Last Updated on November 22, 2023
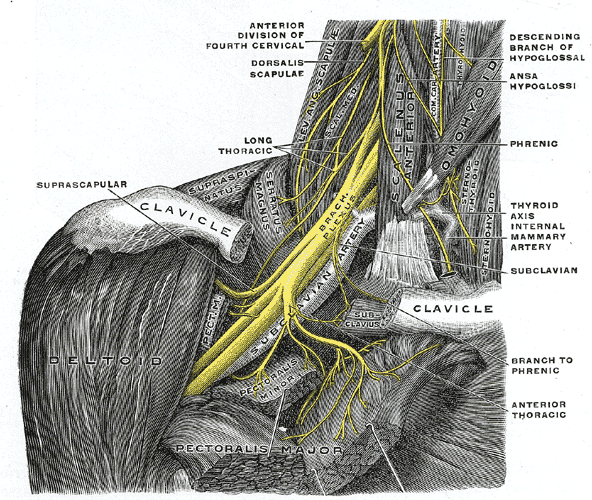
Suprascapular nerve is derived from the upper trunk of brachial plexus and receives fibers from C5 and C6. It is a mixed nerve containing both sensory and motor fibers.
[Read anatomy of brachial plexus]
After it emerges, it sends sensory branches to both the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints. It passes downward, laterally deep to the omohyoid and trapezius muscles & then posteriorly to run under trapezius along with the suprascapular vein and artery, it reaches the suprascapular notch.
Following videos explain the course of suprascapular nerve very well.
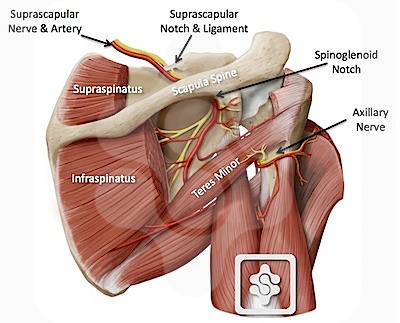
The suprascapular notch or scapular notch is a notch in the superior border of the scapula, just medial to the base of the coracoid process. Transverse scapular ligament converts this notch into the foramen. The suprascapular nerve passes below the transverse scapular ligament whereas scapular artery is above the ligament.
After giving off two branches to supraspinatus, it passes around lateral border of the scapular spine through spinoglenoid notch. and passes under the inferior scapular ligament along with artery. Suprascapular nerve does not innervate the skin.
Clinical Significance of Suprascapular Nerve
Surascapular Nerve Entrapment or Suprascapular Neuropathy
The suprscapular nerve may get entrapped or compressed at various sites.
The nerve may get entrapped within the suprascapular notch or the spinoglenoid notch. The cause of this may be paralabral ganglion cyst pressing on the nerve or thickening or ossification of the transverse scapular ligament.
Major trauma can result in the nerve compression fractured scapula, a tear of the rotator cuff or shoulder arthrodesis can all cause a compression of the nerve. Upper brachial plexus injury as in Erb’s palsy may result in damage to this nerve supply too.
Parsonage Turner Syndrome is an inflammatory condition of brachial plexus which can affect suprascapular nerve and its distribution.
When there is any sort of disruption within the suprascapular nerve, the muscles it supplies (supraspinatus and infraspinatus) lose their innervation.
If the supraspinatus is affected then abduction at the shoulder joint may be affected especially initiation of the abduction. Abduction is the movement that raises arms up from your sides as in overhead clapping.
If the infraspinatus is affected then external rotation may be affected a movement which is done as in grabbing seatbelt from the side while you sit on the seat
Wasting of this muscles is usually visible when looking at the shoulder from behind.
Level of compression would determine if single or both muscles are affected.
Compression at the suprascapular notch and above affects both muscles whereas compression after suprascapular muscles affects infraspinatus only.
Suprascapular Nerve Block
This block is thus very well suited for conservative physiotherapeutic management of frozen shoulder syndromes or for analgesia secondary to shoulder surgery.