Last Updated on July 31, 2019
Patellar translation is the distance between tibial tubercle and trochlear groove and is also called TT-TG distance. It is measured on CT or MRI by overlapping or superimposing axial images of the femoral condyles and tibial tuberosity.
The measurements are used to quantify patellar instability.
The position of the tibial tubercle is crucial for the inferolateral force vector of the patella [a force that acts on inferior and lateral direction].
In a normal joint, the tibial tuberosity lies vertically under the femoral sulcus, directing the force vector inferiorly during knee bending.
But if there is if there is excessive lateralization of the tibial tuberosity, the patella is pulled laterally during flexion as the tuberosity is lateral and thus pull would also be.
If this is the cause of patellar instability, realignment of tibial tuberosity may help the patient with patellar instability.
Method of Measurement of TT-TG distance
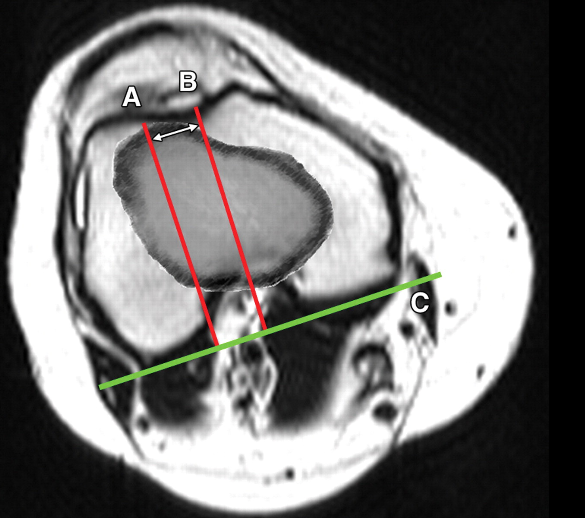
?For calculation of patellar translation or TT TG distance, axial images of tibia with tibial tuberosity are taken. Axial images of femoral condyle are also taken.
Then axial images of femoral condyles and tibial tuberosity are superimposed.
A line is drawn along the posterior femoral condyles.[line C]
Then two lines are drawn perpendicular to this line. [A and B]
The first line bisects the tibial tuberosity[TT] and the second bisecting the trochlear groove sulcus [TG]
The distance between TT and TG line is TT-TG distance or patellar translation. In the image distance between A and B.
Inference of Patellar Translation
A distance of <15 mm is considered normal,
15-20 mm is considered borderline
a distance >20 mm is considered abnormal. A tibial tubercle–trochlear groove distance of more than 20 mm is nearly always associated with patellar instability
The distance has been shown to be slightly less when measured on MRI than CT.
The measurement of the lateral distance between the tibial tubercle and the trochlear groove is less accurate in individuals with severe trochlear dysplasia as the deepest point of the trochlea cannot be defined.