Last Updated on August 29, 2021
Different modalities of imaging in spinal disorders play an important role in In modern spine practice. Imaging has a pivotal role in the diagnosis and treatment of the lesion. In this article, we discuss various modalities of imaging of spine disorders.
X-rays


Conventional plain film radiography initiates the investigation of any suspected spinal pathology. X-ray is the basic investigation, not that sensitive albeit.
X-ray has a very important role in the trauma of the spine intra-operative fluoroscopic assistance.
For other lesions, it is an investigation that catches the lesions late in the stage. Still, it is the first investigation and if does not catch the expected pathology, a better imaging modality may be used.
It is a quick, not expensive and widely available investigation.
Anteroposterior and lateral projections are obtained and collimated views of the region of interest if required. Supplementary oblique views may be necessary to show the intervertebral foramina in the cervical region and the pars interarticularis in the lumbar region. Stability of the cervical or lumbar spine may be studied by lateral views in flexion and extension.

X-rays should be studies for the following elements
- The alignment of vertebrae
- Saggital and coronal plane
- Note the presence of kyphosis or scoliosis should be noted.
- Straightening of the spine may occur due to paraspinal muscle spasm.
- Presence of subluxation or dislocation are noted in trauma patients by a break in the continuity of the posterior spinal or spinolaminar line
- Vertebral deformities
- Congenital vertebral malformation
- Traumatic compression
- Postinfectious vertebral deformity
- Spina bifida
- Variations of anatomy
- Presence of transitional vertebrae
- Sacralization
- Occipitalization of the atlas
- Basilar invagination or platybasia should be excluded
- Spondylolisthesis
- Subluxation and Dislocation
- The craniovertebral Junction
- Atlantoaxial subluxation and dislocation is diagnosed when the atlantoaxial joint space is more than 2.5mm in adults and more than 5mm in the child.
- Vertebral destruction and collapse
- Trauma
- Infection
- Tumors
- Paravertebral soft tissue abscess
- Widening of the retropharyngeal or retro tracheal space in cervical spine indicate soft tissue swelling
- Reduced bone density
- Osteoporosis
- Multiple myeloma
- Hyperparathyroid
- Bone Sclerosis
- Metastases from the prostate, breast, and neuroblastoma
- Neural Arch Lesion
- Osteoblastoma, osteoid osteoma and aneurysmal bone cyst
- Widening of the spinal canal
- Intraspinal masses
- Widening of the intervertebral foramina
- Neurogenic tumors.

Thus the information obtained from plain films may provide a roadmap for further workup of the suspected spinal pathology.
CT Spine

Computed tomography has a crucial role in the radiographic evaluation of the spine and its contents especially in trauma and tumors of the spine.
Visualization of the dura and extradural segments of nerve roots and vessels is facilitated where the epidural fat is relatively thick, due to the different CT attenuation values and hence better contrast as is usual in the high cervical, lumbar and sacral region.
The spinal cord and subarachnoid masses of similar density can be discriminated if they are more than 2.5mm in diameter and separated by 2.0mm channel of cerebrospinal fluid.
The cervical cord is usually demonstrated but the thoracic cord is not shown optimally without intrathecal water-soluble contrast medium.
All the images of the CT scan should be viewed with two types of windowing.
- A narrow window to increase the contrast resolution in the soft tissue i.e. the intervertebral discs, thecal sac, and spinal canal contents
- A wide window better demonstrates the bony structures
Intravenous injection of contrast is required except in cases where a bone or neurogenic tumor, infection or vascular malformation is suspected.
CT is superior to MRI in the visualization of bony anatomy and details of bony lesions. Due to higher spatial resolution, CT is also superior to plain films in the evaluation of bony detail. Thus, vertebral fusions, segmentation anomalies like block vertebrae and hemivertebrae can be seen.
The neural arches can be evaluated free of overlap.
Spinal dysraphism and the degree of spina bifida can be assessed in congenital cases,
CT is particularly useful in spinal trauma – linear vertebral fractures, wedge compression fractures, and fractures of neural arches are well evaluated.
Any bony fragments displaced into the spinal canal are visualized in cases of comminuted fractures.
The craniovertebral junction can be evaluated in trauma patients for atlantoaxial dislocation, fractures, and whiplash injuries.
Basilar invagination, occipitalization or platybasia can be excluded in congenital cases as the software is capable of linear and angle measurements.
Multiplanar reformatted images in the sagittal, coronal and oblique planes may be obtained from axial sections.
3D imaging can also be obtained from contiguous or overlapping thin sections and better demonstrate bony displacements as bony fragments within the spinal canal and fracture of articular facets not seen on axial images.
