Last Updated on November 19, 2019
Elbow arthrocentesis refers to puncture of the elbow joint and the aspiration of its synovial fluid. It is used for synovial fluid analysis to aid in diagnosis and also for therapeutic purposes. Analysis of the removed fluid helps to reach at its etiology.
Anatomy of Elbow Joint
Elbow region is the connecting region between arm and forearm. Elbow joint is formed by the lower part of the humerus, radius bone and upper part of the ulna.
Indications of Elbow Arthrocentesis
Diagnosis
- Acute monoarticular [that affects a single joint] arthritis
- Suspected infection in an elbow (eg, septic arthritis)
- Inflammatory elbow joint effusion
- Gout
- Pseudogout
- Rheumatologic disorders
- Reactive arthropathies
Therapeutic
- To relieve a large painful effusion.
- Instillation of medications
- Repeated arthrocentesis for a septic elbow in carefully selected patients as a means of decreasing bacterial load
Contraindications
- Cellulitis in the overlying skin
- Overlying skin lesions (eg, dermatitis or psoriasis)
- Known bacteremia
- Bleeding disorders
- Patient on anticoagulation medication
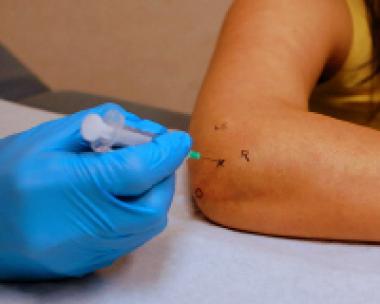
Procedure of Elbow Arthrocentesis
- Place the patient sitting upright on a stretcher. Sedated patients should be in the supine or lateral position.
- Prepare the skin with povidone-iodine solution or chlorhexidine
- Using 1% lignocaine, make a small wheal with a small (25-gauge) needle in the dermis at the determined entry point for aspiration for local anesthesia. Alternatively, a topical vapor coolant, such as ethyl chloride, may be sprayed. Sedation may be used in uncooperative patients but rarely needed.
- With elbow bent to 90 degrees, pronate the patient’s forearm, and rest it with the palm down on a side table.
- Identify the following landmarks. The landmarks may be easier to find if the arm is first extended.
- Olecranon process
- Lateral epicondyle
- Radial head
- Identify the depression [bulge in the large effusion] in the triangle formed by these landmarks. This is the site for entry.
- In smaller effusions, ultrasonography may aid detection of even a small effusion.
- Identify the site of entry, and insert an 18-gauge needle into the depression. It could be done in two ways
- Lateral Approach – The needle is perpendicular to both the skin and radial head from the lateral side. This is the lateral approach and the preferred one.
- Posterolateral approach – Insert the needle perpendicular to the skin but parallel to the radial shaft.
- Advance the needle slowly while aspirating the syringe until synovial fluid is obtained.
- If the aspiration is unsuccessful, draw back, reidentify the landmarks, and correct the needle insertion position. If the bone is encountered, withdraw the needle slightly and redirect it.
- After the procedure is done, remove the needle and dress the puncture site.
- Place the fluid in specimen tubes and send for analysis.
Complications of Elbow Aspiration
- Infection – Rare but occurs due to the introduction of bacteria from the skin.
- Hemarthrosis
- Allergic reaction to the anesthetic agent
- Reaccumulation of the joint fluid.
Read about Synovial Fluid Analysis