Last Updated on November 13, 2019
Knee arthrocentesis refers to puncture of the knee joint and the aspiration of its synovial fluid. It is used for synovial fluid analysis to aid in diagnosis and also for therapeutic purposes.
Knee joint can be approached by multiple approaches [discussed below]
Indications of Knee Arthrocentesis
Diagnosis
- Acute monoarticular [that affects a single joint] arthritis
- Suspected infection (eg, septic arthritis)
- Inflammatory joint effusion
- Gout
- Pseudogout
- Rheumatologic disorders
- Reactive arthropathies
Therapeutic
- To relieve a large painful effusion.
- Instillation of medications
- Repeated arthrocentesis for septic arthritis in carefully selected patients as a means of decreasing bacterial load
Contraindications
- Cellulitis in the overlying skin
- Overlying skin lesions (eg, dermatitis or psoriasis)
- Known bacteremia
- Bleeding disorders
- Patient on anticoagulation medication
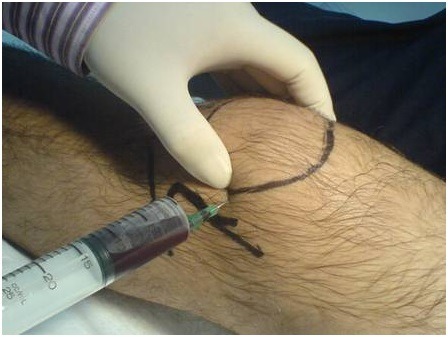
Procedure of Knee Aspiration or Knee Arthrocentesis
Different Approaches
Knee joint aspiration can be done via a parapatellar approach (usually preferred), a suprapatellar approach, or an infrapatellar approach.
Parapatellar Approach
The knee can be approached from the medial side or lateral side. The insertion site is just below the midpoint of either the medial or the lateral border of the patella. The needle is directed inferomedially. The needle is kept perpendicular to the long axis of the femur and points toward the intercondylar notch of the femur.
Suprapatellar Approach
This approach accesses the joint from the superior aspect. It can be done from the midpoint of either the superomedial or the superolateral border of the patella. The needle is directed toward the intercondylar notch of the femur.
Infrapatellar Approach
In this approach, the needle is inserted about 5 mm below the inferior border of the patella and just lateral to the edge of the patellar tendon. Piercing of patellar tendon should be avoided with this approach.
Procedure
- Determine the site of needle insertion. This would depend on the approach chosen.
- Prepare the skin with a sterile solution and drape the part.
- Attach the 18- or 20-gauge needle to the 20-mL syringe. In larger effusions, 50-60 ml syringes may be used. Otherwise, an extra syringe should be kept handy, just in case.
- Stretch the skin between two fingers and insert the needle into the joint while keeping a gentle pull on the plunger. Placement of a towel under the popliteal region to flex the knee to 15-20° may facilitate entry by opening up the joint space.
- Readjust the direction of the needle if it strikes the bone.
- If the needle is in the joint, the fluid would start entering the syringe. Milking the region could help in case the flow is slow.
- Once aspiration is complete, the needle is removed and a bandage applied.
Complications of Knee Arthrocentesis
Dry Tap
This can be caused by
- improper needle placement
- A small amount of effusion
- Mechanical obstruction of the needle against cartilage or thickened synovium
Cartilage Injury
This is minimal with smaller bore needles.
Hemarthrosis
Most hemarthroses are small and self-limited. Correction of coagulopathy may be desired if that is the reason for hemarthrosis.
Infection
It is rare. If there appears a higher risk of infection, prophylactic antibiotics may be started.