pain. The term radiofrequency ablation is also […]