Last Updated on November 23, 2022
Spondylosis as a medical term denotes degenerative changes that occur in the spine as a natural aging process for some other reason. The term degeneration means the wear and tear that accumulates.
The bone spurs and degeneration of intervertebral discs are examples of degeneration.
The term comes from the Ancient Greek word ‘spondylos’ which [plural of spondylus or vertebra] mean vertebrae or spine.
In some cases, physicians also use the term more specifically to describe the presence of spinal osteoarthritis or degenerative disc disease. The degenerative process in osteoarthritis chiefly affects the vertebral bodies, the neural foramina, and the facet joints.
The spondylosis may be present in a person without causing any symptoms, especially in the early stages. The progression of spondylosis may cause symptoms in some persons and the symptoms in these cases depend on the site and severity.
It can cause pain in the neck in the cervical region and pain in back in lower spine regions. Compression of spinal cord or nerve roots can lead to sensory and motor disturbances including radicular pain, paresthesia, and muscle weakness in the limbs.
Types of Spondylosis
Depending on the part of the spine involved, the spondylosis can be
- Cervical
- Thoracic
- Lumbar [or lumbosacral]
- Multiple levels
Terms Sounding similar to Spondylosis but with Different Meaning
Spondylitis is inflammation of one or more vertebrae. For example ankylosing spondylitis. [In contrast to the inflammatory nature of spondylitis, spondylosis is degenerative].
Spondylolysis is a defect in the pars interarticularis which connects upper and lower facets. This defect predisposes to spondylolisthesis.
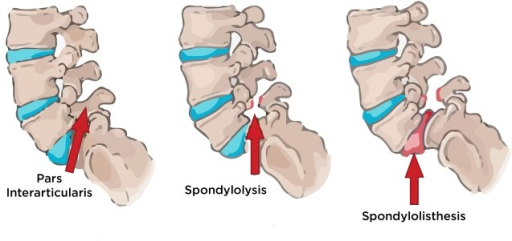
Spondylolisthesis is the displacement of the body of one vertebra in relation to an adjacent vertebra. For example, an anterior slip of L5 on S1 as shown in the image above. But the displaced vertebra would not slip alone, the spine above it slips along too, creating a misalignment of the spine at the level of the slip.
Spondylosis deformans is a probably inflammatory condition where discs degenerate and bony spurs or bridges occur around the disc and nearby joints of the spine.
Risk Factors for Spondylosis
The condition results from the added effect of effects of ongoing wear and tear. But a number of risk factors can increase the likelihood. These risk factors include
- Obesity
- Genetic predisposition
- Trauma
- Participating in high-impact sports
- Anything that leads to increased wear and tear of the spine tissues – discs, tendons, muscles, ligaments, and cartilage.
Here are some of the most common types of spondylosis affecting people
- Degenerative disc disease
- Degeneration of one or more of the intervertebral discs t
- Discs weaken, bulge or rupture
- Compression of nearby nerve roots and even the spinal cord.
- Facet Arthritis
- Arthritis of one or more of the facet joints t
- Wearing of cartilage leads to painful joint movements
- Formation of osteophytes or bone spurs
- Spinal stenosis
- Gradual narrowing of the spinal canal,
- Causes the constriction of the spinal cord or nerve roots
- Usually caused by cumulative effects of other spondylosis like osteophytes or herniated disc.
Clinical Presentation
One may have spondylosis and still have no symptoms as the symptoms do not appear unless the condition has progressed enough or result in some nerve root compression.
Following are the general symptoms, a patient of spondylosis may experience. Not all the symptoms are present in all the patients.
- Pain in the affected area [neck or back] – Pain could be acute or chronic
- Loss of sensation [the site would depend upon the vertebral level where neural tissue is compressed.
- Radiating pain
- In arm and around shoulders [cervical]
- Chest and abdomen [thoracic]
- Pelvic area and lower limbs [lumbar]
- Stiff back
- Muscle cramps esp in lower limb in case of lumbar disease
Diagnostic Work Up
- A good history with the physical examinatio
- Imaging
- X-ray
- Basic investigation
- Shows degenerative changes like osteophytes, reduction in joint space and any change in curvature of the spine.
- Helpful to rule out any other pathology that might be causing the symptoms.
- Do not show soft tissues well. Therefore, the disc and ligaments are not visible on x-rays.
- MRI
- Able to show the status of neural tissue and any compression caused.
- Investigation of choice in case of suspected disc herniations and spinal stenosis
Most of the cases of spondylosis are diagnosed on the clinical basis only. X-rays may be needed in selected patients or patients who do not improve with treatment.
MRI is required in few cases of back pain especially when there is an involvement of neural tissue.
Treatment of Spondylosis
Most cases of spondylosis are managed conservatively. Surgery is required in a small percentage of people either having acute unrelenting symptoms or patients who do not improve on conservative treatment.
Generally, surgical is recommended only after a patient attempts several weeks or months of conservative treatment, but continues to experience symptoms.
Conservative Treatment
Pain Relief Drugs
- Drugs lessen the pain and anti-inflammatory drugs also reduce inflammation and swelling.
- Oral NSAIDs and opioid drugs are often the first line of drugs
- Muscle relaxants can be given to relieve the spasm
- Some patients are benefited by antidepressants like amitriptyline and drugs given for neuropathic pains like pregabalin.
Physical therapy
This is an essential part of spondylosis treatment. The aim is to strengthen core muscles like muscles of the abdomen and pelvis and the spinal musculatures. As muscles strengthen, they take some of the pressure off of your vertebrae and joints. Improving cardiovascular health, increasing flexibility and muscle endurance are other goals of exercise therapy.
The exercises are performed under supervision.
Lifestyle changes
Weight is an important risk factor for progression and people would benefit from weight loss. Weight loss reduces the loads on spine leading to betterment.
Similarly quitting smoking helps to get better blood circulation of the spine and healing potential gets better.
Patient needs to adopt good postures for daily jobs including sitting and sleeping.
At the job station, the ergonomic arrangement of the stuff goes a long way.
Prolonged sitting is to be avoided.
CAM
Though the role of complimentary and alternative medicine is to be established, acupressure, acupuncture and yoga have been claimed to be beneficial.
Steroid Injections
Steroid injections provide longer relief than oral medications and can be considered in patients who are not responding.
Facet joint injections and epidural steroid injections are the two most common types of injections given.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is occasionally indicated.
In cervical spondylosis, surgery is advocated for in patients
- With intractable pain
- Progressive symptoms
- Weakness that fails to improve with conservative therapy.
- Myelopathy.
In lumbar spondylosis, the surgery is indicated if there is a compromise of the canal space with symptoms not improving on conservative treatment.
The basic purpose of the surgery is to decompress the neural tissue and/or fuse the painful joints.
There are many procedural options for surgical decompression.
- Foraminotomy
- Considered when foraminal stenosis is present
- Relieves pressure on a nerve root exiting a foraminal canal
- Laminotomy
- Relieves pressure on the spinal cord by decompressing it
- Discectomy
- Removes a part of a bulging or herniated disc causing compression
- Fusion surgery
- To stop of motion of painful joint
- Can be fixed with an implant
- Bone grafting is done for fusion