Last Updated on February 4, 2020
Head halter traction or cervical halter is a type of spinal traction used in cervical ailments and injuries. It is similar to skin traction used on the limbs and is based on the same principles.
The head halter traction is provided by using head halter traction devices which produce an effect of stretching the neck vertebrae and muscles.
Head halter traction is usually used for shorter periods owing to the discomfort it can cause.
Therefore, head halter traction is often used to treat problems of the cervical spine that require only short-term immobilization.
How Does Head Halter Traction Work?
Any cervical traction works by stretching the spinal vertebrae and muscles which leads to relief from pain and tightness. Thus it is a kind of stretching of neck tissues.
In the soft tissue injuries of the neck, the traction provides rest to the tissues by limiting the movement.
In cervical spine fractures, it is important to keep the injured vertebrae in alignment because the mobile vertebrae may cause or worsen the injury to the spinal cord. Serious ligamentous injuries to the neck also warrant traction for the same purpose.
Indications and Uses of Head halter Traction
Head halter traction as cervical traction can be used in the following situations
- To relieve neck pain and stiffness in various conditions such as cervical spondylosis
- To relive cervical muscle tightness
- In cervical radiculopathy [pain in the upper limb or upper chest or back] due to cervical disc herniation
- Neck sprains
- As a temporary measure to in cervical injuries while waiting for definitive treatment
How to Use Head Halter Traction?
Head Halter traction devices are of two types
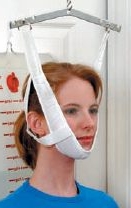
Canvas type is the most commonly used type of head halter traction. It uses placing the respective parts under the chin and occiput bone.
A metal spreader hooks on to the two side pieces to avoid lateral compression of the soft tissues when traction is applied.
A cord from the metal spreader passes over a pulley fixed to the top of the bed or to a stand-in case of traction applied in sitting position.head-halter-traction
The cord is attached to the weights that would provide traction. the maximum weight that can be used is 1.5 – 2.5 kgs.
The head end of the bed must be raised to provide countertraction.
Crile Type uses a padded metal bar resembling horse collar is placed under occiput. Another padded portion that covers the forehead is attached to the one put under the occiput.
Crile type allows chin to be kept free but it is used less commonly than the Canvas type.
Canvas type head halter traction can be used in sitting position and supine position. Injuries of the neck are treated in supine position only.
The angle of pull of the traction should be parallel to the long axis of the body. The traction rope must not be allowed to rub on a high headboard or the mattress.
In the supine position, the head end of should be raised so that body acts as countertraction.
Complications of Head Halter Traction
Chin Pressure
Pain and skin excoriation on the chin are caused by the excessive weight of traction, inadequate padding of the chin strap, or traction pull that is not evenly distributed between the chin strap and the occipital strap.
Roughly speaking, no more than 2.3 kg of weight should be applied to head halter traction.
Excessive pull on the chin can be relieved by changing the direction of the traction rope and apparatus so that more pull is placed on the occipital strap.
The traction should be discontinued temporarily if the pain is persistent.
Occiput Pressure
Pressure on the occiput may cause skin trauma, headaches, or occipital neuritis. Adequate padding can prevent most skin trauma. Occipital headaches are relieved when pressure on the occiput is decreased or the line of pull must be lowered to place more pull on the chin.
Constant dull pain in the occipital area may suggest occipital neuritis. It usually is not relieved by temporary discontinuation of the traction, and the traction may have to be permanently discontinued.
Temporomandibular Joint Pressure
Pain in the temporomandibular area develops when a large amount of weight is used over a long period. The most prominent symptom is pain in the angle of the jaw, often radiating into the ear. The use of a bite block usually relieves temporomandibular pain, but if pain persists, traction should be discontinued.
Other Problems
Mechanical problems include weights resting on the floor, breaking the rope, and tangling the rope in the pulley. Mechanical problems can be prevented by close observation of the traction setup.
When Head Halter Traction should Not be Used?
Uncooperative or patient not able to cooperate are not good candidates for head halter traction. Disoriented or restless patients may be unsuited to this type of cervical traction, and a more rigid traction device may have to be employed.