Last Updated on June 2, 2020
Loose bodies refer to the fragments of cartilage or bone that freely float inside the joint space and can occur as a result of an injury or wear or tear over time.
There can be one or many loose bodies in the joint as determined by severity of the disease.
The loose bodies can be stable or unstable. The stable loose bodies don’t move about inside the joint in contrast to the unstable one.
These most commonly occur most commonly in the knee through the loose bodies have been reported practically in all the joints.
The loose bodies can vary in size from a few millimeters to a few centimeters.
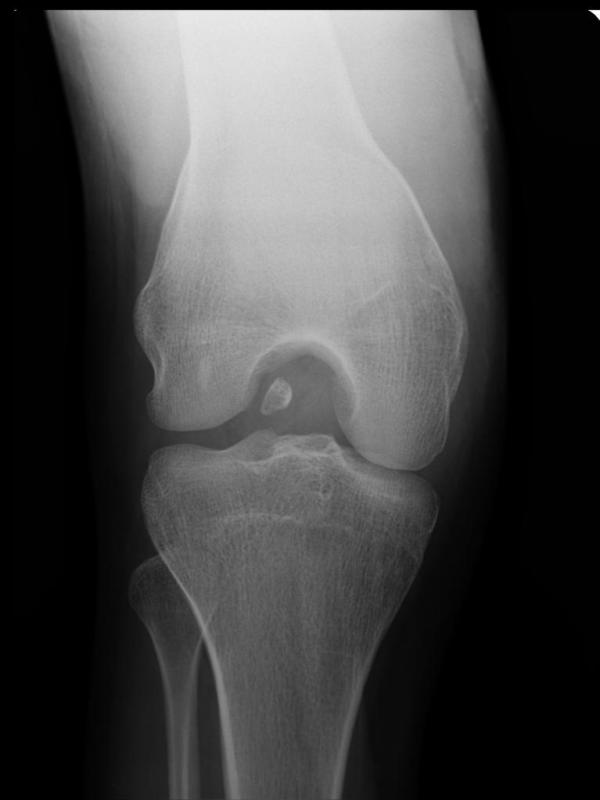
Image Credit: courtesy of Dr Maulik S Patel, Radiopaedia.org. From the case rID: 10104
Classification of Loose Bodies in Joint
The loose bodies have been classified according to their composition. But most of these types are rare and of little clinical significance as they are nothing more than a minor manifestation of some other disease.
From the clinical point, the following causes of loose bodies are most important
However, here is the complete list of origin of loose bodies in joint
- Fibrinous
- Composed of fibrinous material or of the necrotic synovial membrane
- Traumatic -after hemorrhage
- Pathological as in tuberculosis, rheumatoid arthritis, oOsteoarthritis
- Cartilaginous
- Composed entirely of hyaline cartilage
- Intra-articular fractures
- Osteocartilaginous loose bodies
- Osteochondral fractures
- The detachment of portion of the articular surface in osteochondritis dessicans
- Synovial chondromatosis
- Pigmented vilonodular synovitis
- Detachment of osteophytes
- Neuropathic joints
- Sequestra in tuberculosisis
- Introduced foreign bodies
- Tumors
- Lipoma
- Angioma
- Secondary tumors
Diagnosis
A patient may know that he has a loose body as the affected joint could be without any symptoms.
The patient may complain of vague discomfort in the joint and may report hindrance of movement. For example, in cases of loose bodies of the knee joint, the patient may complain of a reduced range of motion at a particular section of flexion-extension arc.
The patient may also complain of the locking of the knee. Locking of the knee is a phenomenon where the knee joint gets suddenly arrested and cannot be moved. This occurs because the bodies get caught in movements.
The imaging modalities may help in confirming the diagnosis.
X-rays of the joint would typically show a bony loose body but it may miss chondral ones. However, in most cases, the loose body due to trauma has a bone chip with it. A big piece of cartilage can produce a visible shadow too.
CT reveals anatomy in greater detail and works best in the cases where a fracture is expected.
MRI is the best modality to look for and at a loose body especially in loose bodies of cartilage origin. It is very good at revealing size, number, and location of the bodies.
MRI would also tell about the disease process that is responsible for the formation of a loose body. It is a useful tool to see the size, number, and location of the loose bodies.
Treatment of Loose Bodies in Joint
No treatment is required in patients who do not have symptoms.
Symptomatic loose joint bodies require surgical removal.
Sometimes, a mobile loose body may displace and move out of joint space. Therefore, certain cases could be managed by waiting and watching.
Physical therapy and anti-inflammatory drugs can be used to help with the symptoms while the patient waits for the surgery.
Arthroscopic removal of joint loose bodies is the gold standard procedure nowadays. Arthroscopy has the advantage of a small incision in contrast to open joint surgeries.
In arthroscopy, a hollow tube-like structure is introduced in the joint which is used to visualize the structure within the joint. Another portal introduces tools to work on joint surgery. thus it saves the major incisions required otherwise.
The arthroscopies to remove the loose bodies in the joint are commonly called cleanout arthroscopies.
Open arthrotomy is less commonly done but can be performed when the loose bodies are very large in number.
It can also be preferred where there is complete synovial involvement.
The conditions causing the loose bodies need to be addressed too.
Intra-articular fractures need to fix anatomically. The causative disease like tuberculosis would require medical treatment.