Last Updated on November 20, 2019
Wrist pain is a common problem and can be caused by many conditions, trivial and serious both. The pain can originate from carpal or wrist bones, ligaments, muscles, tendons, nerves, vessels or connective tissue and other structures in the vicinity. Damage to any of the parts of your wrist can cause pain and affect your ability to use wrist and hand.
Sprains and injuries are common causes but in patients presenting with wrist pain, long-term conditions should also be kept in mind.
Anatomy of Wrist
The wrist is the region between forearm and hands. Its proximal extent is marked by distal ends of radius and ulna [forearm bone] and distal extent is marked by metacarpal heads.
The wrist is a complex joint made up of eight small bones arranged in two rows of four each, connected and stabilized by ligaments connecting wrist bones to each other and to radius ulna and metacarpal bones.

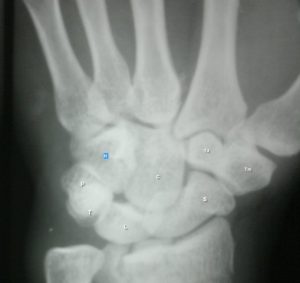
The carpus is formed from eight small bones collectively referred to as the carpal bones. The carpal bones are bound in two groups of four bones:
- Pisiform, triquetrum, lunate, scaphoid proximally
- Hamate, capitate, trapezoid, and trapezium distally
On both flexor and extensor aspects, the wrist is crossed by tendons that flex and extend wrist and fingers. Other structures crossing the wrist are ulnar artery and radial artery, median nerve, ulnar nerve and sensory branch of radial nerve on the flexor aspect.
Transverse strong bands of connective tissue are present on both flexor and extensor aspects called flexor and extensor retinaculum.
Causes of Wrist Pain
Acute Injuries
Fall on the hand or a blow to the wrist can cause injury to the wrist. The injury could be sprain or even fracture
Scaphoid bone is most commonly injured bone of the wrist but any of the carpal bone can get injured. Dislocation of carpal bones can also be a result of an injury. An initial x-ray may not be able to show the fracture so repeat x-ray must be done if the suspicion persists.

In osteoporosis, bones lose mineral mass and become brittle. They become prone to slight trauma and commonly microfractures are associated even without trauma.
The bones of the wrist are among those most commonly fractured in people with osteoporosis.
Acute wrist injury could also lead to tendinitis and bursitis.
Sharp weapon injuries or glass injuries may lead to injuries to nerve, vessels, and tendons and are accompanied by major bleeding.
Repetitive Stress Injury/Tendonitis
This injury occurs when the wrist is subjected to repetitive motion or activity. Any activity that involves repetitive wrist motion– from prolonged writing to playing musical instruments or long drive can hurt the tissues around joints.
De Quervain’s disease is a type of repetitive stress injury and presents with pain in the wrist at thumb base.
Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis [uncommon] can affect the wrist and cause pain. The pain of arthritis is worse in the morning and has associated stiffness that gets better with time.

