Last Updated on October 27, 2023
Lumbar spine surgery is a broad term used for any type of surgery in the lumbar spine or the lower back.
[Read more about spine anatomy]
Lumbar spine surgery can be broadly classified into two types
- Lumbar Decompression
- Lumbar fusion
These two comprise the most common type of lumbar surgeries which are most commonly performed on the lumbar spine.
The two procedures could be performed individually or combined. In the latter case, the surgery becomes decompression and fusion surgery.
Conditions Where Lumbar Spine Surgery May Be Required
Lumbar spine surgery may be considered in some cases of [Not all]
- Degenerative Disc Disease
- Disc Herniation
- Lumbar Canal Stenosis
- Spondylolisthesis
- Spinal Injuries
- Infections
- Tumors
- Spinal Deformity – kyphosis and scoliosis
- Congenital Anomalies requiring surgical treatment
Lumbar Decompression Surgeries
As the name indicates, the goal of a decompression surgery is to relieve the offending compression or pressure. In lumbar spine surgery, the goal of a decompression surgery to relieve the compression on the nerves root(s) in lumbar region which lead to pain and other symptoms.
The pain so produced is called radiculopathy or sciatica.
Lumbar Discectomy
It involves removal of the affected disc through a posterior approach. The offending structure is removed which relieves the nerve of the pressure. There are various procedures and techniques for disc removal which differ in the incision length, the approach to the disc and removal of additional structures like lamina.
Laminectomy is a procedure that removes the lamina. Laminectomy has been described in classical discectomy procedure to enlarge the canal but most of the procedures done today make an approach to disc between two laminae and laminectomy is rarely used in discectomy.
Laminotomy is done instead wherever required.
Lumbar Laminotomy
Laminotomy means removal of minimal removal of lamina for enlarging the spinal canal. This surgery is done for lumbar canal stenosis at one level. The stenosis could be central or lateral. Laminotomy for central and lateral stenosis is done when the stenosis is at one level.
Lumbar Laminectomy
This is done in cases of for central and lateral stenosis at several levels and involves removal of the lamina at the desired levels.
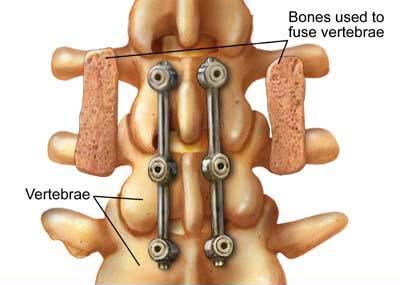
Lumbar Fusion Surgeries
Lumbar fusion surgeries are done with a goal to stop the painful motion segment in the lower back.
This surgery is performed for pain and disability caused by lumbar degenerative disc disease or a spondylolisthesis.
Fusion surgeries require using a bone graft to be put at the site of intended fusion so that it could stimulate bone formation at the fusion site.
When the fusion occurs, a motion of the vertebral segment is stopped which decreases the pain associated with that movement.
The bone graft could be taken from patient’s iliac crest, called autograft or from preserved human bone grafts which are called allograft.
A fusion surgery would sometimes also require the use of a spinal device to fix the mobile segment till the fusion occurs.
Lumbar spine fusion surgeries are named according to the approach to the fusion.
Multilevel fusion surgeries are also done.
Lumbar Spinal Posterolateral Gutter Fusion
This type of spinal fusion involves placing bone graft material in the posterolateral portion of the spine. Bone graft is harvested from the posterior iliac crest.
Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion
After removal of the disc through the posterior approach, a bone graft is directly inserted into the disc space.
Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion
Anterior lumbar interbody fusion is similar to posterior lumbar interbody fusion except that approach is anterior.
Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion
It is a quite popular procedure for lumbar degenerative disk disease, spondylolisthesis, degenerative adult scoliosis, spinal stenosis, and recurrent disk herniation.
The spine is approached posteriorly and the disc is accessed through a far lateral portion of the vertebral foramen. The procedure allows complete removal of the disc and placement of an interbody support transforaminally.
Spine Fusion Instrumentation
Bone tends to fuse better in an environment with as little motion as possible. The role of spine fusion instrumentation is to decrease motion at the segment undergoing fusion and to provide additional spinal stability.
The 3 major types of spine surgery instrumentation are
- Pedicle screws
- Anterior interbody cages
- Posterior lumbar cages.
Newer Procedures In Lumbar Spine Surgery
Motion Preservation Surgeries
In addition to the traditional one-level fusion or decompression surgery that is done for lumbar degenerative disc disease or spinal stenosis, respectively, there are a number of surgical alternatives available.
The hallmark of these newer procedures is the preservation of motion and involve are a wide variety of posterior motion preservation devices which do not cause loss of motion associated with fusion surgeries.
In this regard, lumbar spine treatment is evolving just like hip and knee which already have moved from an era of arthrodesis [loss of motion] to the era of replacement [motion preserved].
These procedures are in various stages of development and clinical trials.
Total Disc Arthroplasty
This procedure has been used for lumbar discogenic pain, with and without radicular symptoms..
Artificial disc replacement has shown results similar to fusion in the short term, but long-term results are not known.
Also in development are nucleus replacement devices, which seek to address discogenic pain by replacing only the disc nucleus while leaving the outer portion of the disc intact.
Read more about disc anatomy.
Posterior Motion Preservation Devices
The pain that originates from the facet joints, ligaments, tendons, or muscles needs different addressal altogether.
These devices can be put into three general categories:
Interspinous Process Spacers.
These devices work by distracting the central canal and foramen,. These are used in spinal stenosis and sometimes in degenerative disc disease.
Posterior Dynamic Stabilization Devices.
This is a kind of internal brace on the spine that allows controlled motion in such a way as to achieve more normal movement of the spine. These devices are typically used to treat patients with spondylolisthesis and degenerative disc disease. These devices are being used for aiding spinal fusion but are not approved for use in a standalone basis yet.
Facet Replacement or Total Element Replacement Devices
These devices are also used for spinal stenosis facet pain by limiting motion limit. As the name indicates, the devices are either for replacement of facets or replace all the elements in the back of the spine.
Vertebral Augmentation Surgeries
These surgeries are done to treat pathological fractures from tumors or osteoporosis.
Vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty are examples of vertebral augmentation surgeries.
Radiofrequency-targeted vertebral augmentation (RF-TVA) is a type of kyphoplasty of recent origin that does not use a balloon and based on filling the cavity with controlled delivery of bone cement after creating a cavity. It theoretically penetrates the small cracks and avoids potential leakage of the bone cement outside of the fractured bone.
There are a number of other vertebral augmentation systems currently in development.