Last Updated on August 15, 2022
Woven bone and lamellar bones are types of bone that are differentiated on basis of their microscopic arrangements. These two bone structures have different functions. Whereas woven bone is the haphazard bone, lamellar bone is a more structured bone.
Woven bone is immature bone or primitive bone. it is found in the embryo, the newborn, growing bone ends, and initial bone laid fracture healing.
Ultimately, the woven bone gets replaced by highly organized lamellar bone.
Thus the differentiation between the woven and lamellar bone is microscopic.
Composition of Bone
Bones are mainly composed of bone matrix. the matrix contains both organic and inorganic components.
The osteoblasts lay down the bone matrix and it is called osteoid. The osteoid is hardened with inorganic salts, such as calcium and phosphate, and by the chemicals released from the osteoblasts through a process known as mineralization.
Bone is formed by the hardening of this matrix entrapping the cells. For example, when are trapped in the matrix, they become osteocytes.
The inorganic component of the bone is mainly crystalline mineral salts and calcium and the organic part of the matrix is mainly composed of Type I collagen.
[More on bone anatomy and physiology]
On the microscope, two types of bone can be identified
- Woven bone
- Lamellar bone
These bones differ in the pattern of collagen forming the osteoid.
Lamellar bone
Lamellar bone represents main bone in mature skeleton. Lamellar bone is characterized by the organized arrangement of collagen fibers into layers or lamellae. This gives it a greater stiffness when compared to the haphazard arrangement of the woven bone.
Lamellar bone is a secondary bone created by the remodeling of woven bone. Lamellar bone has a regular parallel alignment of collagen into sheets (lamellae) and is mechanically strong. It is highly organized in concentric sheets with a much lower proportion of osteocytes to surrounding tissue.
The lamellar bone can be called compact bone (cortical bone) in the long bones and trabecular bone (cancellous bone). The differentiation is based on arrangements of the osteons.
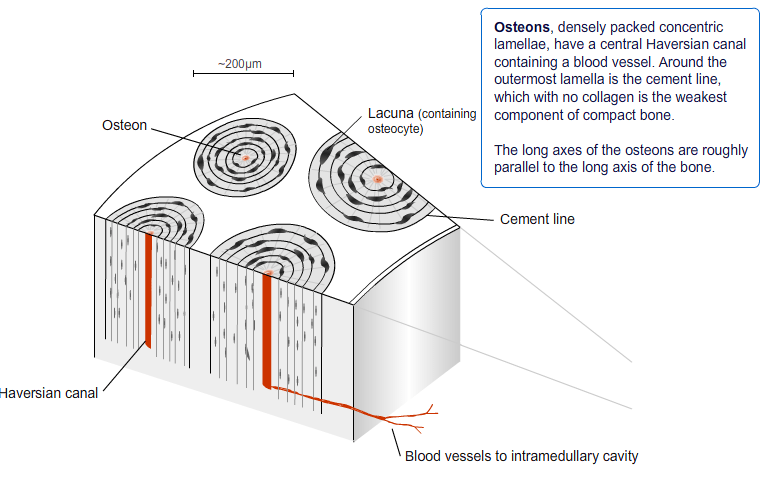
Lamellar bone is stronger and filled with many collagen fibers parallel to other fibers in the same layer (osteons).
In cross-section, the fibers run in opposite directions in alternating layers. This kind of structural arrangement assists in the bone’s ability to resist torsion forces
Osteon is the basic building block or microscopic structural unit of cortical or cancellous bone. Osteons of cortical bone are called Haversian system whereas osteons of cancellous bone are called packets. Haversian systems are cylindrical in shape, are approximately 400 mm long and 200 mm wide at their base
In cortical osteons, outer lamellae form first, whereas in trabecular packets the first lamellae are formed toward the center of the trabeculae. Each successive lamella in a cortical osteon is laid concentrically inside the preceding one while in trabeculae packets they are stacked in parallel layers away from the center of the trabeculae toward the bone surface.

Woven bone
Woven bone is characterized by haphazard organization of collagen fibers and is mechanically weak.
Woven bone is produced when osteoblasts produce osteoid rapidly.
It is present in
- All fetal bones are initially when the bone is laid down. Later it gets replaced by lamellar bone.
- After fractures, the initial bone that unites the fracture is woven bone. It too gets replaced by lamellar bone.
- Paget’s disease
Woven bone is weaker, with a smaller number of randomly oriented collagen fibers, but forms quickly.
It has been named due to the woven appearance of the fibrous matrix.
Woven bone is basically either immature bone or pathologic bone. It is not stress oriented. Compared to the lamellar bone, woven bone has more osteocytes per unit of volume and a higher rate of turnover.
Woven bone is weaker and more flexible than lamellar bone.
Significance of Woven Bone
In an adult skeleton, normally, the woven bone is not found. It is only found in pathological conditions like
- Paget’s disease
- Osteosarcoma
- Following injury
The woven bone is formed when the body has to make bone faster. That is why it results in the disorganization of structure because the speed precludes the orderly deposition of the collagen fibrils.
In the fetus, the woven bone provides woven bone with enhanced flexibility while sacrificing some stiffness. This is important as it allows a baby to safely pass through the birth canal without skeletal trauma being caused.
After injury too, early restoration of mechanical integrity of the bone is ensured. Later, this woven bone will get resorbed and replaced by lamellar bone.
References
- Rabeb Ben Kahla, Abdelwahed Barkaoui.Chapter 1 – Bone multiscale mechanics, Editor(s): Rabeb Ben Kahla, Abdelwahed Barkaoui, Bone Remodeling Process, Academic Press,2021, Pages 1-47, ISBN 9780323884679,
https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-88467-9.00005-9. [Link] - Gorski JP. Is All Bone the Same? Distinctive Distributions and Properties of Non-Collagenous Matrix Proteins in Lamellar Vs. Woven Bone Imply the Existence of Different Underlying Osteogenic Mechanisms. Critical Reviews in Oral Biology & Medicine. 1998;9(2):201-223. doi:10.1177/10454411980090020401