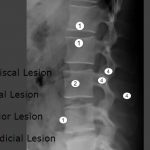
Atypical spinal tuberculosis refers to the presentation of tuberculous disease of spine in a manner that is not usual presentation. The usual presentations of spinal tuberculosis have been discussed in great detail in the following article. Tuberculosis of Spine- Presentation, and Treatment Atypical spinal tuberculosis may involve other parts of the vertebra or it may […]
Infections
Cold Abscess Causes, Presentation and Treatment
The term cold abscess refers to an abscess [An Abscess is a collection of liquefied tissue(pus) in the body] where typical signs of abscess [warmth, redness, tenderness,] are absent. The prefix cold indicates that the abscess is not hot because that is the usual case. Thus a cold abscess is not accompanied by the classical […]
What is Spinal Tumor Syndrome?
Spinal tumor syndrome is not a condition in itself. It is a clinical label for the patient’s condition with many differentials in the offering. Most often, the term is used in cases of spine tuberculosis where there is no apparent osseous lesion. To understand spinal tumor syndrome one must first know about the typical presentation […]
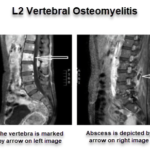
Pyogenic Vertebral osteomyelitis Presentation and Treatment
Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis is a type of spinal infection which may result from direct trauma, the spread of infection from adjacent structures or hematogenous spread from the distant focus of infection. It can have devastating complications if untreated which could be a pathological fracture, epidural infection, and compression of the neural structures. Vertebral osteomyelitis is […]
IDSA 2015 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Native Vertebral Osteomyelitis in Adults
The guidelines are published by the Infectious Disease Society of America. These guidelines include evidence and opinion-based recommendations for the diagnosis and management of patients with native vertebral osteomyelitis treated with antimicrobial therapy, with or without surgical intervention. Native vertebral osteomyelitis in adults is often the result of hematogenous seeding of the adjacent disc space […]
Pott’s Paraplegia or Spinal Tuberculosis with Neural Involvement
Spinal tuberculosis with neural deficit can occur in the lesions when disease comrpresses the cord. Potts paraplegia is term for this deficit in TB spine Spinal tuberculosis is the most common form of skeletal tuberculosis accounting for 50 percent of osteoarticular tuberculosis. Neural compression in spinal tuberculosis may lead to tetraparesis-tetraplegia or paraparesis-paraplegia. Pathology of […]
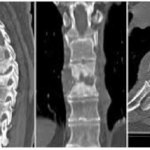
Pyogenic Infection of Spine
Pyogenic infection of the spine is rare, constituting only about 2-8% of overall pyogenic infection. The spectrum of pyogenic infections includes spondylitis, discitis, spondylodiscitis, pyogenic facet arthropathy, epidural infections, meningitis, and myelitis. The incidence of spinal infections has increased recently due to globalization, improved life expectancy, comorbidities like diabetes, overuse of antibiotics, immunosuppression and other immunocompromised […]
Pyomyositis or Muscle Abscess – Causes and Treatment
Pyomyositis is characterized by suppuration within skeletal muscles, manifesting as single or multiple abscesses. It is also known as tropical pyomyositis as it affects tropical people more commonly. Pyomyositis is common in tropical regions but is rare in temperate climates but showing rise and association with HIV infection or other immunosuppressive conditions, including diabetes mellitus, […]
Infectious Myositis Causes and Treatment
Infectious myositis is an acute, subacute, or chronic infection of skeletal muscle. It was considered a tropical disease once but now seen in temperate climates as well, particularly with the emergence of HIV infection. Viruses, bacteria (including mycobacteria), fungi, and parasites can cause infectious myositis. Infectious myositis has a male predominance and is typically seen […]
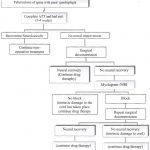
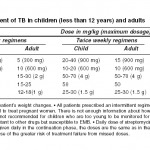
Antitubercular Chemotherapy in Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis
Antitubercular chemotherapy is the mainstay of the treatment of osteoarticular tuberculosis. It is complemented by rest, nutritional support and splinting, as necessary. The drugs and regimens are fundamentally similar to those for pulmonary TB. But there is a lack of consensus on the appropriate duration of treatment. Overview of Osteoarticular Tuberculosis The spine is probably […]