Last Updated on October 29, 2023
Tumor mineralization means deposition of additional mineral in and around focal lesions of bone.
Tumor mineralization is seen as
- Mineralization of tumor matrix
- Reactive bone proliferation
- Mineral deposition in areas of degeneration or necrosis
The characteristic mineralization patterns have diagnostic significance.
Depending on the mineralization pattern, bone tumors and tumor-like conditions can be divided into categories of matrix-producing lesions, non—matrix producing lesions, or as a combination.
Mineralization of Tumor Matrix
Matrix refers to the acellular/intracellular substance produced by mesenchymal cells and includes
- Osteoid produced by osteoblasts
- Chondroid produced by chondroblast
- Myxoid and collagen fibers produced by fibroblasts.
Osteoid matrix
Mineralization of osteoid elaborated by neoplastic osteoblasts is the final in the creation of tumor bone.
Osteoid tissue mineralizes in a confluent manner that results in a radiographic density ranging from a hazy ground-glass appearance to a dense ivory-like pattern.
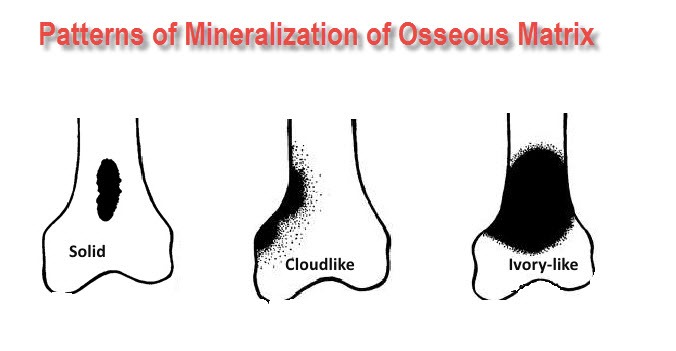
Rapidly growing tumors such as osteosarcoma usually produce immature bone which is seen as ill-defined poorly structured clouds of density.
On the other hand, slowly growing, osteoid-producing tumor such as parosteal osteosarcomas produces solid mature tumor bone which is seen as well-defined heavily mineralized masses radiographically.
The mineralization of neoplastic bone is initially observed in the center of the lesion where cellular maturity is the greatest.
Tumor bone is occasionally produced by a fibroblastic cell that has converted to functional osteoblasts through the mechanism such as fibrous dysplasia. The patterns of bone formed is woven or fibrous in appearance.
The woven bone of this type is usually less densely mineralized than tumor bone formed directly from neoplastic osteoblasts. The result is a hazy ground glass appearance.
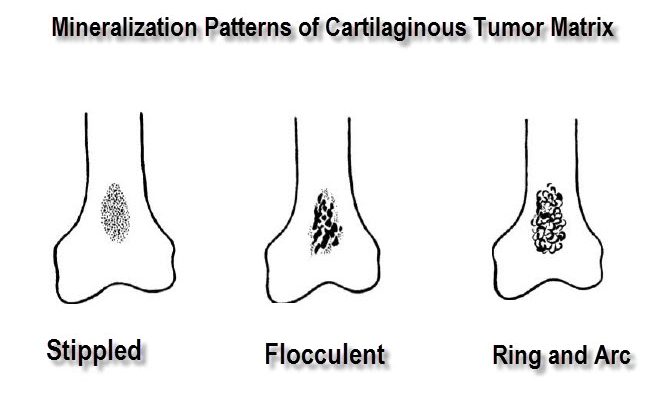
Chondroid matrix
In neoplastic cartilage, calcification in the form of stipples, floccules, arcs, and ring—like shapes conforms to the lobulated configuration of the cartilaginous matrix. Since this calcification usually occurs in the most mature cartilage, it is characteristically found in the center of a lesion.
A mixture of stipples and floccules is seen within both benign and malignant cartilaginous tumors.
Reactive bone mineralization
Reactive bone is formed either through modulation of normal marrow or soft tissue elements to osteoblastic activity or from the periosteal reaction at tumor margins.
Slowly progressive neoplasms including certain malignant lesions such as primary lymphoma of bone and Ewing’s tumor can stimulate reactive mineralization.
This results in bone activity. The results in a coarsened and mottled trabecular pattern of combined radiolucency and increased radiodensity.
Endosteal and trabecular and increased sclerosis can also be stimulated by an inflammatory disorder such as chronic low—grade osteitis and osteomyelitis.
Dystrophic mineralization patterns
Dystrophic calcification results from the deposition of mineral salts in degenerating or necrotic tissue, primarily necrotic fat and densely hyalinized connective tissue.
The mineralization of bone infraction occurs in the periphery of a lesion.
This process can result in stipples flocculent solid patchy and linear density patterns in bone. This type of mineralization can be seen in such lesions as ossifying lipomas, bone infarct and in areas of bone radiation necrosis.
Uncommonly, necrotic portions of non-matrix-producing tumors, e.g. Ewing tumor and primary lymphoma of bone will mineralize which can be misleading.
Read more about dystrophic calcification