Last Updated on December 7, 2023
An interfragmentary screw or lag screw is the screw that is used to compress fracture fragments. The screw is placed perpendicular to the fracture after it has been reduced and drilled in a way that while it engages the distal cortex, it just slides through the hole in the near cortex.
As the screw is tightened, the screw head abuts the near cortex resulting in pulling the distal cortex and thus compressing the fracture fragments.
Where is Interfragmentary Screw Used?
An interfragmentary screw or lag screw is used in the following situations
- Spiral or oblique fractures of the shaft of a bone
- As an adjunct to plating
- Often as an initial fixation holder to secure application of a plate in a neutral mode in the reduced fracture.
- Fixation of osteotomies
In a spiral fracture, one may need to use more than one screw across a fracture site so that fractured fragments are apposed and compressed to each other. The resultant compression is called interfragmentary compression.
The interfragmentary screw is put in a direction perpendicular to the fracture. Therefore in case of a spiral fracture, the screw direction may vary as the fracture plane changes.
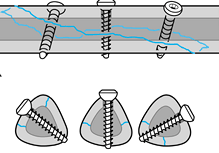
Image Credit:Muller ME, Allgower M. Schneider RW, 30. et al: Manual of Internal Fixation. New York. Springer- Verlag, 1979.
Types of Interfragmentary Screws
Compressing two objects together is sometimes termed lagging. The screw is a means of compressing objects together. In bone fracture fixation, stabilization of fragments provides a basis for early mobilization of the limb and will prevent excessive movement of metal implants which could lead to failure through metal fatigue.
Interfragmentary screws can achieve a lag effect in the bone in two ways:
- They can be designed specifically as lag screws. These screws are partially threaded so that the threads engage only the distal cortex. As there is no engagement in the near cortex because of the lack of threads, there is no need for overdrilling in the case of these screws. These types of screws are often used as lag screws in cancellous bone fractures.
- A fully threaded screw can be used as a lag screw by making the drill hole size larger in the proximal fragment so that threads passing through it do not take hold in the proximal fragment. The screw holds in the distal fragment and causes compression.
Technique of Interfragmentary Screw Placement
When a fully threaded screw is to be used as an interfragmentary screw, we require drilling a hole as big as the screw thread diameter so that screw can glide. This is achieved by drilling a bigger diameter using a suitable bit, and is called a glide hole.
However, in the far cortex, the screw thread needs to engage the bone, and an appropriate hole is drilled for that purpose. This is called a threaded hole and has a hole diameter equal to the core diameter of the screw (not the thread diameter).
One of the ways to achieve this is to drill both cortices with the thread hole-sized drill and then overdrill the near cortex.
Another method is to drill the gliding hole and drill the far cortex through a drill sleeve to keep both holes aligned.
One of these methods i described below
- Fracture is reduced and held temporarily with reduction forceps and or K-wires
- A hole is drilled in the near cortex (gliding hole)
- The drill bit needs to be oversized (equal to the outer diameter of the screw) than the drill in far cortex so that screw just glides and compresses two surfaces of fracture.
- Far cortex** should not be drilled with this drill bit.
- Insert a drill sleeve into the over-drilled cortex. Use an appropriately sized drill bit to drill the far cortex
- Tap the bone using an appropriately sized tapper
- Use a screw length to allow the screw to protrude 2 mm beyond the far cortex
**Note- The bone is like a hollow cylinder. The shell of the cylinder is the cortex and the empty hollow is the medulla. When drilling one would encounter bone [or near cortex)followed by the relatively empty feeling of medulla followed by striking the bony surface from within on the other side {far cortex} in the path of the drilling.
Lag screw fixation of an oblique or spiral fracture requires neutralization by a plate if sufficient stability is to be achieved to allow immediate rehabilitation without external protection.
Lagging as a means of fixing bone is a very powerful technique and great forces of compression can be generated. It is essential to position interfragmentary screws accurately so that the forces they generate are evenly distributed across fractures, otherwise, distortion of reduction can occur