Last Updated on May 27, 2019
Intertrochanteric fractures are one of the three types of hip fractures, other two being fractures of the femoral neck and subtrochanteric fractures of femur.
A trochanteric hip fracture occurs along the intertrochanteric line which is the line between the greater trochanter and the lesser trochanter.
Fractures of the femoral neck are proximal or cephalad to trochanteric fractures, and subtrochanteric fractures, are distal to or below the trochanters.
The mean age for this fracture is around 80 years. Osteoporosis and the propensity of older patients to fall are major causes.
In populations >60 years, intertrochanteric fractures occur more than twice as often in women as they do in men.
In the age group between 11 and 60 years, where high energy trauma is the major cause, males sustain more fractures than females.

Relevant Anatomy
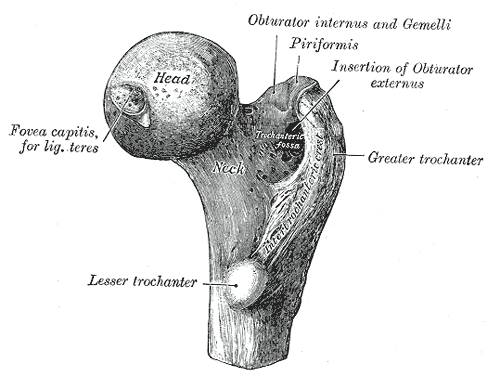
The intertrochanteric area of the femur is distal to the femoral neck and proximal to the femoral shaft.
Broadly speaking it is the region of the femoral trochanters, the lesser and the greater trochanters (see the image below).
It is the region where the femur changes from an essentially vertical bone to a bone angling at a 45° angle to the acetabulum or pelvis.
The femoral artery and nerve are anterior. The sciatic nerve is posterior.
The greater trochanter gives attachment to the gluteus medius and lesser trochanter to the iliopsoas. Their forces contribute to the fracture displacement, depending on the fracture patterns and also hinder the reduction.
The attachment of the gluteus maximus to the lateral femoral shaft is opposite to the posteromedially placed lesser trochanter. This acts as a guide to the level of the lesser trochanter.
The proximal lateral shaft is covered by vastus lateralis which is either cut or elevated for placing the side plate of sliding hip screw implant used in the management of these fractures.
Classification of Intertrochanteric Fractures
For many years, the standard system for classifying intertrochanteric hip fractures was the one devised by Byod and Griffin. They described four fracture types based on the fracture pattern and the amount of comminution
- Nondisplaced intertrochanteric fractures (type I),
- comminuted intertrochanteric fractures (type II) [three part or four part fractures]
- Intertrochanteric fractures with subtrochanteric extension (type III)
- Oblique fractures of the proximal femur (reverse obliquity)
Evans observed that the key to a stable reduction was restoration of posteromedial cortical continuity. He divided intertrochanteric hip fractures into two types differentiated by the status of this anatomic area.
Stable fractures
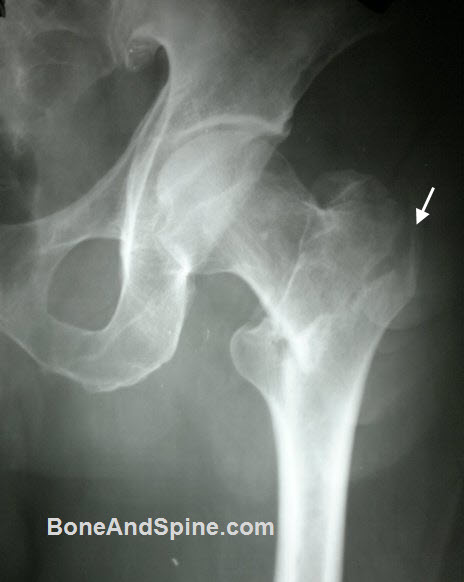
- Intact posteromedial cortex
- Resists medial compressive loads once reduced
Unstable fractures
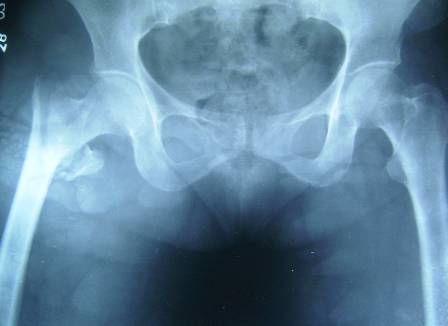
- Comminution of the posteromedial cortex
- Fracture will collapse into varus and retroversion when loaded
- Examples
- Fractures with a large posteromedial fragment i.e., lesser trochanter is displaced
- Subtrochanteric extension
- Reverse obliquity – Oblique fracture line extending from medial cortex both laterally and distally
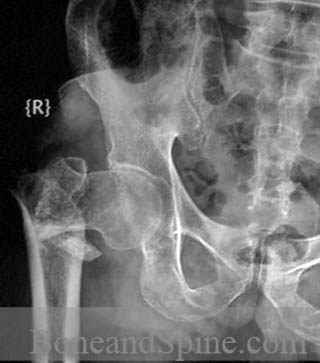
Here is another unstable intertrochanteric fracture
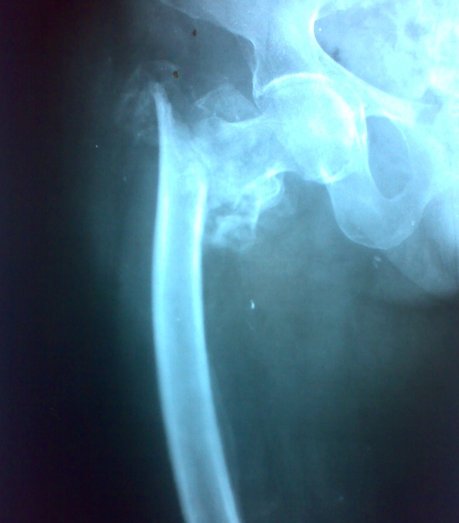
Biomechanics
