Last Updated on November 20, 2019
Renal rickets is the term used for rickets where the primary cause is not vitamin D deficiency but a renal disease leading to events that cause rickets or osteomalacia.
Renal rickets is known by various names. Renal dwarfism, renal pseudorickets, and renal osteitis fibrosa cystica are forms of renal-caused rickets or osteomalacia.
Note: Hypophosphatemic rickets which is a group of genetic disorders, and involves malfunction in renal phosphate mechanisms are discussed separately.
Pathophysiology
Renal insufficiency, whether a result of glomerular or tubular disease, is associated with compensatory parathyroid hyperplasia, which deprives the skeleton of calcium.
When the renal factor is present at birth, it is due to congenital cystic disease or congenital hydronephrosis. Later in life chronic glomerulonephritis, chronic interstitial nephritis, and the nephroses due to heavy metal poisoning are etiologic factors.
Congenital kidney conditions have an insidious slowly progressive effect throughout childhood, usually becoming clinically manifest at about puberty or adolescence.
Changes typical of rickets occur and interfere with endochondral ossification at the epiphyseal plates, thereby restricting longitudinal growth.
Renal Disease with Phosphate Retention
Kidney diseases causing retention of nitrogen is almost always associated with the retention of phosphorus.
In patients with chronic kidney disease, there is a high anion gap acidosis due to the retention of anions such as phosphate, sulfate, urate, and hippurate due to reduced glomerular filtration rate. Reduced formation of 1,25(OH)2 D, administration of aluminum, and secondary hyperparathyroidism also contribute.
It leads to a reduction in serum calcium levels because it adjusts to the high serum phosphorus level. The parathyroids glands hypertrophy to excrete more hormone, which acts either by promoting excretion of serum phosphates and by promoting resorption of bone tissue.
Renal Disease with Excessive Phosphate Excretion
Two separate conditions can be distinguished in which tubular function failure results in excessive phosphate excretion.
Renal Tubular Acidosis
Distal tubular acidosis is a disease of defective urinary acidification, which is caused by insufficient net acid excretion by the kidneys.
It leads to the passage of alkaline urine in the presence of systemic metabolic acidosis. Patients are acidotic and dehydrated, with marked hypokalemia but with normal renal excretory function. Acidosis leads to increased bone resorption leading to increased calcium loss in urine.
Decreased serum calcium which leads to a low serum phosphorus level. Low levels of serum calcium and phosphorus cause the failure of mineral deposition in bone. Rickets or osteomalacia develops.
Hypokalemia is common.
Fanconi’s Syndrome.
In Fanconi’s syndrome, the renal tubules fail to absorb phosphates, glucose, and many of the amino acids leading to bicarbonaturia, glucosuria, phosphaturia, uricosuria aminoaciduria, tubular proteinuria marked hypophosphatemia without hypercalcemia.
The mechanism of production of late rickets and osteomalacia seems to be an acidosis due to increased urinary excretion of base secondary to increased urinary excretion of organic acids.
Symptoms of this disorder appear early in childhood and become progressively worse.
Clinical Presentation of Renal Rickets
Clinically, in children before the union of the epiphyses, in addition to bony changes of osteitis fibrosa cystica, changes are seen at the epiphyseal line almost identical with those of rickets. Retardation of longitudinal growth is a constant finding.
In adults, osteomalacia changes are noted.
[Read more on presentation of rickets]
[Read more on presentation of osteomalacia]
Moreover, in adults following findings may be noted
- Longstanding and severe renal insufficiency
- Nitrogen and phosphorus retention
- Normal or slightly low serum calcium level
- Severe acidosis with a low CO2 combining power of the serum
- High serum chloride or low serum sodium level
- Monckeberg type arteriosclerosis (medial arteriosclerosis)
- High serum phosphatase level
- Sometimes calcium deposits around joints
- Generalized skeletal decalcification with a cystic or motheaten appearance seen on x-rays.
Differential diagnosis
Hypophosphatasia
Diagnosis of Renal Rickets
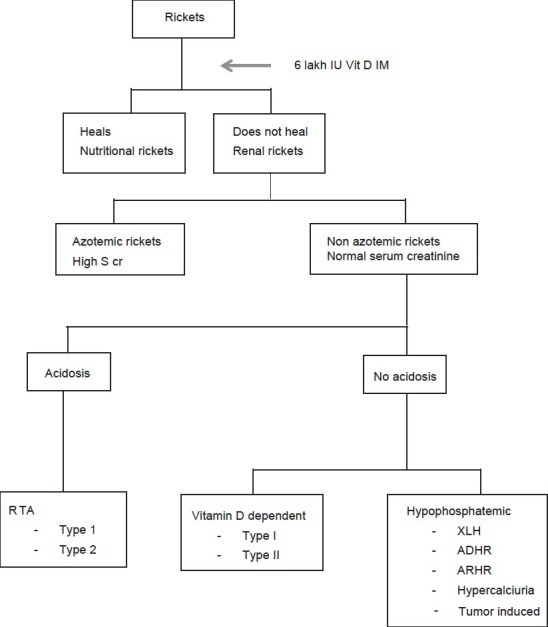
Image Credit: IJEM
Laboratory investigations
- Alkaline phosphatase is raised and is a very good marker of disease activity.
- The serum calcium is usually decreased in nutritional, vitamin D dependent rickets or renal tubular acidosis (RTA) and renal failure rickets [also called calcipenic rickets]. In phosphate deficiency rickets, levels are normal. Serum phosphorus concentrations usually are low in both the types.
- Serum creatinine is raised in renal failure rickets.
- Arterial blood gas analysis shows a high anion gap in renal failure rickets. In all other varieties, the arterial blood gas is normal.
- Urine pH is >5.5 in distal renal tubular acidosis while it is <5.5 in proximal
- A generalized aminoaciduria occurs from hyperparathyroidism. Glycosuria and bicarbonaturia are seen in Fanconi’s syndrome.
- The serum concentration of parathyroid hormone typically is quite raised
- Serum concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25OHD) and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D may be decreases whereas in hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets 1,25(OH)2 D may be elevated
Following is a summary of lab studies.

Treatment of Renal Rickets and Osteomalacia
Deficiency of vitamin D or calcium is addressed if present. The treatment of root cause would reverse the changes in due course.