Last Updated on November 12, 2019
Hand pain could be due to many causes many causes, including injury and disease. Fortunately, many of those causes can be treated and the symptoms eased.
Here are some of the most common conditions that cause hand pain. But first an overview of the anatomy of hand.
Anatomy of Hand

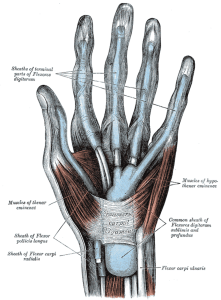
Each hand contains 27 distinct bones that give the hand a range and precision of motion. Most of the hand muscles originate from lateral and medial epicondyles of humerus, and forearm bones.
Distal surfaces of carpal bones, articulate with the metacarpal bones and held by the palmar carpometacarpal ligaments.
Metacarpals are five in number. Each metacarpal is numbered I to V with metacarpal I connecting to the bones of the thumb, II connecting to the index finger, III connecting to the ring finger, and so on.
The distal head of the metacarpals is rounded to form a condyloid (oval) joint with the phalanges of the fingers.
There are three phalanges in each digit except for the thumbs that contain only. Phalanges that articulate with the metacarpals at the base of the digits are known as the proximal phalanges.
Muscles in the forearms flex and extend the phalanges by pulling on long tendons that run through the wrist and hand.
Dorsally, on the distal ends, phalanges bear nails.
The hand has got two surfaces, palmar surface [side of the palm] and dorsal surface.
Causes of Hand Pain
Arthritis
All type of arthritides can affect hand as well. Arthritis leads to the destruction of cartilage leading to painful joints. Most common areas affected with arthritis are base of the thumb, interphalangeal joints. Different forms of arthritis affect different regions of the hand.
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis and often affects the base of the thumb and interphalangeal joints making the joints painful and swollen.
It becomes difficult to perform manual tasks such as writing, opening jars or turning keys.
[Read more about osteoarthritis]
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that can affect the wrist and joints of hand as well.
Psoriatic arthritis is another form of arthritis which is associated with the disease psoriasis.
Crystal deposition diseases like gout and pseudogout may also affect the hand and cause arthropathy.
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
De Quervain tenosynovitis is a tenosynovitis of the tendons within the first extensor compartment at the wrist resulting in pain during thumb motion.
De Quervain syndrome is thought to be a repetitive strain injury especially in repeated postures where the thumb is held in abduction and extension to be predisposing factors. Repeated pinching, grasping, pulling or pushing have been considered at increased risk. Intensive mouse/trackball use and typing have also been implicated. Bowling, golf and fly-fishing, piano-playing, and sewing and knitting have associated.
Extensor retinaculum, over the radial styloid, makes a tunnel through which tendons of abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis pass. When tendons thicken from acute or repetitive injury, the gliding of tendons is restrained resulting in pain.
The sheath surrounding the tendon becomes swollen and thick, and moving your thumb will be very painful.
De Quervain’s tendinitis may develop gradually or suddenly. Movements like making a fist, grasping or holding objects or turning the wrist can be difficult.
The pain results from swelling of the wrist tendons at the base of the thumb, which is caused by irritation or inflammation. Repetitive activities and overuse are often responsible for the onset of de Quervain’s.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that occurs because of compression of the median nerve in the wrist and results in pain, numbness and a tingling sensation in the hand and fingers. The median nerve passes through the carpal tunnel which is a narrow space where it can get compressed.
Injuries
The hand is the terminal organ of the upper limb and is prone to get injured to cuts, crushes, fractures, burns, and bites.
A fracture, or a break in a bone, can cause a great deal of hand pain.
A sprain is an injury to a ligament is called a sprain.
Tenosynovitis
Tenosynovitis is pain and inflammation of the sheath that surrounds a tendon. It’s a relatively rare cause of hand pain that can affect the wrist or the fingers.
The cause is not always known. It may be brought on by a series of small injuries to the tendon, a previous injury or strain, infection, or rheumatoid arthritis.
Ganglion
A ganglion is a fluid-filled swelling that develops near a joint or a tendon. It usually appears on the dorsal side of the wrist but can be seen in tendon sheaths of thumb or fingers as well.
Size of the ganglion varies, it is a smooth, soft lump under the skin that contains thick, jelly-like fluid, called synovial fluid and often communicates with the joint of the wrist.
Most of the ganglions are painless but they can often become painful.
Trigger Finger or Thumb
Trigger thumb or finger usually occurs after middle age but can be congenital also. Both are different entities.
In congenital trigger thumb, the child is brought during early months or years because the child does not extend the involved digit and keeps it flexed.

Adult trigger thumb or finger is a condition in which a finger catches or becomes locked when you try to straighten or bend it. Women get the condition more often than men do. And trigger finger is more common in adults between ages 40 and 60.
It develops gradually. When the person forces the motion on the finger, it snaps quickly. It is a form of a stenosing tenosynovitis which usually affects the thumb or ring finger, though it can affect any finger.
Dupuytren’s Contracture
Dupuytren’s contracture is a localized formation of scar tissue beneath the skin of the palm of the hand leading to flexion of digits. Usually, it is painless but pain may occur in some cases.
Peripheral Vascular Disease
Peripheral vascular disease refers to diseases of the arteries and veins located outside the heart and. There are many types of peripheral vascular diseases and could be a cause of hand pain.
Hand infections
Hand infections can vary from minor boil to osteomyelitis. Nail bed, pulp spaces and various compartment of the hand can harbor the infection. Hand infections could be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Thoracic outlet syndrome is a condition where symptoms are produced from compression of nerves or blood vessels because these get compressed in the thoracic outlet. There is radiating pain that involves the hand as well.
Diagnosis of Hand Pain
Most of the issue are minor and hardly require investigations and work up.
In other cases, lab investigations and imaging may be required.
Lab Studies
CBC, ESR, C-reactive protein are markers of inflammation and could also suggest the presence of infection when correlated clinically. RF, anti-CCP are done in cases of suspected rheumatoid arthritis cases.
Other special investigations as required can vary from case to case.
Imaging
Xrays are basic imaging study and are very useful in showing bony changes such as in osteomyelitis, bone tumors, fractures, and dislocations.
CT is able to show bony details in greater detail. MRI is useful in soft tissue involvement and is able to show lesions where x-rays could be passed as normal.
Treatment of Hand Pain
Treatment of hand pain depends on the cause. Minor injuries and minor pains a could be managed at home with rest, fomentation and over the counter pain drugs
Following are the treatment modalities which are used in hand pain treatment. Treatments are discussed in greater details in the in-depth articles for individual disorders.
- Rest to the hand and wrist
- Anti-inflammatory or analgesic painkillers
- Drugs specific to the ailment, like anti-gout drugs or disease-modifying anti rheumatoid drugs
- Wrist splints
- Steroid injection
- Physical therapy
- Surgery