The stability of an intertrochanteric fracture is defined by the amount of contact between the proximal and distal main fragments. A two-part fracture is very stable because once the two fragments are reduced, they are impacted on each other and provide inherent stability for the implant.
Medial contact is most important. Therefore, in a three-part fracture, the stability of the fracture is inversely proportional to the size of the lesser trochanteric fragment.
Loss of medial contact causes varus collapse and shortening and may also lead to implant failure.
Instability occurs when more than 50% of the calcar is affected. A fracture with a large lesser trochanteric fragment, is, therefore, considered unstable.
Same holds true for four-part fracture where or if the greater and the lesser trochanter are separate.
Broken lateral trochanteric wall, the portion of the greater trochanter that extends from the vastus ridge (the attachment of the vastus lateralis) to the tip of the greater trochanter is another factor for instability.
Fracture of this wall would also lead to the collapse of the fixation and implant cut.
Generally speaking higher the instability, more difficult is reduction and its maintenance.
Stable fractures can be treated with a sliding hip screw–plate device but unstable ones need a cephalomedullary fixation [see below]
Cause of Intertrochanteric Fractures
- Low energy falls in elderly
- High energy trauma in young
In case of low energy fractures, the increased bone fragility of the intertrochanteric area and decreased muscle tone secondary to aging are contributory factors.
Decreased bony fragility in the elderly occurs due to osteoporosis and osteomalacia secondary to
- Lack of sufficient ambulation
- Lack of antigravity activities,
- Decreased hormone levels
- Increased levels of demineralizing hormones
- Decreased intake of calcium or vitamin D
- Aging processes.
A fracture occurs when direct or torsional forces are greater than the strength of the bone in the intertrochanteric area.
Clinical Presentation
Young adults usually present with a history of a motor vehicle accident or some other high energy trauma.
In the elderly, there would be a history of fall either during walking or history of a slip.
The patient would complain of pain in the affected hip.
On examination, there would be a shortened, externally rotated lower extremity.
In young adults, there could be other concomitant injuries present. In elderly, intertrochanteric fractures occur as an isolated injury.
The patient should undergo a complete musculoskeletal examination lest something should be missed.
Elderly patients may have coexisting conditions that might affect the treatment of the fracture. Hypertension, cardiac problems, diabetes are common issue encountered in elderly. Complete medical evaluation should be done
Lab Studies
These are required to evaluate cardiac, laboratory, and pulmonary status.
The studies that may be indicated are
- Complete blood count
- Urinalysis
- Biochemical profile
- Chest radiography
- ECG
Additional tests may be required, depending on the clinical findings, the past and current medical history.
Imaging Studies
AP view of the pelvis including both hips and either a cross-table lateral view or a frog lateral view of the hip. The pelvis radiograph is useful for preoperative planning, particularly to determine the neck-shaft angles for placement of cephalomedullary nails.

