Last Updated on October 28, 2023
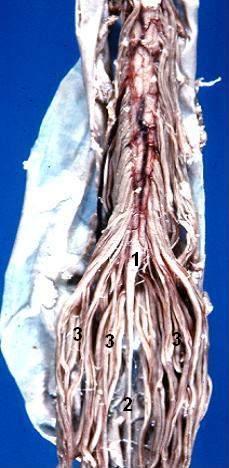
The cauda equina is a structure within the lower end of the spinal column of most vertebrates, that consists of nerve roots and rootlets from above[from second lumbar to coccygeal nerve] which originate in the conus medullaris of the spinal cord.
Cauda equina is named so because it resembles horse’s tail.
In humans, the spinal cord stops growing in infancy but the bones of the spine continue growing. At the birth, the spinal cord ends at L3 level but in adults, it ends at about the level of the vertebra L1/L2. However, there is some variation in adults and the cord may end anywhere between vertebrae T12 to L3.
Individual spinal nerve roots arise from the spinal cord as they do closer to the head, but as the differential growth occurs the top end of the nerve stays attached to the spinal cord and the lower end of the nerve exits the spinal column at its proper level.

This results in a “bundle”-like the structure of nerve fibers that extends caudally from the end of the spinal cord, gradually declining in number further down as individual pairs leave the spinal column.
At the base of the Cauda Equina, there are approximately 10 fiber pairs, 3-5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and the single coccygeal nerve.
All these roots and rootlets down the vertebral column give the appearance of a horse’s tail, which is the meaning of the Latin name cauda equina.
Significance of Cauda Equina
Spinal Tap
Cauda equina is the part of the spinal cord where a lumbar puncture is performed in order to obtain a sample of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for diagnostic purposes. Lumbar puncture.
It is commonly referred to as a “spinal tap” and is usually performed at the L3 or L4 intervertebral level. Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is a serious neurologic condition in which there is an acute loss of function of the neurologic elements (nerve roots) of the spinal canal below the termination (conus) of the spinal cord.
Cauda Equina Syndrome
Cauda equina syndrome is a characteristic pattern of weakness involving the spinal nerves that causes a motor weakness in the lower limb, urinary bladder weakness and typical sensory deficit in the perineal area.
Typical symptoms are back pain, pain radiating to lower limb [unilateral or bilateral], saddle sensory anesthesia.
There would be bladder and bowel dysfunction too.