Last Updated on July 31, 2019
Suprascapular neuropathy or infraspinatus syndrome is a less common cause of shoulder pain, especially in athletes with overhead sports activity. Volleyball, basketball, and tennis are examples of such sports which increase the risk of rotator cuff tendinopathy, injuries to the glenoid labrum and suprascapular neuropathy.
The incidence of suprascapular neuropathy appears highest in volleyball players.
[Anatomy of Suprascapular Nerve]
[anatomy of scapula and structures attached to it]
Causes of Suprascapular Neuropathy
Suprascapular nerve entrapment or injury is the prime cause of suprascapular neuropathy. A suprascapular notch or the spinoglenoid notch, latter being more common are two sites where nerve could be affected. Sports like volleyball and direct trauma are key causes.
Repeated traction and microtrauma, direct compression by surrounding structures or compression space-occupying lesions, and ischemia of the nerve from repetitive trauma are suggested mechanisms of injury.
Massive tears of rotator cuff and injuries to glenoid labrum, space-occupying lesions such as ganglion cysts arising from the glenohumeral joint are known causes of suprascapular neuropathy.
When the upper limb is abducted and externally rotated, the suprascapular nerve becomes vulnerable to direct compression at the spinoglenoid notch. This mechanism is important in sports requiring overhead activity.
Migration of posttraumatic microemboli from the suprascapular artery to the vasa nervorum is also suggested as a plausible cause.
Genetic causes are thought to play a role, but the specific factors are not known yet.
Presentation of Suprascapular Neuropathy [Signs and Symptoms]
Quite a number of people with suprascapular neuropathy are not symptomatic.
Vague shoulder pain in the dominant limb [usually] is the most common presentation. The pain is described as a deep and dull ache.
Some may present with supraspinatus and/or infraspinatus weakness [weakness of abduction and external rotation of shoulder]. The level of compression determines whether both the muscles are involved or single.
Involvement of both the muscles suggests compression before spinoglenoid notch, whereas if infraspinatus only is involved, it is at spinoglenoid notch.
The lesion that affects both the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles are more likely to have pain that affects only the infraspinatus.
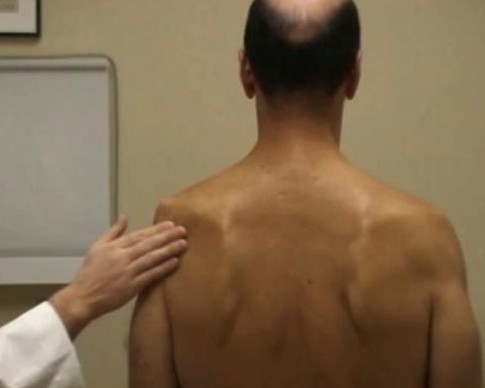
On examination, atrophy of the supraspinatus and/or infraspinatus muscles may be present on the physical examination, depending on the site of the nerve entrapment. Supraspinatus involvement may be frequently overlooked because of the bulk of the overlying trapezius.
Overhead motions include weakness and compromised endurance in performing overhead and muscle testing may reveal relative weakness. Cross-body adduction or internal rotation of the ipsilateral upper limb may result in pain.
Pressure applied over the suprascapular or spinoglenoid notches may cause tenderness.
Differential Diagnoses
Cervical disc Injuries, cervical radiculopathy, rotator cuff injury, shoulder impingement syndrome should be ruled, superior Labrum injuries need to be ruled out as well.
Lab Studies
Not generally required.
Imaging
Routine radiographs are often normal. Cervical spine x-rays are required to rule possible radicular cause.
Shoulder MRI may reveal paralabral cyst, ganglion cyst with suprascapular nerve compression. Acute cases show supraspinatus or infraspinatus muscle edema whereas in chronic cases fatty infiltration may be seen.
Ultrasonography can reveal for ganglia or masses in parascapular region or cysts in spinoglenoid notch especially in thin people.
The confirmation of diagnosis can be done with electrodiagnostic testing.
Treatment of Suprascapular Neuropathy
Initial treatment for suprascapular neuropathy is conservative which consists of symptomatic medication and mobilization exercises. NSAIDs and gabapentin may provide some pain relief.
Activity modification/repetition is advised. Heat application, nerve blocks etc may help to relieve the pain. The injection of an anesthetic and/or corticosteroid mixture into the suprascapular notch may provide temporary benefit.
If there is a compression, it should be relieved surgically without putting a patient on conservative treatment. Early decompression provides a better chance of regaining full muscular strength and bulk.
If conservative treatment fails to relieve the symptoms, surgical intervention simple widening of the spinoglenoid notch or suprascapular notch may be considered.
In some patients, radiofrequency ablation may be considered as a palliative procedure.
In the recovery phase, shoulder mobilization and strengthening exercises are started gradually.