Last Updated on October 29, 2023
Gonococcal arthritis is caused by Gonococcal bacteria, that cause sexually transmitted disease, Gonorrhoea. Gonococcal arthritis is the most common type of septic arthritis constituting 70 percent of episodes of infectious arthritis in persons under 40 years of age.
Pathophysiology and Etiology
The infection typically results from bacteremia arising from gonococcal infection which may be asymptomatic and unnoticed.
Disseminated infection is thought to play a major role in the pathogenesis of gonococcal arthritis and is said to occur in about 5% cases of gonorrhea.
Females are two to three times more likely than men to develop disseminated gonococcal infection and arthritis. The risk is greatest during the menstrual period and pregnancy. Persons with complement deficiencies, which are needed for defense against gonococci are prone to recurrent episodes of gonococcemia. Persons with iv drug use, HIV infection and multiple sexual partners
There are some organism related factors also related to increased chances of disseminated infection.
Gonococcal infection mostly affects persons aged 15-29 years, however, older adults may be affected. The disease is 3-4 times more common in females than in males.
Presentation of Gonococcal Arthritis
Approximately 60% of patients present with symptoms consistent with the bacteremic form[Dermatitis-arthritis syndrome] and the remaining 40% present with symptoms of more localized infection.
Bacteremic form
In the bacteremic form (arthritis-dermatitis syndrome), migratory arthralgias are the most common presenting which are typically asymmetric and tend to involve the upper extremities more than the lower extremities. The wrist, elbows, ankles, and knees are most commonly affected.
The tenosynovitis most commonly occurs over the dorsum of the wrist and hand, ankles, and knees. Dactylis can occur.
Other symptoms present may be myalgias, fever, malaise, and rashes.
Septic Arthritis Form
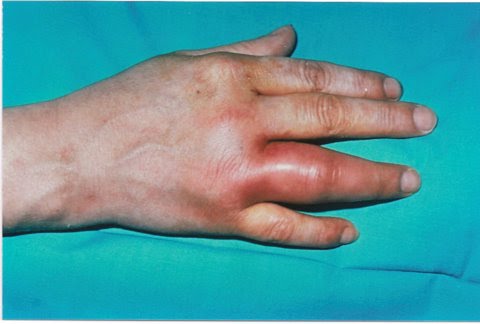
The joint becomes affected within days to weeks of gonococcal infection. Patient presents with pain, redness, and swelling of the affected joint.
It most commonly involves the wrists, hands, knees, and elbows.
Lab Studies
A complete blood count in gonococcal arthritis would reveal mild leucocytosis. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate and CRP would be elevated.
Positive culture results help confirm the diagnosis and provide antibiotic sensitivities for the particular infecting strain of the organism.
Patients should also be tested for other sexually transmitted infections, including HIV, hepatitis B, chlamydia, and syphilis.
Synovial fluid would reveal a higher WBC count [>50,000/microL ]. Synovial fluid cultures are positive for N gonorrhoeae in no more than 50% of cases and alone are insufficient to establish the diagnosis. Cultures of blood, cervix, rectum, urethra, and pharynx should be obtained. Polymerase chain reaction-based assays are extremely sensitive in detecting gonococcal DNA in synovial fluid.
Cervical samples are positive in 90% and male urethral samples in 50-75%.
Nucleic acid amplification tests may be used as an adjunct to cultures and can be performed on samples from the cervix, urethra, rectum, urine, pharynx, synovial fluid, and skin. These tests can help to confirm a diagnosis of DGI when cultures are negative.
Imaging
Plain radiograph would reveal the articular damage if present
Treatment of Gonococcal Arthritis
When septic arthritis is suspected, the patient should be put on empiric antibiotics directed against likely pathogen until confirmation and sensitivity of pathogen are available.
The joint should be put to rest and repeated arthrocentesis is done for drainage. If the patient does not improve then open surgical drainage is considered.
Initial drug treatment of choice for gonococcal arthritis or disseminated gonococcal infection in adults is ceftriaxone iv/im. ceftizoxime 1 g IV every 8 hours and cefotaxime 1 g IV every 8 hours.
After, 48 hours At this time, the patient can be shifted to oral antibiotics like cefixime.
Pregnant patients with gonococcal infections should be treated with a recommended cephalosporin or, azithromycin.
Associated complications like endocarditis and meningitis, though rare now, warrant more aggressive approach.
With immediate and adequate treatment, full recovery can be expected.