Last Updated on October 28, 2023
Methylene blue injection is an easy and safe way to rule out or confirm breakage of the joint capsule when there is an injury near or around the joint, thus establishing or ruling out the presence of open joint injury.
Open joint injuries consist of are skin and soft-tissue injuries which communicate with the joint.
It is important to identify open joint injury early so that further aggressive workup and management could be undertaken timely.
Many of the injuries are clearly open but others appear doubtful because the injury to the capsule may not be evident.
Intra-articular injection of methylene blue would lead to extravasation of dye in case of an open from the wound site is highly suggestive of open joint injury.
However, the absence of extravasation does not entirely rule out the possibility of open joint injury.
The reported sensitivity of the procedure is as high as 90%. Some studies though report only 30% sensitivities.
The relevance of the procedure is also controversial, with some authors saying that the test is not clinically relevant whereas others asserting its relevance.
Indications for Methylene Blue Injection
The injection is indicated in soft-tissue injury associated with at least one of the following-
- Periarticular fracture
- Visible joint capsule
- Any of the following injuries in proximity to a joint
- Skin laceration
- A visible joint capsule through a wound
- Open fractures
- Extravasation of serous or serosanguineous fluid from a wound
Contraindications
Following cases are considered clear-cut open joint injuries and therefore the injection is not necessary
- Open fracture with obvious joint involvement on X-ray
- Air or foreign bodies in joint on x-ray
Methylene blue may increase serotonin levels in the central nervous system and caution should be taken in patients on sertonergic drugs.
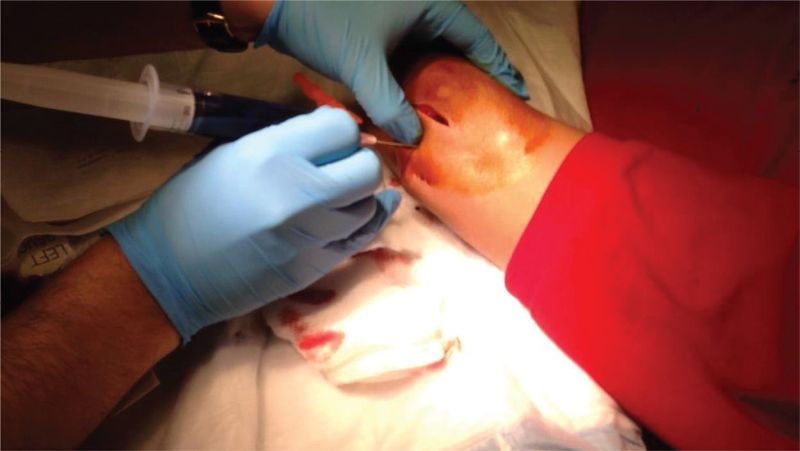
Intra-articular injection of methylene blue dye works by creating enough dye pressure to distend the joint capsule and maximize the chances of visualizing dye extravasation from the wound.
The dye is injected through one of available site, far from the wound using an 18-gauge needle. As the procedure involves injection and capsular distension, the procedure is painful.
Therefore, parenteral analgesia and local anesthesia are indicated.
Intra-articular injection of methylene blue that demonstrates extravasation of dye from the wound site is highly suggestive of open joint injury. However, the open joint injury may still be present in the absence of dye extravasation
In patients who are allergic to methylene blue, injection of sterile fluorescein in normal saline (NS) solution into the joint space.
Procedure of Injection of Methylene Blue Into Joint
Patient Preparation
Obtain consent for the procedure
The positioning of the patient varies according to the joint that is to undergo injection.
Preparation of Solution of Methylene Blue
Using sterile envrionment mix 1-2 ml of methylene blue to the bowl of normal saline to create a dark colored solution. Fill 20- or 30-mL syringe with this solution.
Part Preparation
Identify the injection site. Select an approach for injection that is as far as possible from the skin wound. Make sure to avoid any neurovascular structures. Prepare the part after providing appropriate parenteral analgesia by scrubbing a wide field with a sterile preparation or a surgical scrub. As a rule after scrubbing the desired field once, it is repeated 2-3 times more for active aseptic preparation.
Local Anesthesia
At the desired site, elevate a skin wheal of local anesthetic [1-2% lidocaine] and then inject the anesthetic deeper into the subcutaneous tissue and further until the joint space is entered. [Confirmed by increased ease of injection and by aspiration of joint fluid].
Secure Needle into Joint Space
After joint is entered, secure the needle in the joint space by the other hand that holds the hub of the needle. Remove the syringe while the needle is held secure and switch the syringe with the syringe that contains the methylene dye solution.
Injecting the Methylene Blue Dye into Joint
Inject the solution into the joint until it is fully distended. THe volume required for distention would vary from joint to joint.
Watch the wound for extravasation of the methylene blue dye.
Once a satisfactory observation has been made, aspirate back as much fluid as possible followed by needle withdrawal.
Clean the skin and wound and apply a sterile dressing over the wound and injection site.
Conclusion
If extravasation is present, the injury to the joint is open in nature. Administration of IV antibiotics, further evaluation by specialist and decision for exploration and irrigation is considered.
If no extravasation is present and clinical evaluation is in sync with the finding, the injury is treated as closed and appropriate treatment measures are taken.
In case of no extravasation but strong clinical suspicion, an evaluation by a specialist is desirable.
Complications of Methylene Blue Injection
Potential complications of intra-articular injection of methylene blue include the following:
- Infection
- Bleeding or nerve injury
- False-negative results from the injection
-
- Small open defects in a joint capsule [The dye will leak through and the joint would not distend enough for extravasation]
- The dye is not injected into the joint [some false track is created]