Congenital malformations of the spine like scoliosis, infections, tumors, postoperative spinal fusions; degenerative changes [spinal canal stenosis or lateral recess stenosis] and disc herniation [extruded or sequestrated fragments] are also important indications for 3D imaging and multiplanar reconstructions.
For the study of degenerative disc herniation, axial sections are oriented parallel to the disc and performed at each level from the pedicle above to the pedicle below.
Axial sections should include the level of suspected disc herniation as well as the levels above and below, contiguous 3-5mm thick sections are used in the lumbar spine and thin 1 to 2 mm sections are taken in the cervical spine. Thus posterocentral, posterolateral, foraminal and migrated or sequestered disc can be visualized.
The spinal canal can be assessed for canal stenosis by measuring the AP diameter at mid-body level.
In spinal infections, the vertebral and disc destruction and any bone debris in the spinal canal compressing the cord are demonstrated. Extradural and paravertebral erosion and enlargement of the neural foramen can be well seen in neurogenic tumors. The neural arches are better evaluated on CT.
Subtle lytic erosions or sclerotic deposits in metastatic disease missed on plain films are detected on CT examinations.
Sclerosis and expansion of the affected neural arch in osteoblastoma and the low-density nidus with or without a sclerotic center in osteoid osteoma are better evident on CT than plain films.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging [MRI]
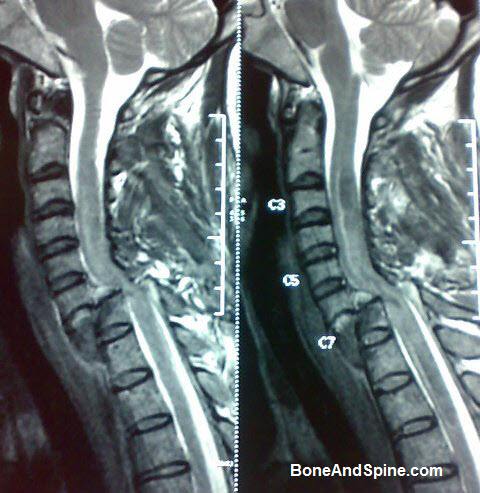
Magnetic Resonance Imaging or MRI, since inception, has completely changed the workup of a patient with any suspected spinal pathology. It has progressed to become the modality of choice in the evaluation of spinal disorders.
MRI scores over other modalities as it is not only non-invasive does not have radiation but it also provides direct visualization and distinction between cord, subarachnoid spaces and epidural structures without the need for any intrathecal contrast.
The limitations of MRI are the patients with an aneurysmal clip, on life-saving equipment with the ferromagnetic foreign body, on insulin pump cannot be taken up for the study. Another disadvantage of MRI is, the bony and calcified lesions cannot be evaluated with high sensitivity.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging is the modality of choice for any suspected spinal pathology including the spinal trauma.
Characteristic features of MRI in different pathologies are given below
Spinal Dysraphism
Spinal dysraphism designates a heterogeneous group of spinal anomalies with the common feature of imperfect fusion of midline mesenchymal, bony and neural structures.
Scans obtained in sagittal and axial/ paraxial plain demonstrate precise regional structural contours and allows distinction between the spinal cord, nerve root, spinal fluid, fat and soft tissues. It also permits distinction between normal tissues and abnormal parenchymas such as tumor and syrinx. Such a distinction is best demonstrated on T1W images. MRI alone can localize and characterize the anatomical alterations associated with spinal dysraphism and can also exclude the presence of surgically remedial spinal dysraphism.
MRI is additionally important because of the demonstrably beneficial results of an anticipatory neurosurgical approach to both the repair of the dysraphic lesion and to the repair of tethering occurring at the site of initial repair.
Syringomyelia
By virtue of direct demonstration of the cord and direct sagittal scan availability, not only the diagnosis can be made easily but also the entire extent of the syrinx can be easily demonstrated on T1W images. It also rules out any underlying cause of the syrinx and associated Arnold Chiari malformation.
Trauma
MRI is the recommended imaging modality for evaluation of spinal trauma. This is the only modality which can demonstrate simultaneously the malalignment or fracture of the vertebral bodies, pre/paravertebral or epidural collection, the extent of cord compression, the traumatic disc herniation and neural and soft tissue changes. The integrity of the cord, the extent of cord contusion is best demonstrated by MRI on which depends the planning of management as well as the outcome.
In the acute stage, MRI imaging permits the visualization of changes in the traumatized cord. Any retro pulsed bone fragment or disc fragment impinging upon the cord can be well shown on MRI. In cases of the penetrating injury, the acute transaction of the cord may be well demonstrated on sagittal and/or coronal scan
In the chronic stage, MRI can demonstrate intramedullary cysts, myelomalacia, cord atrophy or adhesions.