The pain is affected by a change of weather as well.
A previous history of writs trauma or wrist instability puts the wrist at the risk of developing degenerative changes over time.
Juvenile arthritis is arthritis which begins before 16 years of age. There are several different types of juvenile arthritis that can cause pain and swelling in the wrist and joints of the hands.
Gout and is crystal deposition diseases where crystals of uric acid, needle-shaped monosodium urate crystals are deposited in tissues of the body, including the joints. Usually big toe of the foot is affected first but subsequently, other joints also get affected.
Another crystal deposition disease that may affect the wrist joint is pseudogout.
After years with the disease, lumps of uric acid, called tophi, may occur beneath the skin of the hands.
Reactive arthritis is a chronic form of arthritis that often occurs following an infection of the genital, urinary or gastrointestinal system.
Inflammation occurs in the joints, eyes, and structures within the gastrointestinal or genitourinary tracts, such as intestines, kidneys or bladder.
Lupus
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease and can affect the joints as well. The wrist and small joints of the hands are among those most commonly. Many other organs such as the skin, heart, lungs, and kidneys can be affected.
Infectious arthritis
Wrist joint may get involved by various infectious agents. Infectious arthritis or septic arthritis is often caused by bacteria that spread through the bloodstream to the joint. Sometimes it is caused by viruses or fungi.
Septic arthritis is associated with severe pain in the joint, swelling of the joint and stiffness of the joint. It is accompanied by fever and other systemic symptoms. There is acute leucocytosis. Aspiration yields pus. Antibiotics and drainage are mainstays of therapy.
Tuberculous arthritis of the wrist would generally present without systemic symptoms.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve gets compressed at the wrist because of swelling.
Common complaints are aching, burning, numbness, or tingling in the palm, wrist, thumb, or fingers. There can be a weakness of thumb muscles.
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs because of repetitive injury to wrist in occupations that use a computer or in jobs like, sewing, painting, writing, or using a vibrating tool. It is also found in pregnancy.
Ganglion
Ganglions are cysts that commonly occur on the volar aspect of wrist and bases of fingers and thumb [metacarpophalangeal joins]. They are generally not painful but in some cases can cause the pain. Sometimes, they are self-limiting.
Tumors
Tumors usually present in a painless manner but the involvement of surrounding tissues may result in pain.
Diagnosis of Wrist Pain
The diagnosis of wrist pain begins with a detailed history, followed by clinical examination and investigations.
Here are important points in the history
- Nature and site of pain
- When did the pain begin?
- Any antecedent injury of trauma
- What makes the pain worse or better? List the activities that make wrist pain worse.
- Pain in any joint other than the wrist
- Systemic symptoms like fever, malaise or loss of appetite
- Any medical history?
- Any family history
The examination of the wrist depends on the presentation. The wrist is looked for tenderness, swelling, the range of motion and deformities.
Imaging for Wrist Pain
X-ray
Xrays are basic investigations and can be used to assess the status of bones, joint space, bone spurs and fractures
CT
CT scans may be used to diagnose wrist fractures that don’t show up on X-ray. In case of severe injuries, CTs are able to show the fracture pattern clearly because of 3-dimensional imaging.
MRI
MRI shows the soft tissues as well as the bones and is able to show injuries to the cartilage, tendons, and ligaments as well as tissue edema clearly.
MRI is also useful to diagnose nontraumatic soft tissue afflictions like carpal tunnel syndrome.
Bone scan
Bone scans are useful to diagnose stress fractures caused by repetitive injury. It is also important in the diagnosis of tumors and osteomyelitis.
Electrodiagnostic Tests
Nerve conduction studies and electromyography are used to diagnose nerve compressions such as carpal tunnel syndrome and nerve injuries
Lab Studies
Depending upon the probable cause of pain, a combination of tests from the following investigations may be done.
- CBC
- ESR
- CRP
- Rheumatoid factor
- Antinuclear antibodies
- Aspiration of fluid – biochemical tests, cytological studies, gram staining, mycobacterial staining etc
- Culture and sensitivity of aspirated fluid
- Serum uric acid levels
Treatments for Wrist Pain
The treatment of wrist pain depends entirely on the cause of the problem.
Rest & Modification of Activity
Rest to the joint is often the first treatment. Rest helps to reduce the inflammation, further injury and provides the optimum environment for healing.
The amount and degree of rest would depend on the condition that is causing the wrist pain.
Some conditions do not require complete imm0bilization, but rather relative rest and avoidance of specific activities that do not irritate the joint.
Immobilization could be by plaster or braces, as the condition requires.
Ice application or Heat Application
Ice packs and heat pads relieve the pain. In cases of injury, ice application would reduce the inflammation and provide relief. Conditions like tendonitis also respond to the ice application.
Warmth provides relief by increasing the circulation of the affected area and washing away the chemicals that cause pain.
Drugs
- Anti-inflammatory drugs like NSAIDs are are some of the most commonly prescribed medications for pain. They work by reducing the inflammation by inhibiting the inflammatory pathways.
- Local anti-inflammatory gels
- Antibiotics in case of infection
- Antitubercular drugs for tuberculosis of wrist
Steroid Injections
Local steroid injections can be useful in cases of De Quervain’s disease, bursitis etc. They work locally to reduce inflammation and provide pain relief.
Surgery
Some conditions do not respond to conservative methods. Surgical procedures are needed in this scenario. Choice of surgery depends on the condition. It may be an internal fixation of fracture or removal of the tumor, repair of a ligament, fusion of bones or drainage of abscess
Corrective Measures and Prevention of Wrist Pain
Ergonomic Arrangement
To avoid overuse injury you may need to make adjustments to your work habits and environment:
- Keep your keyboard low enough so as not to bend your wrist while you type. Special keyboards for wrist pain are available
- Take frequent breaks from activities that aggravate the pain. Even when typing, take frequent breaks and rest your hands. You may even massage and manipulate your hands.
- Wearing a wrist splint at night while you sleep may reduce the swelling.
- Reduce your alcohol intake
- Reduce weight if you are overweight.
- Drink plenty of water.