Last Updated on October 15, 2023
Cortical bone and cancellous bone are two types of osseous tissues of the human skeleton which differ in their structure and distribution. The difference in their structures and distribution is designed to carry different functions.
What is Cortical Bone
Cortical bone refers to the thick outer surface of typically a long bone [for example humerus or femur shaft] that ensheathes the cavity of the bone called medulla. The sheath or outer shell formed by the cortical bone is called cortex. Cortical bone is also called compact or lamellar bone and provides strength to all the long bones of the body, for example, femur.
Cortical bone contributes about 80% of the weight of a human skeleton. It is much denser than cancellous bone, harder, stronger and stiffer.
At the microscopic level, the structural arrangement of a cortical bone is different than cancellous. Compact bone consists of closely packed osteons or Haversian systems. The osteon consists of a central canal called the osteogenic (Haversian) canal, which is surrounded by concentric rings (lamellae) of the matrix.
[See diagram below]
Between the rings of the matrix, the bone cells (osteocytes) are located in spaces called lacunae. Small channels (canaliculi) radiate from the lacunae to the osteonic (Haversian) canal to provide passageways through the hard matrix.
The Haversian systems are packed tightly together to form what appears to be a solid mass. The osteonic canals contain blood vessels that are parallel to the long axis of the bone. These blood vessels interconnect, by way of perforating canals, with vessels on the surface of the bone.
[Read more on Anatomy and Physiology of bone]
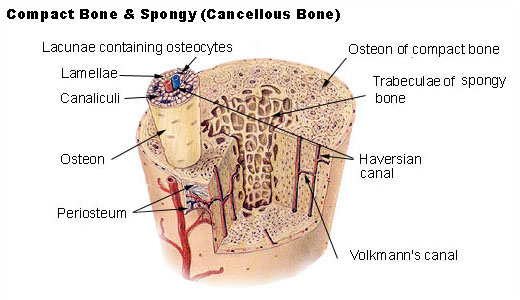
Image Credit: Public domain image, from Wikipedia
Cortical bone is arranged for facilitating the following functions
- To support the whole body weight
- Protect organs
- Provide levers for movement
- Store and release calcium.
Cancellous Bone or Spongy Bone
Cancellous bone is also called trabecular bone or spongy bone.
Compared to compact bone, which is the other type of osseous tissue, it has a higher surface area but is less dense, softer, weaker, and less stiff.

Image Credit:OERPUB
It typically occurs at the ends of long bones, proximal to joints and within the interior of vertebrae.
For example, distal end radius, proximal humerus or proximal femur, all are examples of cancellous bone.
Microscopically, cancellous bone consists of plates (trabeculae) and bars of bone adjacent to small, irregular cavities that contain red bone marrow.
The canaliculi connect to the adjacent cavities, instead of a central Haversian canal, to receive their blood supply. It may appear that the trabeculae are arranged in a haphazard manner, but they are organized to provide maximum strength similar to braces that are used to support a building.
The trabeculae of spongy bone follow the lines of stress and can realign if the direction of stress changes.
Cancellous bone has a greater surface area and is ideal for metabolic activity e.g. exchange of calcium ions.
In osteoporosis, cancellous bone is more severely affected than cortical bone.
Cancellous bone is highly vascular and frequently contains red bone marrow where hematopoiesis, the production of blood cells, occurs. Bone marrow also acts as a source of stem cells.
All the procedures for the study of bone marrow are done in spongy bone
Both cortical and cancellous bones together form the skeleton and serve their respective functions.