Last Updated on November 22, 2023
This article is an introduction to total joint replacement. Specific types of joint replacement — such as for the hip, knee, shoulder, or wrist are discussed separately.
Joint replacement surgery is last resort but a highly effective method of treating joint problems including joint pain and deformity and restoring mobility. Joint replacement surgery is very commonly performed the procedure in modern orthopedics and one of the divisions of orthopedics that has changed the outcome of many chronic diseases.
It is also called replacement arthroplasty or in common usage simply arthroplasty. Arthroplasty otherwise involves a broader spectrum of treatments like replacing, remodeling or realignment of the joint.
A joint is where the ends of two or more bones meet. Total joint replacement is a surgical procedure in which parts of a diseased joint are removed and replaced with a prosthesis, an artificial device designed to replicate the movement of a normal, healthy joint.
If only a part of the joint is replaced, it is called partial arthroplasty.
For example, a hip joint that is affected by osteoarthritis may be replaced entirely with a prosthetic hip by replacing both the acetabulum and the head and neck of the femur.
How Total Joint Replacement is Done?
The surgery is performed in a hospital which well equipped for performing these types of surgeries. The patient undergoes pre-anesthetic work-up to determine his or her fitness for surgery and to gauge the risk involved during and after the procedure. Patients with known diseases like heart diseases, stroke, venous thromboembolism, pneumonia and urinary tract infection are at increased risk.
During the surgery, the damaged cartilage and bone is removed from the joint and replaced with prosthetic components made of metal, plastic, or ceramic. The prosthesis mimics the shape and movement of a natural joint.
For example, in an arthritic hip, the upper end of the femur is replaced with a metal ball attached to a metal stem that is fitted into the femur, and a plastic socket is implanted into the pelvis, replacing the damaged socket.
There are two broad divisions of implants in joint replacement surgery. The implant can be fixed with cement or is press fit in which case it is cementless.
Cement forms a bond with the bone strong enough to transmit the loads easily. In the case of a cementless prosthesis, the bone needs to be allowed to grow into the implant.
After the procedure and immediate postop care, mobilization is begun early. It is done as soon as the patient is able to tolerate ambulation with walking aids.
The time of stay in the hospital varies from one day to two weeks. The duration depends on the joint involved and the patient’s preoperative health status.
On an average, the patient spends 4–7 days in the hospital.
Though ambulation is started as soon as possible, the gaining of the complete function takes a longer time, and the patient requires physiotherapy and rehabilitation exercises. These include a range of motion exercises and strengthening exercises.
Joint replacement surgery is kind of resurfacing of the damaged joint and relies on the patient’s muscles and ligaments for support and function
The three most common joint replacement surgeries are hip, knee, and shoulder.
Indications
Various conditions can cause joint pain and disability of the disease causes patients to consider joint replacement surgery. In many cases, joint pain is caused by damage to the articular cartilage—either from arthritis, a fracture, or another condition.
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Avascular Necrosis
- Congenital Hip dysplasia
- Acetabular dysplasia
- Joint Ankylosis
- Secondary Arthritis
- Severe Joint Injuries
Candidates for joint replacement surgery often have severe joint pain, stiffness, limping, muscle weakness, limitation of motion, and swelling. Depending on the joint affected and the amount of damage, ordinary activities such as walking, putting on socks and shoes, getting into and out of cars, and climbing stairs may become difficult.
Complications of Joint Replacement
Early Complications
- Component malpositioning – Inaccurate anteversion, eccentric positioning, improper implant length, inadequate fixation leading to instability.
- Fracture of the adjacent bone
- Neurovascular damage
Immediate Complications
- Infection – Prosthetic infection is an uncommon complication but quite a serious one.
- Dislocation of the joint
- Deep Vein Thrombosis
Late Complications
- Dislocation
- Implant loosening
- Joint stiffness
- Muscle weakness
- Persistent infection
- Joint debris due to wear and tear of implant
Hip Joint Replacement
Total hip replacement is a surgical procedure for replacing the hip socket called acetabulum and the head of the femur. The surgeon resurfaces the socket and ball where cartilage and bone have been lost. An artificial ball and socket are then implanted into healthy bone.
