Last Updated on September 26, 2020
The term thumb hypoplasia refers to underdeveloped thumb. The degree of thumb underdevelopment may vary. Thus, thumb hypoplasia refers to a spectrum of thumb underdevelopment which ranges from working small thumb to rudimentary or absent.
Before we move further let us differentiate between different often used terms.
Malformation means there is an abnormal formation of the tissue due to abnormal cell formation.
Deformation in contrast is a change in normal tissue due to insult or injury to the cells.
Dysplasia, however, denotes that cells are normal but the organization of these cells is abnormal.
Hypoplasia refers to a tissue or organ which contains a lesser number of cells. Another term for this is under development. The tissue is smaller in size and may be non-functional
Hyperplasia is the opposite of hypoplasia. It means there is an increased number of cells in the tissue leading to enlarged size.
Thumb hypoplasia has an incidence of 1 in 100,000 live births. Both genders are equally affected.
Relevant Anatomy
Causes of Thumb Hypoplasia and Associated Conditions
The exact cause and mechanism of the thumb hypoplasia is not clearly understood. It is a type V congenital malformation of the hand and is due to underdevelopment.
About 60% of cases occur in isolation whereas others are associated with defects of the radius bone.
The RIght side is more affected in unilateral affections.
The condition is bilateral in about two-thirds.
Therefore it becomes important to rule out associated abnormalities
Thumb hypoplasia may be associated with many other congenital conditions like
- Thumb duplication
- Transverse deficiencies
- Symbrachydactyly
- Brachydactyly
- Cleft hand complex
- Ulnar longitudinal deficiency
- Congenital constriction ring syndrome
- Syndromes like
- Apert syndrome
- Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome
- Holt-Oram syndrome
- Thrombocytopenia-absent radius syndrome
- VACTERL [ vertebral, anal, cardiac tracheoesophageal, renal, limb]
- Fanconi anemia
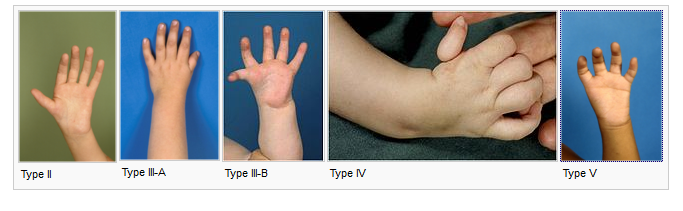
Classification of Thumb Hypoplasia [Blauth]
- Type I
- Mildest
- Minor hypoplasia
- Small in size but the complete thumb
- Type II
- All bony structures present
- Ulnar collateral ligament instability at metacarpophalangeal joint
- Underdeveloped thumb muscles [Thenar hypoplasia]
- Type III
- IIIA
- Musculoskeletal structures are deficient [muscle, bone]
- Absence of active motion at the metacarpophalangeal joint or interphalangeal joint though joints are intact
- IIIB
- IIIA + absence of base of 1st metacarpal
- Deficient carpometacarpal joint.
- Type IV
- The remnant of thumb
- Attached to hand by the skin and digital neurovascular structures
- Also called a floating thumb
- Type V
- Complete absence of the thumb
Clinical Presentation
The thumb hypoplasia varies from a small normal thumb to a rudimentary or absent thumb. The function may be normal and such thumbs will not require any treatment.
For other thumbs, we need to evaluate the structure and function of the thumb which includes
- Examination of metacarpal and phalanges
- Stability of joints especially the 1st metacarpophalangeal joint.
- Muscles of thumb [thenar muscles]
- Absence of skin creases indicating muscle or tendon abnormalities
The metacarpophalangeal joint may be in the abduction. There may be laxity of the ulnar collateral ligament of 1st metacarpophalangeal joint.
The first webspace [between index finger and thumb], may be tight.
A detailed examination should be done for cardiac and other abnormalities.
Grasp and prehension functions of the thumb are affected.
Lab Studies
As Fanconi anemia is one of the possible associations, it is pertinent to rule that out by peripheral blood smear examination and complete blood count should be done.
Imaging
X-rays of both hands should be done to note any bony and joint abnormalities. X-rays of both forearms should be done to rule out radius bone involvement.
Treatment of Thumb Hypoplasia
The aim of the treatment of thumb hypoplasia is to have a functional thumb. The approach is guided by the stage of the disease and the presence of carpometacarpal joint stability.
| Type I | No surgical treatment required |
| Type II, IIIA |
|
| Type IIIB- type V | Thumb amputation & pollicization |
In type I hypoplasia, augmentation of thumb abduction is not necessary and these patients generally do not need surgical treatment.
However, the type I cases with insufficient thumb abduction would need opponensplasty. It is a procedure where a tendon transfer is done to replace the function of absent or weak tendon.
The timing of surgery is usually between 6 and 12 months of age.
The condition of the first metacarpal joint is of prime importance in thumb reconstruction. A stable metacarpophalangeal joint is the critical determinant of the reconstructive plan.
If it is unstable, thumb amputation and pollicization is chosen.
Surgical Options and Techniques for Thumb Hypoplasia
Opponensplasty
It is also called opposition transfer and involves the transfer of muscle-tendon unit to carry out the function of opposition.
It is performed usually by using the following
- Flexor digitorum superficialis or
- Abductor digiti minimi
Deepening of First Web Space
It is performed to widen the movement allowed in the first web space and is done usually with Z-plasty
Stabilization of Metacarpophalangeal Joint
The stabilization of the metacarpophalangeal joint is achieved either by arthrodesis or reconstruction with augmentation of
- Flexor digitorum superficialis
- FREE TENDON GRAFT.
Pollicization
This procedure is done to substitute a functioning digit to the deficient thumb. Usually, the index finger is used to replace the deficient thumb and is given the shape of a thumb to suit its functions.
It also involves reattachment and balancing of musculotendinous units.
References
- Buck-Gramcko D. Congenital malformations of the hand and forearm. Editions Scientifiques et Medicales. 2002;21:70–101. [Link]
- Egloff DV, Verdan Cl. Pollicization of the index finger for the reconstruction of the congenitally hypoplastic or absent thumb. J Hand Surg. 1983;8:839–48. [Link]