Last Updated on December 9, 2019
Rolando fracture is a three-part intraarticular fracture-dislocation of the base of the thumb. This is an unstable injury that requires surgical reduction and fixation. It is named after Silvio Rolando, an Italian surgeon who described it first.
Relevant Anatomy, Mechanism of Injury and Pathophysiology
The carpometacarpal joint is between the base of thumb and trapezium bone.
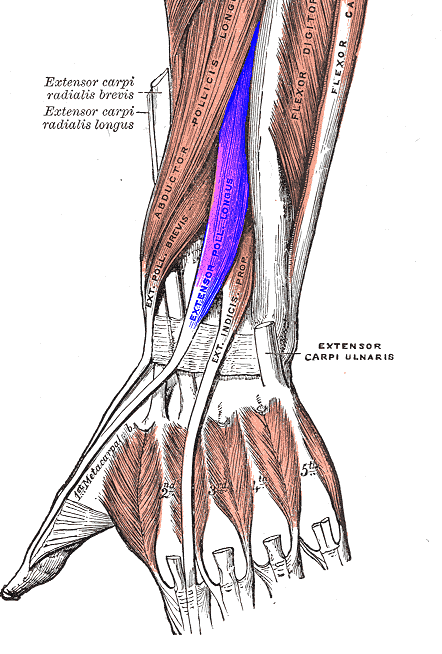
The joint allows motion parallel and perpendicular to the plane of the palm. Thumb function constitutes about 50% of hand function as a whole. The thumb metacarpal base is a unique that it allows a wide range of motion while maintaining stability for grasp and pinch.
Therefore, it is very important that accurate reduction and aggressive rehabilitation is carried when
Base of thumb fractures are mainly extraarticular and intraarticular. Intraarticular fractures are namely Bennet fracture, Rolando fracture, and comminuted fractures.
The Rolando fracture usually occurs due to axial loading in a partially flexed metacarpal, such as a fistfight. It can also occur as a result of indirect forces such as falling on a thumb.
Punching is the most common mechanism but other causes like motor vehicle accidents, work-related injuries and falls are also common.
The resting tone present in the multiple tendons that act on the thumb further lead to the displacement.
These include extensor pollicis brevis and extensor pollicis longus which shorten the thumb ray along with pull from the flexor pollicis longus.
The adductor pollicis pulls the distal metacarpal toward the palm and in conjunction with the abductor pollicis longus [acts on the metacarpal base] leads to varus at the metaphyseal-diaphyseal junction.
The fracture line is typically T- or Y-shaped.
Clinical Presentation
After the injury, the patient presents with swelling and pain in the base of the thumb region. The region is tender and movements are painful.
Neurovascular and tendon injuries are not commonly associated with this fracture.
Imaging
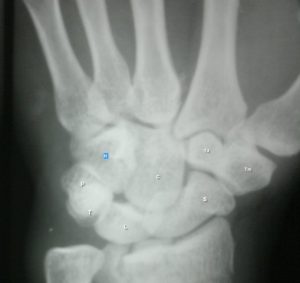
The fracture is confirmed by x-ray imaging.
Anteroposterior (AP) and lateral radiographs are the routine x-rays sought. If the routine x-rays are not able to reveal the full extent of comminution, a Robert radiograph (a hyperpronated view of the thumb base) can be tried.
Rolando fracture is very similar to Bennett fracture but it divides the metacarpal base into two, three and sometimes many fragments. Rolando fracture is also called as Y or T shape fracture.
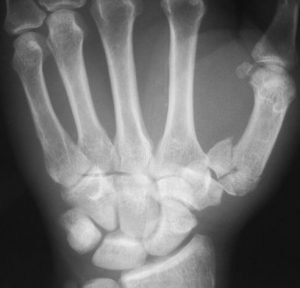
CT is able to display the fracture configuration better.
Differential Diagnosis
- Bennett Fracture
- Extra-articular fractures through the first metacarpal base
- Comminuted fractures of -part intra-articular fracture through the first metacarpal base
Treatment
Most of the Rolando fractures are displaced and therefore treated by surgery. Only minimally displaced fractures should be considered for thumb spica.
All fractures with articular stepoff more than 1-2 mm would require surgical treatment.
Various treatment options can be used as follows
- Large articular fragments – plate-and-screw fixation.
- Massive comminution- traction or ligamentotaxis and external fixators.
- Open fractures – Prefer pin fixation or external fixation
After the surgery and sufficient union, the patient is put on exercises which include stretching and strengthening exercises of wrist, hand and thumb in particular. These include
- Opposition Stretch:
- Wrist Flexion-extension
- Grip Strength.
- Finger Stretch
Complications
Complications are often directly related nature of the injury and the extent of the comminution. Usually, these are
- Pin-tract infection
- Screw pullout and loss of fixation
- Neural damage
- Joint stiffness
References
- Breen TF, Gelberman RH, Jupiter JB. Intra-articular fractures of the basilar joint of the thumb. Hand Clin. 1988 Aug. 4 (3):491-501
- Mumtaz MU, Ahmad F, Kawoosa AA, Hussain I, Wani I. Treatment of Rolando Fractures by Open Reduction and Internal Fixation using Mini T-Plate and Screws. J Hand Microsurg. 2016 Aug. 8 (2):80-5.
- Gelberman RH, Vance RM, Zakaib GS. Fractures at the base of the thumb: treatment with oblique traction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979 Mar. 61 (2):260-2