In some cases, computed tomography with or without reconstituted images may be necessary.
Treatment of Intertrochanteric Fractures
General Approach
Non-Operative treatment has a very limited role in the management of intertrochanteric fractures.
Closed/open reduction and internal fixation is indicated for all intertrochanteric fractures unless the medical condition makes patient unfit for any kind of anesthesia
Total hip arthroplasty has a limited role in treatment and is still evolving. It could be used in very osteoporotic skeleton or as salvage of failed surgery.
External fixation is a rarely used option for quick fixation in patients who may not tolerate anesthesia.
Surgery may not be done in a patient with a stable, nondisplaced intertrochanteric fracture who can tolerate nonsurgical care and declines surgery for personal reasons. Operative management allows early rehabilitation and offers the patient the best chance for functional recovery.
It is the treatment of choice for almost all intertrochanteric fractures.
The patient with an intertrochanteric fracture is ready to proceed with surgery after the medical or trauma evaluation has been completed and the medical conditions have been stabilized within a reasonable time period.
Non-operative Treatment
Nonoperative treatment is indicated in following cases
- Nonambulatory patients
- High-risk patient
- Patient declines surgery
Before the introduction of suitable fixation devices, treatment for intertrochanteric fractures was nonoperative but now the role of non-operative treatment is very limited to cases who refuse the surgical treatment or are not medically fit for surgery..
Two different approaches are there in non-operative management
The first approach is directed at early mobilization within the limits of the patient’s discomfort. Ambulation is delayed, but the early bed to chair mobilization is allowed to prevent many of the complications of prolonged recumbency.
This approach does not attempt to treat the fracture specifically and accepts the deformity that invariably ensues.
The second approach is to achieve a reasonable reduction via skeletal traction until fracture union occurred. However, in this method too, an acceptable position is difficult to achieve and maintain. Moreover, it poses issues of nursing care.
The first approach is usually preferred when non-operative treatment is chosen as avoiding the complications inherent in prolonged bed rest is more important.

Operative treatment
Fracture reduction and Fixation with Sliding Hip Screw
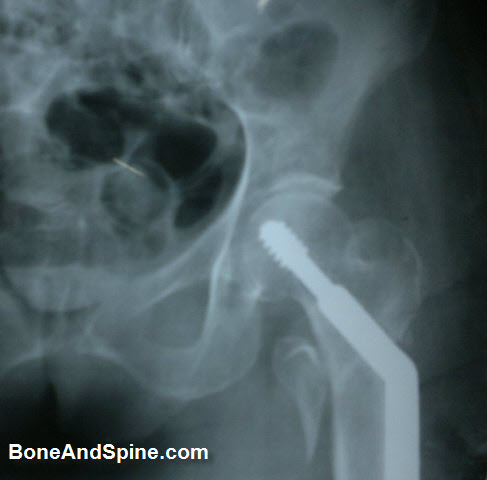
The intertrochanteric fractures are reduced closely or after opening and fixed with a fixation device.
The sliding hip screw is currently the most commonly used implant for stabilization of intertrochanteric fractures. It is a two –piece device consisting of a large diameter cannulated lag screw that articulates within a sideplate and barrel. Sliding hip screws are available with plate angles from 125 degree to 155degree. The 135 degree and 150 degree devices are the most popular.
The goal is to obtain correct neck-shaft relationship and fixation with minimum risk of failure. For this, the reduction and fixation is done under C-arm image intensifier. The screw should be fixed till subchondral bone of the head.
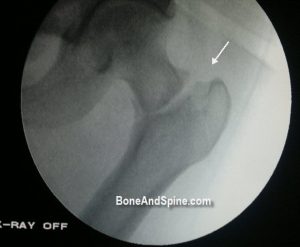
A tip apex distance >25 mm is associated with increased failure rates
Dynamic or sliding hip screw allows dynamic interfragmentary compression and is cost-effective.
But because it is open technique, it is associated with greater tissue trauma and increased blood loss.
It is most useful in stable fracture types and not advisable in unstable fracture patterns where it may result in collapse, limb shortening and medialization of shaft
The need for proximal femoral osteotomies e.g. medial displacement osteotomy [Dimon-Hughston osteotomy], valgus osteotomy[Sarmiento osteotomy] to stabilize unstable intertrochanteric fractures has been largely eliminated since the development of better implants. These osteotomies were commonly used before the advent of the sliding hip screw or cephalo-medullary nail.
However, it provides equal outcomes when compared to intramedullary hip screws for stable fracture patterns.
Cephalomedullary fixation [intramedullary hip screw]
The cephalomedullary nailing technique is a treatment alternative for intertrochanteric fractures.
Cephalomedullary fixation offers the following advantages over the sliding hip screw.
- Helps in reduction of unstable fractures
- Prevents collapse and thus shortening [The nail acts as calcar and lateral wall replacement to support the femoral neck].
- Less blood loss
- Earlier full weight-bearing
However, it is technically demanding and has had a high rate of femoral shaft fractures below the nail tip.
Its use has been steadily increasing in the last decade. Longer implants are available
Arthroplasty
While arthroplasty is accepted standard treatment in fracture neck of femur, hemiarthroplasty and total arthroplasty were reluctantly considered for intertrochanteric fractures due to the loss of bone at the calcar region of the femur and the difficulty of maintaining the proper abductor muscle tension because of fracture of the trochanter attachments of these muscles.