Vascular Lesions
MRI can demonstrate the abnormal vascular flow as areas of the signal void within the subarachnoid, subdural and epidural/paravertebral spaces of the spinal cord.
It can demonstrate the areas of subacute and chronic hemorrhage. MRI is highly sensitive as well as specific in the evaluation of vascular lesions.
The capability of MRI to assess the spinal cord parenchyma allows for morphological correlation with the clinical findings to diagnose cord infarction.
In the early stage, the infarct gives a high signal on T2W images in the anterior horns bilaterally generating an “owl eye” appearance. With the progression of the disease high signal spreads to the dorsal horns and then to the lateral fasciculi.
Progression of the cord signal intensity appears to correlate with a decline in the patient’s conditions. In later stages, cord atrophy evolves and abnormal signal in the cord is the result of myelomalacia.
Infections
MRI is extremely useful in the evaluation of infective lesions of the spine irrespective of the type of infective organism. It allows early detection, improved specificity and provides additional anatomic information about the epidural extension and involvement of the thecal sac.
Increase in signal intensity on T2W images in infection helps in early detection before conventional radiography becomes positive. The effect on the cord, the extent of extradural compression and associated pre/ paravertebral collection can be well seen on MRI. The changes and the effect of the disease process on the cord help in deciding about the management.
An epidural abscess can be easily and confidently demonstrated on MRI However, signal intensity changes in epidural abscess are variable and they may not always display the increased signal intensity on T2W images.
Intramedullary tuberculomas which were considered to be very uncommon and were earlier diagnosed on operation table or in the mortuary can be diagnosed with high sensitivity and specificity by MRI. MRI with paramagnetic contrast material may be very helpful in the evaluation of these lesions. Intramedullary tuberculomas follow the signal intensity patterns of cranial parenchymal tuberculomas.
Disc Herniations
Disc diseases are the commonest spinal disorders and are resulting in heavy work hour losses due to the morbidity caused by them. Disc herniation and disc degeneration are commonest in the lumbar region followed by cervical region.
In the absence of a well defined clinical level of myelopathy MRI is the examination of choice. MRI examination is the modality
of choice for any suspected disc herniation as it not only tells us the status of the disc but also tells us the extent of herniation and the compression over the nerve root and or the cord/conus/filum terminale.
MR imaging is the modality of choice. It displays in an excellent way the relationship between the disc herniation, the subarachnoid space, and the spinal cord.
MRI scores over all other modalities in the evaluation of failed back surgery syndrome. Contrast MRI is advised in the evaluation of all these patients.
Spinal Tumors
MRI is single most informative and complete modality for the diagnosis of spinal cord tumors. It shows precise definition, location, and extent of the tumor. Spinal tumors can occur in any of the three compartments: the extradural, the intradural extramedullary and intramedullary.
In extramedullary space, metastatic deposits are the commonest tumors.
In intradural extramedullary space neurofibroma, schwannomas and meningioma are the common tumors. The first two may be difficult to differentiate from each other on MRI.
The commonest intramedullary tumors are gliomas and ependymomas. In the intramedullary space, MRI has proved far superior to myelography and post myelo CT [both of them are not used commonly now]. Subtle cord enlargement which was difficult to detect with older techniques is picked up easily on MRI.
Nuclear Imaging: PET and SPECT Scans
PET Scans (Positron Emission Tomography) and SPECT Scans (Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography) are non-invasive imaging techniques which use small amounts of radionuclides (radioactive isotopes) to measure cellular/tissue change.
These radionuclides are absorbed by the healthy tissue at a different rate than tissue undergoing a disease process.
These are able to gauge the function of the tissue in comparison to other imaging modalities like MRI which take a snapshot of anatomy only.
Women who are pregnant are not able to undergo PET or SPECT Scanning because of the radioactive isotopes used.
PET Scans
A PET image can do the following
- Map the biological function of an organ
- Detect subtle metabolic changes
- Determine if a disease is active or dormant
- Tell if the lesion is benign or malignant (
- Stage certain types of cancer.
The test begins with the injection of a radionuclide (tracer) specific to the function/metabolism to be investigated. Within a short period of time, the tracer collects in the specific body area and images are taken. The data is analyzed by a computer to produce cross-sectional images.
A PET Scan is an expensive test. It requires sophisticated computer equipment, a cyclotron, and highly trained specialists. A cyclotron is a machine – an accelerator that propels charged particles.
SPECT Scan
A SPECT scan can provide information about blood flow to tissue. It is used to detect stress fracture, spondylosis, infection (e.g. discitis), and tumor (e.g. osteoid osteoma).
The principle is similar to PET Scan and a radionuclide is injected intravenously, absorbed by the tissues and imaged after computer analysis.