Hip surgery is most commonly performed for arthritic changes. The surgery is considered when other means of treatment have stopped helping the patient and activities of daily living are affected by the condition.
Hip joint replacement is also performed for femoral neck fractures in persons older than 65 years.
After the surgery, most of the patients can be allowed to stand at their bedside on the first day after surgery and can begin exercising. Patients are allowed to walk with aid by the second day or third day. In the case of some intraoperative complication or poor tolerance by the patient, the walking may be delayed.
Gradually the aids are reduced and the patient is advised to walk with a cane for 6-12 weeks. Thereafter, the person can stop using the cane or walker. Patients with weaker muscles may need to use the cane or walker for a longer period.
Patients with successful hip replacements can walk, ride bicycles, ski, play golf and perform other, similar activities. However, activities that transmit high load like athletic sports should be avoided.
Most the hip joint prostheses last for 15 to 20 years or more.
Knee Joint Replacement
Knee joint replacement surgery is performed to treat advanced e arthritis which has progressed to a point that it is not being helped by medical treatment, and the deformity and/or pain are affecting activities of daily living.
In knee joint replacement surgery, the articular bone is cut on both the femoral side and tibial side and replaced by the prosthesis. In some surgeries, articular surface of the patella is also removed.
Most patients who undergo total knee surgery experience a dramatic improvement within 3 months of the surgery. The pain caused by the damaged knee is relieved when a new gliding surface is constructed. Patients who have knee replacement surgery are usually standing and moving the joint the day after surgery. After about 6 weeks, most patients are walking comfortably with minimal support, however, it may take 6 months to 1 year before the optimal benefit is achieved. After muscle strength is restored, patients who have knee replacement surgery can enjoy most activities (except running and jumping).
When knee replacement procedures were first performed in the early 1970s, it was thought that the average total knee implant would last approximately 10 years. It is now known that approximately 85 percent of the knee implants will last 20 years. Improvements in surgical techniques, prosthetic designs, bearing surfaces and fixation methods may allow these implants to last even longer.
Shoulder Joint
Total shoulder joint replacement is indicated in following conditions
- Arthritis
- Severe trauma
Similar to hip, the shoulder joint is ball and socket joint and the shoulder joint replacement surgery consists of replacing the glenoid cup and humeral head with a prosthesis. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty is also known where ball like prosthesis is put on the glenoid side and cup-like is put on the humeral side.
The outcome of shoulder joint replacement is very much determined by meticulous exercises to stretch and strengthen muscles.
It may take 6 months to 1 year to achieve the optimal benefit.
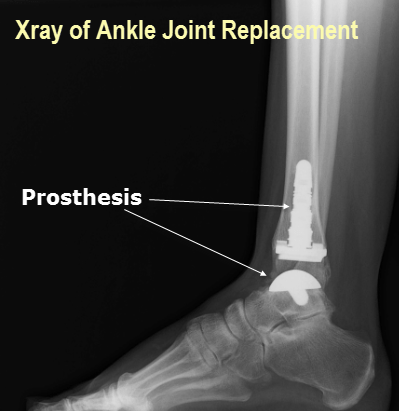
Ankle
In the ankle, joint replacement is done in cases of arthritic changes in ankle following disease or trauma.
Ankle joint replacement provides a pain-free, stable ankle joint.
The patient is kept non weight-bearing for a few weeks. Weight-bearing is started when x-rays show good healing.
Elbow
Elbow joint is not replaced that frequently but may be required in unsalvagable trauma or rheumatoid arthritis.
The replacement of elbow joint involves changing of three component
- Humeral component
- Radial head
- Ulnar component
Some forms of elbow arthroplasty change only humeral and ulnar component.
Following video explains more about elbow joint replacement.
The surgery is followed by mobilization and physiotherapy to regain the elbow movements.
Future of Joint Replacement Surgery
The research is on to find a material which has properties as similar as a bone so that patient, after surgery has near normal experience. The use of computer-assisted techniques would provide more accuracy and precision for better placement of prostheses.
Gender-specific implants and permanently antibacterial implants are also expected to arrive.
Last edited: 17/12/2018