But an improvement in technology is changing that and is increasingly used now.
Long-stem, long- neck, calcar-replacing type is prosthesis is used for replacement in intertrochanteric fractures.
Bone graft of the calcar region may be required to provide the medial support for the prosthesis.
Arthroplasty produces functional results similar to those of compression hip screws or cephalomedullary nails.
It is associated with greater blood loss, longer operating time, and higher cost.
It enables possible earlier return for full weight-bearing
Indications are
- Severely comminuted fractures
- Preexisting symptomatic degenerative arthritis
- Severe osteoporosis which risks failure
- Salvage for failed internal fixation
Post-operative Care
Preventive DT protocol is followed after surgery.
Physical therapy includes muscle strengthening and ambulation training.. Depending on the patient profile walkers, crutches, four-post canes, and other canes may be used.
Complications
Systemic complications can occur as consequences of the anesthesia (general or spinal) used in the procedure and the stress of the surgery on body.
Local complications are mostly because of failure to achieve and maintain fracture reduction.
Local orthopedic complications can occur if an adequate stable reduction of the fracture is not obtained and maintained. Common orthopedic complications are.
Implant failure and cutout

It is the most common complication with the sliding hip screw and usually occurs within the first 3 months. It is often due to greater than prescribed tip-apex distance [broadly speaking distance between the tip of the screw and outer surface of the head. A greater tip apex distance means that screw head has not reached stronger bone part of the head i.e. subchondral bone]
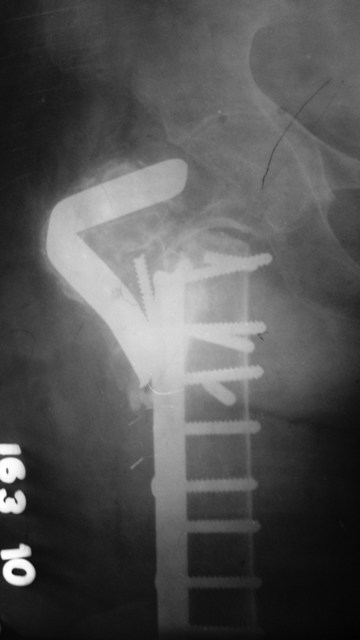
In young patients, corrective osteotomy and/or revision open reduction and internal fixation is done. In elederly, total hip arthroplasty is considered.

Anterior perforation of the distal femur
This can occur following intramedullary screw fixation due to mismatch curvature of the femur and implant.
Nonunion
It occurs in <2% of cases. The treatment is revised fixation with bone grafting. Arthroplasty can be considered in elderly patients.

Malunion
Malunion is more common than non union. Elderly patients tolerate mild to moderate malunion quite well and the decision to treat should not be taken just based on x-rays.
Young patients should be treated with corrective osteotomies
Prognosis
A stable and acceptably fixed intertrochanteric fracture heals quite well.
The activity level usually drops in elderly patients after recovery from this injury. The mortality is 20-30% during the first year.