Last Updated on February 13, 2023
Chondrocalcinosis means the streaking of articular cartilage with calcium. It is also used as a synonym for calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease because the finding of chondrocalcinosis has been mostly associated with calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease, a disease that is caused by the deposition of calcium pyrophosphate crystals.
In fact, chondrocalcinosis articularis was an early term for calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease. But these do not mean the same thing and should not be used as an equivalent terms.
Chondrocalcinosis is a radiological finding and non-specific, CPPD being one of the causes. Moreover, it has been noticed that depositions that present as chondrocalcinosis in the articular cartilage are also found in other tissues as well.
[Pesudogout is another name used for pyrophosphate deposition disease but actually, pseudogout is just one form of pyrophosphate deposition disease presentation.]
Chondrocalcinosis is a finding on the imaging study like x-ray and means deposition of calcium in the cartilage. But depositions have been found in other tissues like hyaline cartilage, synovial tissue, capsule, meniscus, labrum, ligamentum flavum, soft tissue of the hand, and temporomandibular joint as well.
It has a reported prevalence of 5-15% and is thought to increase with age.
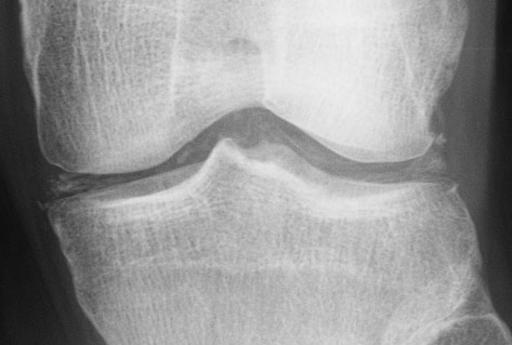
Causes of Chondrocalcinosis
- Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease [ the most common cause]
- Dicalcium phosphate dihydrate
- Calcium hydroxyapatite deposition
- Hypercalcemia especially hyperparathyroidism
- Soft tissue calcification is more common that joint depositis
- Gout
- Wilson disease – Liver disease caused by copper deposition
- Hemochromatosis – Iron storage disease
- Ochronosis or alkaptonuria
- A rare multisystem autosomal recessive metabolic disorder
- Bluish black discoloration of certain tissues, such as the ear cartilage and the ocular tissue.
- Joint injury
- Hypomagnesaemia [ Decrease of serum magnesium levels]
- Hypothyroidism – Decrease in thyroid hormone levels
Important causes are briefly discussed below
Pyrophosphate Arthropathy
This is caused by calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition. It is the most common cause of chondrocalcinosis and is also known as pseudogout.
The distribution is diagnostic. It mainly involves
- Wrist- radiocarpal joints
- Hand – Metacarpophalangeal joint especially nd and third row
- The patellofemoral joint of the knee
- Symphysis pubis & acetabular labrum calcify
This condition is often asymptomatic and found incidentally. Commonly asymptomatic and found incidentally
Hemochromatosis
The deposition is often bilaterally symmetric. Metacarpal heads may show beaks like osteophytes in 2nd- 5th metacarpals. Flattening of metacarpal heads may be observed especially in
Flattening of 2nd and 3rd metacarpal heads.
Osteoarthritis and Chondrocalcinosis
The association between osteoarthritis and chondrocalcinosis has been known for years.
Moreover, crystals of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate may be found in the synovial fluid of patients who have osteoarthritis.
It is not clear if chondrocalcinosis is the cause of osteoarthritis or if it develops due to changes in the metabolism of the chondrocyte or in the extracellular matrix of the cartilage.
Furthermore, chondrocytes from patients with osteoarthritis who do not exhibit CC produce as much pyrophosphate. It needs to be studied if these contribute to osteoarthritic changes.
Some cross-sectional studies have reported an association between the presence of calcium pyrophosphate dihydratecrystals in synovial fluid and severe radiographic changes whereas other studies failed to observe this.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Chondrocalcinosis is not a clinical entity but a finding on an imaging study. The finding may be an incidental finding in patients without symptoms.
As most of it is associated with calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease, in most of the patients, the presentation would be similar to pseudogout or calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease.
[Read more about Pseudogout]
The pseudogout is seen involving the knee, wrist, shoulder, ankle, elbow, and hands. Not all cases of chondrocalcinosis are symptomatic and most of them are seen as incidental finding only. Rarely, the temporomandibular joint and ligamentum flavum of the spinal canal is involved.
Other than arthritis, crystal deposition may cause intervertebral disk and ligament calcification with restriction of spine mobility and rarely spinal stenosis.
Gout can be distinguished from pseudogout by examining the crystals under a microscope. Gout crystals are of sodium urate and are needle-shaped and have negative birefringence. Pseudogout crystals (calcium pyrophosphate) are rod or rhomboid shaped and have no or weak positive birefringence.
Pseudogout may have had an aggressive onset and flares within hours. It causes pain, swelling, heat, and redness of the involved joint. The natural course is a spontaneous resolution over a few days or, at most, weeks.
The presentation in other cases would depend on the primary disease causing chondrocalcinosis.
The x-rays would reveal typical punctate and linear densities in hyaline and/or fibrocartilage.
Treatment of Chondrocalcinosis
The treatment would also depend on the disease that has led to chondrocalcinosis.
As we noted previously that chondrocalcinosis is just a manifestation and image finding. The treatment of the underlying cause would address the issue of this condition as well.
References
- Landis R, Haskard D. Pathogenesis of crystal-induced inflammation. Curr Rheumatol Rep2001;3:36–41. [abstarct]
- Neame RL, Carr AJ, Muir K, Doherty M. UK community prevalence of knee chondrocalcinosis: evidence that correlation with osteoarthritis is through a shared association with osteophyte. Ann Rheum Dis 2003;62:513.